AbstractBackground/AimsIn this study we aimed to determine the rate of concordance of endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)-guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) diagnosis with the final diagnosis obtained by surgery or endoscopic resection and follow-up in upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions.
MethodsWe retrospectively studied patients with subepithelial lesions who underwent EUS at our center from 2007 to 2011.
ResultsWe had a final diagnosis in 67 patients (mean age±SD, 51.23±12.48 years; 23 [34.3%] female, 44 [65.6%] male). EUS-FNA was performed in all of the patients. On-site pathology was not performed. In nine of the patients, the obtained material which was obtained was insufficient. The cytologic examination was benign in 31 and malignant in 27 of the patients. Based on the final diagnosis, the EUS-FNA had a sensitivity of 96%, a specificity of 100%, and a diagnostic yield of 85%.
INTRODUCTIONSubepithelial lesions represent a spectrum of lesions located beneath the mucosal lining of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. They are relatively common at routine upper GI endoscopy with an incidence of 0.3%.1 Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) can differentiate an intramural lesion from an extramural one. It can identify the GI wall layer from which the lesion originates and can detect if the lesion is cystic or solid.2 EUS and fine needle aspiration (FNA) cytology is useful in the evaluation of subepithelial lesions of the upper GI tract.3
In this study we evaluated the consistency of the EUS-FNA diagnosis with our final diagnosis reached by surgery, endoscopic resection or endoscopic follow-up. As a secondary aim, we investigated the factors which could be important to result in insufficiency of the material obtained by EUS-FNA.
MATERIALS AND METHODSIn this retrospective study, we evaluated the EUS examinations performed for upper GI subepithelial lesions from 2007 to 2011 at our endoscopy department. All patients underwent a standard upper endoscopy before EUS examination. EUS examinations were performed with curvilinear-echoendoscope (Pentax FG-34 UA; Pentax, Tokyo, Japan) in left lateral decubitus position. All EUS-FNAs were performed with a 22-gauge Echotip needle (Wilson Cook, Winston-Salem, NC, USA). Doppler ultrasound was employed to ensure the absence of intervening vessels before FNA procedure. All EUS examinations were performed by an experienced endosonographer. Lesions were defined as intramural or extramural as well as solid or cystic. Size, shape and delineation, and echo pattern were noted. In this study lesions resulted from compression of other normal organs were excluded. Cytology specimens were prepared for direct smears or thin prep with routine Papanicolaou staining. There was no on-site cytopathologist. Cytologic results from EUS-FNA were categorized as benign, malignant, or inadequate. Inadequate specimen was defined as a sample from which the cytopathologist could not make a diagnosis by examining the direct smears or the cell block in case it was obtained. The diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) was made according to mitotic figure and cellular atypia of the spindle-type cells and the c-kit staining obtained from the cell blocks of the patients. Patients with submucosal tumors who had clinical and/or morphologic criteria consistent with overt or potential malignancy underwent surgery. The final diagnosis was established according to the endoscopic and surgical resection, or according to the clinical follow-up findings.
We determined the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy of EUS-FNA to differentiate a malignant subepithelial lesion from a benign subepithelial lesion. Mean values were calculated unless otherwise indicated. Intragroup comparison of operating characteristics was done using the chi-square test. The factors which can be important in failing to obtain a sufficient FNA material were investigated by univariate and multivariate analyses. The statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS software version 13.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Statistical significance was set at p<0.05.
RESULTSDuring the period of the study, 87 patients were referred to our center due to subepithelial lesions. Of that 15 were identified as epithelial lesions. Eight of these lesions were esophageal cancer and seven were gastric cancer. In five of the cases, final diagnosis was established by EUS and visual findings. These cases were diagnosed as lipoma, based on the pillow sign and with the EUS findings (four of these lesions were in the stomach and one was at the duodenum). EUS-FNA was performed in 67 patients (mean age±SD, 51.23±12.48 years; range, 25 to 72; 23 [34.3%] female, 44 [65.6%] male). The mean number of FNA passes was four (range, 3 to 5). There were no procedure-related complications.
