AbstractBackground/AimsApproximately 5% to 10% of common bile duct (CBD) stones are difficult to remove by conventional endoscopic methods. Percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic lithotomy (PTCSL) can be an alternative method for this condition, but is not well established yet. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of PTCSL for removal of difficult CBD stones.
MethodsThis study is a retrospective review of 34 consecutive patients who underwent unsuccessful removal of CBD stones using conventional endoscopic methods between December 2008 and July 2010 and were subsequently treated using PTCSL.
ResultsAmong 443 patients with CBD stones, 34 patients (7.8%) failed to achieve stone removal using conventional endoscopic methods. Of these 34 patients, 33 were treated using PTCSL. In all 33 cases (100%), complete stone removal was achieved using PTCSL. Most complications (15/17, 88.2%) were mild and transient. Major complications occurred in two patients (6.1%) who experienced hemobilia, and percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage tract disruption, respectively; which were fully recovered without mortality.
INTRODUCTIONCommon bile duct (CBD) stones can bring about various clinical events such as biliary colic, jaundice, and sepsis. In the treatment of this condition, stone removal is the primary intervention for dealing with clinical symptoms. Among the various methods for stone removal, the standard treatments are endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST) and stone extraction using a basket or balloon catheter. Between 80% and 90% of CBD stones can be successfully extracted using these conventional techniques1-3 and mechanical lithotripsy (ML) has been used as a second line therapy for difficult cases. Approximately 5% to 10% of CBD stones are difficult to remove with the above methods, however. These difficult CBD stones most often involve difficultly in approaching the bile duct (periampullary diverticulum, Billroth II gastrectomy, or Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy), large (>15 mm) stones, impacted stones, and stones above the narrow duct segment.4-6
For the removal of difficult CBD stones, alternative methods such as percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic lithotomy (PTCSL), peroral cholangioscopy (POC) using a "mother-baby" endoscopic system with electrohydraulic lithotripsy (EHL), laser lithotripsy, and extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy (ESWL) may be required, and recently developed methods such as direct POC using ultraslim endoscopy7 and SpyGlass system (Boston Scientific Corp., Natick, MA, USA)8 have been introduced. However, these methods present still several limitations. Particularly, POC using a "mother-baby" endoscopic system and direct POC using the ultraslim endoscopy or Spyglass system involve serious problems such as the difficulty in approaching the bile duct in altered anatomy, extreme fragility of the baby scope and expenses related to additional processor and video monitor requirements.
PTCSL with EHL for removal of CBD stones was first introduced by Mo et al.9 PTSCL, with the added advantage that it can also be effective in difficult CBD stone removal, is now commonly used for removal of intrahepatic duct (IHD) stones to overcome the difficult of approach with conventional endoscopic methods. The primary advantages of PTCSL include easy approach to the bile duct and easy management of stones compared with other new methods. The majority of previous studies have focused on POC using a "mother-baby" endoscopic system for treatment of difficult CBD stones and PTCSL for treatment of IHD stones.1,4,10-13 However, clinical studies on PTCSL for the treatment of difficult CBD stones were still relatively few and had small cases.14-17 This study is designed to add to the limited knowledge available on the clinical efficacy and safety of PTCSL for removal of difficult CBD stones.
MATERIALS AND METHODSPatientsDuring the period between December 2008 and July 2010, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) was performed on 719 patients. Of these 719 patients, ERCP for CBD stones was performed in 443 patients. The majority of patients achieved successful stone removal using conventional endoscopic methods such as EST and stone extraction by basket or balloon catheter with or without ML. In 34 patients (7.8%), these methods failed to successfully remove CBD stones. Thirty-three patients of these difficult cases were treated using PTCSL while the remaining patient underwent open surgery (Fig. 1).
Exclusion criteria included isolated or combined IHD stones, persistent coagulopathy (international normalized ratio >1.5) or low platelet counts (Ōēż50,000/mL), and continuous anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy. All the patients provided written informed consents to undergo the procedure, and this study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital.
