Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is an invaluable procedure for managing biliopancreatic disorders. Successful side-viewing scope insertion into the descending part of the duodenum is the first step in ERCP. However, delivering the side-viewing scope into the descending part of the duodenum is difficult in some patients with a cascade stomach, as the scope is deflected in the stomach. Forced insertion of a side-viewing scope in such patients may tear the gastric mucosa and result in gastric perforation and bleeding due to excessive shearing force on the gastric wall.1,2 To overcome this problem, we used a large-diameter overtube designed for colonoscopy in patients in whom side-viewing scope insertion into the descending part of the duodenum was difficult due to a cascade stomach.
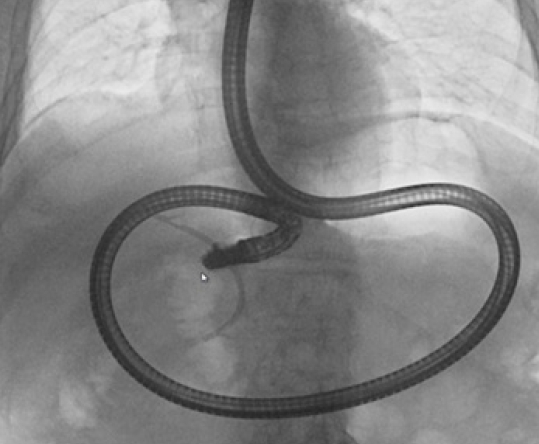
An 88-year-old man who had required biliary stent insertion for acute cholangitis caused by bile duct stones 2 months prior was admitted to our hospital for removal of the biliary stent and bile duct stones. However, scope insertion into the descending part of the duodenum using a side-viewing endoscope (TJF-260V; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) during ERCP was difficult because the patient had a cascade stomach that deflected the scope (Fig. 1).
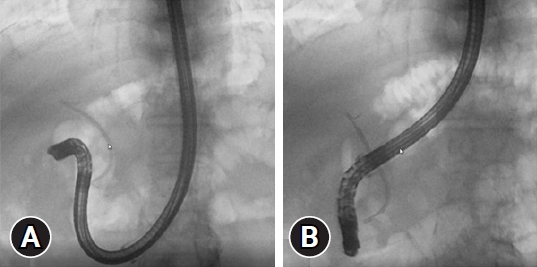
Hence, a large-diameter overtube designed for colonoscopy (ST-CB1; Olympus) was used (Supplementary Video 1). The overtube had a length of 770 mm and outer and inner diameters of 16.2 mm and 13.8 mm, respectively (Fig. 2). We found it better to attach the top hood of the scope to the TJF-260V scope after attaching an overtube. The side-viewing scope with the overtube was easily inserted into the duodenum, as the overtube reduced scope deflection in the stomach (Fig. 3A). After the scope reached the duodenum, it was carefully straightened (Fig. 3B). The biliary stent and bile duct stones were successfully removed without complications.
In conclusion, the large-diameter overtube designed for colonoscopy can be useful for ERCP in patients in whom side-viewing scope insertion into the descending part of the duodenum is difficult due to scope deflection in the stomach.