The mean size of the FNA performed subepithelial lesions was 30.8±12.28 mm (range, 5 to 70). The location, size, EUS layer of origin and echo pattern of the lesions are summarized in Table 1. In nine of 67 patients (13.4%) who underwent FNA, the biopsy material was insufficient for histopathological examination. We did not repeat FNA in these subjects. Surgery was performed in one (final diagnosis was GIST) and mediastinoscopy was performed in another of them (final diagnosis was Langerhans cell histiocytosis). The final diagnosis was obtained by endoscopic follow-up in five patients (these lesions were considered as leiomyoma). In two of the cases, endoscopic submucosal dissection was performed to the lesions, which were diagnosed as ectopic pancreatic tissue.
Of 58 patients, in whom EUS-FNA was diagnostic, surgery was performed in 26 cases and the final diagnosis was GIST. In five cases the final diagnosis was obtained by endoscopic resection (ectopic pancreas in two, granular cell tumor in one, fibroma in one, and hyperplastic polip in one of the cases). In 27 patients, the final diagnosis was assumed by endoscopic follow-up: leiomyoma in 21 and cyst of duplication in four patients. In two patients the diagnoses of lung cancer and melanoma metastasis were made by other radiological or clinical findings (Fig. 1).
The comparative results of the EUS-FNA diagnosis and final diagnosis according to the location is showed in Table 2. Diagnostic yield of FNA was 85%. When the cases with an insufficient material were excluded, the concordance of EUS-FNA with the final diagnosis was 98.2%. The diagnostic accuracy of EUS-FNA was 78.5% (11/14) in esophageal lesions and 86.5% (45/52) in gastric lesions. When nine patients with insufficient material were excluded from the study, the EUS-FNA had a specificity of 100% (95% confidence interval [CI], 90.4 to 100), sensitivity of 96.4% (95% CI, 86.2 to 96.4), PPV of 100% (95% CI, 89.4 to 100), and NPV of 96.8% (95% CI, 87.5 to 96.8) to differentiate a malignant lesion from a benign lesion (Table 3).
In 27 patients the final diagnosis of GIST was obtained by cytological examination of the surgical material and all of these lesions were CD 117 (c-kit) positive. Cell blocks were obtained from only seven of these 27 patients (26%) by EUS-FNA and all of them were positive for c-kit. A patient with a lesion that was considered to be a leiomyoma due to the lack of c-kit positivity in cell block and another patient in whom the material obtained was insufficient were sent to surgery because of the suspicious characteristics of EUS findings. In these patients' lesions, postoperative c-kit was positive. Diagnostic accuracy of EUS combined with FNA for GIST was 92.5%.
In the univariate analysis for inadequate material, the frequency of failing to obtain an adequate material was significantly higher in patients with a lesion size below 25 mm (p=0.04). However, multivariate analysis showed that the size of the lesion did not predict the adequacy of the material (p=0.8). In univariate analysis, other characteristics of the lesion (lesion echo pattern, origin of the lesion, location of the lesion) did not appear to have an effect on diagnostic yield of FNA.
DISCUSSIONEUS has an increasing role in the evaluation of subepithelial lesions. It enables endoscopists to differentiate an extramural lesion from an intramural one and shows the layer of origin. Besides, ultrasonographic appearance may also suggest a possible diagnosis. EUS-FNA is an invaluable adjunct in most of these instances. Forceps biopsies from the mucosal surface are usually nondiagnostic and more aggressive biopsy techniques using snares or puncture may be hazardous if the cause of bulging is not definitive. However, there are still some caveats about the accuracy of EUS and EUS-FNA in the diagnosis of subepithelial lesions. First, differentiation of the layer of origin is not perfect.4 Second, differentiation of a GIST from a leiomyoma is not always possible.5 Third, due to the firm nature of GISTs, cytologic yield may be poor and overly blood-stained material may be difficult to interpret.6
The specificity and sensitivity of EUS in subepithelial lesions were reported between 88% to 100% and 84% to 92%, respectively.7,8 In this study, the specificity and sensitivity of EUS-FNA to distinguish the malignant potential of subepithelial lesions were 100% and 96.4%, respectively. Our results are concordant with findings in the literature.