MethodsPTCSL was managed by employing two procedures. The first procedure was to make a tract between the skin and the IHD by percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage (PTBD) and dilatation of the tract for passage of a cholangioscope. The second procedure was to insert a cholangioscope in order to facilitate the fragmentation and removal of CBD stones.
Prior to the PTBD procedure, systemic antibiotics were administered intravenously and patients were premedicated with meperidine, midazolam, and local lidocaine. After puncture with an ultrasound-guided needle and the introduction of a guidewire into the bile duct through the puncture needle, 8.5 Fr PTBD drainage tube (Dawson-Mueller Drainage catheter; Cook, Bloomington, IN, USA) was inserted through the guide wire. On the third day of PTBD, the tract was dilated to 16 or 18 Fr in one or two session using a dilator (Amplatz Renal Dilator Set; Cook) within 1 week except in the patients with persistent cholangitis. Approximately 10 to 14 days after the final dilatation, a cholangioscope (CYF-VA2; Olympus Optical Co., Tokyo, Japan) was introduced safely into the biliary tree.
PTCSL was performed under the intravenous administration of meperidine for pain control and systemic antibiotics for the prevention of cholangitis. Large or impacted stones were then fragmented by EHL (Lithotron EL2; WALZ Elektronik GMBH, Rohrdorf, Germany), and then CBD stones were removed percutaneously by baskets or forceps or by pushing them into the duodenum (Fig. 2).
If repeated treatment was required, PTCSL was performed at 2- or 3-day intervals after reinsertion of a PTBD drainage tube. If no additional symptoms occurred during the 1- or 2-day period of PTBD tube clamping after complete stone removal, the PTBD drainage tube was removed.
RESULTSA total of 33 patients (28 men and five women with a mean age of 72.7 years) were treated for difficult CBD stone removal using PTCSL. Major reasons for performing PTCSL included difficult in approaching to the major papilla due to postoperative stomach (16 patients, 48.5%), impacted stones (11 patients, 33.3%), the failure of selective cannulation of the bile duct (three patients, 9.0%), the intolerance of ERCP due to cardiopulmonary instability (two patients, 6.1%), and stones located above the ductal stricture (one patient, 3.0%).
Baseline characteristics of the patients are described in Table 1. The majority of patients (29/33, 87.9%) had one or more of the following symptoms; abdominal pain (25/33), fever (22/33), jaundice (15/33), sepsis (5/33), or pancreatitis (5/33). Fifteen patients had prior cholecystectomies, and 16 patients had altered anatomy due to previous operations (B-II gastrectomy in seven patients, Reux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy in eight patients, and bypass gastrojejunostomy in one patient). PTBD catheters were inserted into the right IHD in 25 patients and into the left IHD in eight patients.
Complete stone removal was achieved in all patients (100%). The mean number and time intervals of PTCSL were 2.8 and 41.4 minutes (range, 1 to 8 and 10 to 80), respectively. EHL was performed in most patients (32/33, 94.1%) because of large stone size compared to the PTBD tract or because of the hard consistency of stones. The numbers of EHL session were as follows: one session in 16 patients (16/33, 48.5%), two sessions in nine patients (9/33, 27.3%), three sessions in five patients (5/33, 15.2%), and more than four sessions in two patients (2/33, 6.1%). Successful stone fragmentation with EHL was achieved in all patients. Following EHL, the stones were removed percutaneously by baskets or forceps or by pushing them into the duodenum or jejunum. In 12 patients, additional transpapillary stones extraction was performed for rapid removal of stones after stone fragmentation with EHL (Table 2).
