CME for
KSGE members
Kim: Esophageal Lesions: A High Index of Suspicion is Important for Diagnosis
Quiz
A 55-year-old woman visited the hospital after experiencing heartburn and dysphagia for several months. She underwent endoscopy screening 2 years prior, at which time there were no remarkable findings. This time, endoscopy revealed longitudinal furrows and multiple papilloma-like nodules in the esophagus ( Fig. 1). There was no mucosal break at the esophagogastric junction. A biopsy of the esophageal lesions was performed ( Fig. 2). What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer 
Considering the endoscopic and pathologic findings, the diagnosis would be eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). EoE is an antigen-mediated disease of the esophagus in which chronic eosinophil-rich inflammation promotes symptoms and esophageal dysfunction [ 1]. EoE is distinguished by several endoscopic characteristics; hence, a high index of suspicion is warranted for endoscopic diagnosis. These characteristics include linear furrows (vertical lines), esophageal rings (concentric rings), edema (decreased vascularity), plaques (white spots, exudates), strictures, and a crepe paper-like esophagus (mucosal fragility) [ 2]. Hirano et al. proposed an endoscopic classification system for EoE in an attempt to standardize the method of endoscopic diagnosis ( Table 1) [ 3]. Based on this classification, an endoscopic reference scoring system referred to as EREFS (an acronym consisting of exudates, rings, edema, furrows, and strictures) was created. Endoscopic features play an important role in clinical suspicion, but the diagnosis should ultimately be based on biopsies and histopathology. A biopsy of the regions within the esophagus depicting abnormal findings should be performed. The European guidelines on EoE recommend biopsies of both the proximal and distal halves of the esophagus [ 4]. In addition, reference biopsies of the stomach and duodenum are necessary to exclude eosinophilic gastroenteritis, a secondary cause of eosinophilic infiltration in the esophagus. EoE is diagnosed when at least 15 eosinophils per HPF are detected. In this case, the biopsy of the esophagus showed significant intraepithelial eosinophilic infiltration of more than 15 eosinophils per HPF.
Fig.┬Ā1.
Endoscopic findings revealed longitudinal furrows and multiple papilloma-like nodules in the esophagus (A, B). There was no mucosal break at the esophagogastric junction (C). 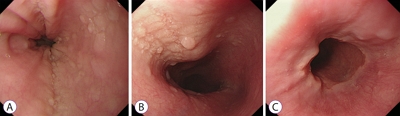
Fig.┬Ā2.
Microscopic findings showed significant intraepithelial eosinophilic infiltration more than 15 cells/HPF. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin, ├Ś100. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin, ├Ś400. 
Table┬Ā1.
Endoscopic Score EREFS for Grading Eosinophilic Esophagitis
|
Endoscopic findings |
Scoring |
|
Exudates |
0- Absent |
|
1- Mild (<10% of the esophageal surface area) |
|
2- Severe (Ōēź10% of the esophageal surface areas) |
|
Rings |
0- Absent |
|
1- Mild (subtle circumferential ridges) |
|
2- Moderate (distinct rings) |
|
3- Severe (rings that impair passage of a standard adult diagnostic endoscope) |
|
Edema |
0- Absent |
|
1- Present (loss of vascular markings) |
|
Furrows |
0- Absent |
|
1- Mild (present but without visible depth) |
|
2- Severe (visible depth or mucosal indentation) |
|
Strictures |
0- Absent |
|
1- Present |
|
|