Watson et al.9 reported that the diagnostic yield of EUS-FNA was 74% irrespective of the presence or absence of an onsite cytopathologist. In another study, the diagnostic yield of EUS-FNA was reported to be as 100% in the presence of an onsite cytopatologist.10 In our study, despite the absence of an onsite cytopathologist, the diagnostic yield of EUS-FNA was 85%.
We found that lesion characteristics had no significant effect on the adequacy of FNA material in multivariate analyses. However, the adequacy of EUS-FNA obtained from a lesion larger than 25 mm was significantly better in univariate analyses. Mekky et al.8 have reported that the size and echo pattern of the lesion were significant factors in obtaining sufficient material through FNA in univariate analyses. However, the size has turned out to be statistically insignificant in multivariate analysis. Hoda et al.11 reported that there were no identifiable factors that affected the yield of EUS-FNA.
GISTs are often discovered during routine endoscopy as a submucosal bulge or a raised lesion with an overlying normal mucosa. Endosonographically, GIST appears as hypoecoic round or oval mass, most often arising from the muscularis propria. In a prospective study of 23 patients with GISTs, EUS features alone had a diagnostic accuracy of 78%.12 EUS features alone are inadequate in distinguishing benign from malignant or potentially malignant stromal cell tumors.13 Thus, to fully characterize a subepithelial lesion and achieve a definite diagnosis, a tissue specimen is usually required. In previous studies, sensitivity and diagnostic accuracy of EUS completed with FNA in GISTs have been reported between 78% to 91%.11,12 This rate was 92.5% in our series. In seven GIST patients we obtained cell block (26%). It was reported that the rate of cell block obtainment in GIST patients was 25%.14 Undoubtfully with cell block examination the diagnostic accuracy of FNA will be increased but to have enough material from these firm tumors with FNA is difficult.
The frequency of esophageal submucosal tumors is low. They are usually benign and asymptomatic. Wehrmann et al.15 reported the diagnostic accuracy rate of FNA for the esophageal submucosal lesions as 81.8%. The diagnostic yield of EUS-FNA in the esophageal lesions was reported as low as 43% by Watson et al.9 In our study, this was 78.5%. EUS-FNA can be performed much easier in the esophagus in contrast to other locations because of the straight position of the scope which results in easier advance of the needle within the lesion. However, the tangential position and respiratory oscillations can still influence the diagnostic yield.
An incidentally detected subepithelial lesion could be due to compression of a mediastinal lesion. Recent studies have shown high accuracy rates of EUS in the diagnosis of a mediastinal adenopathy of unknown origin (94%).16 In our series, EUS-FNA was performed due to extrinsic pressure on esophagus in three patients. One patient was diagnosed with lung carcinoma and another with mediastinal metastasis of malign melanoma based on FNA. In the third patient FNA was nondiagnostic and the final diagnosis of Langerhans cell histiocytosis was obtained by mediastinoscopy. Another lesion which causes esophageal external compression is a duplication cyst. Although these cystic lesions are generally intramural and are found in the mid and lower parts of the esophagus, they may also have an extramural origin as this was the case in one of our patients.
In conclusion, in case of necessity, EUS completed by FNA is an invaluable method in the diagnosis of subepithelial lesions. Taking into account the inevitable shortcomings of FNA, EUS features judged by an experienced endosonographer may be very important in some cases and, even in the absence of an on-site cytopathologist, the diagnostic yield can still be high.
References1. Hedenbro JL, Ekelund M, Wetterberg P. Endoscopic diagnosis of submucosal gastric lesions. The results after routine endoscopy. Surg Endosc 1991;5:20â23. 1871670.
2. Nesje LB, Laerum OD, Svanes K, Ădegaard S. Subepithelial masses of the gastrointestinal tract evaluated by endoscopic ultrasonography. Eur J Ultrasound 2002;15:45â54. 12044852.
3. Caletti GC, Brocchi E, Ferrari A, et al. Guillotine needle biopsy as a supplement to endosonography in the diagnosis of gastric submucosal tumors. Endoscopy 1991;23:251â254. 1743123.
4. Buscarini E, Stasi MD, Rossi S, et al. Endosonographic diagnosis of submucosal upper gastrointestinal tract lesions and large fold gastropathies by catheter ultrasound probe. Gastrointest Endosc 1999;49:184â191. 9925696.