Seventeen patients (17/33, 51.5%), among the 33 patients, experienced complications, which were mostly mild and transient (15/17, 88.2%). Major complications occurred in two patients (2/33, 6.1%); one was a PTBD related complication (hemobilia) and the other a PTCSL related complication (PTBD tract disruption). Complications related to PTBD occurred in two patients (2/33, 6.1%); one patient who exhibited hemobilia during the first tract dilation was treated by transarterial embolization; the other patient who exhibited hemoperitoneum during the first tract dilation was recovered by conservative management without blood transfusion. Complications related with PTCSL, including fever (12/33), pancreatitis (1/33), hemobilia (1/33), and disruption of the PTBD tract (1/33), occurred in 15 patients (15/33, 45.5%). Among them, most (14/15, 93.3%) except disruption of PTBD tract were transient and were recovered with conservative managements (Table 3). The case of hemobilia was a result of injury to the bile duct caused by incorrect focus of shock waves resulting from inadequate visual control, but was managed by epinephrine irrigation and reinsertion of PTBD tube. The case of PTBD tract disruption occurred during the first PTCSL after PTBD tract dilation (16 Fr) and was managed by immediate reinsertion of PTBD tube for the maintenance of the PTBD tract. After 14 days, complete stone removal by PTCSL was achieved without other complications.
DISCUSSIONMost CBD stones were successfully treated by conventional methods, such as EST and stone extraction by basket or balloon catheter with or without ML.1-3 But 5% to 10% of CBD stones are difficult to remove by conventional methods and alternative methods may be required for successful removal. Alternative methods for difficult CBD stone removal include PTCSL, POC using a "mother-baby" endoscopic system with EHL, laser lithotripsy and ESWL, and recently, direct POC using ultraslim endoscopy7 and SpyGlass system8 have been introduced.
POC using a "mother-baby" endoscopic system is one of the useful methods for dealing with difficult CBD stones. However, this method can be difficult to manage and it requires the presence of two skilled endoscopists. For these reasons, relatively few referral centers are able to perform POC. In response, direct POC with ultraslim upper endoscopy or SpyGlass system was introduced to address these problems. However, these methods also have limitations including a low and inconsistent success rate due to the difficult approach into the bile duct using the ultraslim upper endoscopy and the expensive system involved with the SpyGlass system. Another disadvantage of POC is that the approach into bile duct is very difficult in Billroth II gastrectomy and Reux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy. This is due to the fact that maneuvering the side-view duodenoscopy through the long afferent loop in a retrograde manner is required for the stone removal. Many studies reported lower success rates and higher complication rates of ERCP in Billroth II gastrectomy when compared with an intact stomach.18-23
Percutaneous lithotripsy using a basket with or without a balloon sphincteroplasty under the fluoroscopic guidance is another method. Complete stone removal rates and major complications using this method are ranged between 86.7% to 93% and 0% to 7.6%, respectively.24-26 Moreover, four procedure-related deaths have been reported in two separate studies using this method.24,25 This method has several limitations including difficulty in capturing large stones or impacted stone in the distal CBD or ampulla of Vater, the risk of massive bleeding, and fatal pancreatitis or rupture of the bile duct induced by balloon sphicteroplasty without sphincterotomy. Another problem is the potential for remnant stones because small stones and fragments are not well visualized using fluoroscopy in bile duct dilation.
PTCSL was introduced to treat hepatolithiasis in 1981 by Nimura.27 The procedure is also a useful alternative therapy for conditions such as complicated retained stones, biliary stones in poor surgical candidates, and altered anatomy in patients who had received gastrectomy previously.15,28 Mo et al.9 first performed percutaneous transhepatic choledochoscopic (PTCS) EHL in 10 patients with difficult CBD stones. To date, most published studies have been regarding PTCS-EHL for hepatolithiasis with or without CBD stones11-14 but there were only few clinical reports focusing only on difficult CBD stones.15-17
PTCSL is a technically easy and useful treatment for removal of CBD stones because of its easy approach and direct visualization of bile duct stones. However, this procedure has been generally restricted to cases in which conventional endoscopic procedure were unmanageable or unsuccessful. Additionally PTCSL is generally safe and well tolerated by patients despite long procedure time, especially so for those with old age or in poor condition. In this study, complete stone removal using PTCSL demonstrates a success rate of 100% with most complications being mild and transient despite old age (mean, 72.7 years).