5. Stelow EB, Stanley MW, Mallery S, Lai R, Linzie BM, Bardales RH. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration findings of gastrointestinal leiomyomas and gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Am J Clin Pathol 2003;119:703â708. 12760289.
6. Wiersema MJ, Wiersema LM, Khusro Q, Cramer HM, Tao LC. Combined endosonography and fine-needle aspiration cytology in the evaluation of gastrointestinal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc 1994;40(2 Pt 1):199â206. 8013822.
7. Vander Noot MR 3rd, Eloubeidi MA, Chen VK, et al. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal tract lesions by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Cancer 2004;102:157â163. 15211474.
8. Mekky MA, Yamao K, Sawaki A, et al. Diagnostic utility of EUS-guided FNA in patients with gastric submucosal tumors. Gastrointest Endosc 2010;71:913â919. 20226456.
9. Watson RR, Binmoeller KF, Hamerski CM, et al. Yield and performance characteristics of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for diagnosing upper GI tract stromal tumors. Dig Dis Sci 2011;56:1757â1762. 21360279.
10. Sepe PS, Moparty B, Pitman MB, Saltzman JR, Brugge WR. EUS-guided FNA for the diagnosis of GI stromal cell tumors: sensitivity and cytologic yield. Gastrointest Endosc 2009;70:254â261. 19482280.
11. Hoda KM, Rodriguez SA, Faigel DO. EUS-guided sampling of suspected GI stromal tumors. Gastrointest Endosc 2009;69:1218â1223. 19394006.
12. Ando N, Goto H, Niwa Y, et al. The diagnosis of GI stromal tumors with EUS-guided fine needle aspiration with immunohistochemical analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2002;55:37â43. 11756912.
13. Kojima T, Takahashi H, Parra-Blanco A, Kohsen K, Fujita R. Diagnosis of submucosal tumor of the upper GI tract by endoscopic resection. Gastrointest Endosc 1999;50:516â522. 10502173.
14. Gu M, Ghafari S, Nguyen PT, Lin F. Cytologic diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors of the stomach by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy: cytomorphologic and immunohistochemical study of 12 cases. Diagn Cytopathol 2001;25:343â350. 11747229.
Table 3Performance Characteristics of Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration for Differentiating Benign from Malignant Subepithelial Tumors 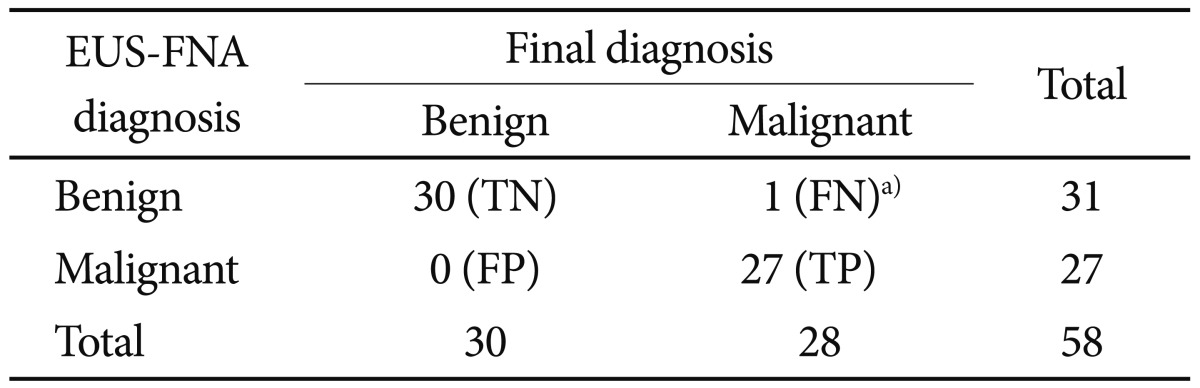 EUS, endoscopic ultrasonography; FNA, fine needle aspiration; TN, true negative; FN, false negative; FP, false positive; TP, true positive. a)One patient who had the diagnosis of leiomyoma by FNA, referred to operation due to the size of 40 mm and the presence of cystic structures. Final diagnosis was gastrointestinal stromal tumor. |
|