The major drawbacks of PTCSL are the need for invasive procedures like PTBD, the temporary decline of quality of life due to external bile drainage, and additional time required for dilatation and maturation of the PTBD tract. In the past, Bonnel et al.29 reported a series of 50 patients with intrahepatic and CBD stones who received PTCS-EHL with 100% fragmentation rate and 92% final stone clearance rate. However, the complication and mortality rates were substantially higher at 22% severe complications rate and an 8% mortality rate. In this study, the overall complication rate was relatively high with 51% but most complications (88.2%) were mild and transient. Major complications with clinical significance occurred in only two patients who were fully recovered without mortality. Therefore, the current study and other studies16,17 clearly demonstrate that PTCSL is safer and better tolerated than other options. This can be attributed to improvements in instruments and technology including small caliber cholangioscope design, EHL, improvements in balloon dilator design and interventional developments. Also, an additional advantage of PTCSL is the ability to perform precise examination of the intra or extrahepatic bile duct compared with other methods.
There are several limitations to this study. The number of patients observed in this study is relatively small and we have not compared PTCSL with other methods such as percutaneous lithotripsy under the fluoroscopic guidance. For a more precise conclusion, a larger population of patients and a comparative study is required. Despite the high complication rate, the overall complete stone removal rate of 100% and low rate of major complications without mortality in this study support the evidences that PTCSL is an effective and safe method for dealing with CBD stones that are difficult to remove with conventional endoscopic methods.
In conclusion, considering the high success rates and low major complications, PTCSL is an effective and safe treatment for CBD stones that are difficult to remove with conventional endoscopic methods, despite the prolonged hospital stay and temporary decline of quality of life.
AcknowledgmentsThis study was supported by a grant from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (A0 91047).
References1. Adamek HE, Maier M, Jakobs R, Wessbecher FR, Neuhauser T, Riemann JF. Management of retained bile duct stones: a prospective open trial comparing extracorporeal and intracorporeal lithotripsy. Gastrointest Endosc 1996;44:40ŌĆō47. 8836715.
2. Binmoeller KF, Schafer TW. Endoscopic management of bile duct stones. J Clin Gastroenterol 2001;32:106ŌĆō118. 11205644.
3. Ellis RD, Jenkins AP, Thompson RP, Ede RJ. Clearance of refractory bile duct stones with extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy. Gut 2000;47:728ŌĆō731. 11034593.
4. Neuhaus H. Endoscopic and percutaneous treatment of difficult bile duct stones. Endoscopy 2003;35:S31ŌĆōS34. 12929051.
5. Arya N, Nelles SE, Haber GB, Kim YI, Kortan PK. Electrohydraulic lithotripsy in 111 patients: a safe and effective therapy for difficult bile duct stones. Am J Gastroenterol 2004;99:2330ŌĆō2334. 15571578.
6. McHenry L, Lehman G. Difficult bile duct stones. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol 2006;9:123ŌĆō132. 16539873.
7. Larghi A, Waxman I. Endoscopic direct cholangioscopy by using an ultra-slim upper endoscope: a feasibility study. Gastrointest Endosc 2006;63:853ŌĆō857. 16650553.
8. Chen YK, Pleskow DK. SpyGlass single-operator peroral cholangiopancreatoscopy system for the diagnosis and therapy of bile-duct disorders: a clinical feasibility study (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2007;65:832ŌĆō841. 17466202.
9. Mo LR, Hwang MH, Yueh SK, Yang JC, Lin C. Percutaneous transhepatic choledochoscopic electrohydraulic lithotripsy (PTCS-EHL) of common bile duct stones. Gastrointest Endosc 1988;34:122ŌĆō125. 3366328.
10. Adamek HE, Buttmann A, Wessbecher R, Kohler B, Riemann JF. Clinical comparison of extracorporeal piezoelectric lithotripsy (EPL) and intracorporeal electrohydraulic lithotripsy (EHL) in difficult bile duct stones: a prospective randomized trial. Dig Dis Sci 1995;40:1185ŌĆō1192. 7781432.
11. Jan YY, Chen MF. Percutaneous trans-hepatic cholangioscopic lithotomy for hepatolithiasis: long-term results. Gastrointest Endosc 1995;42:1ŌĆō5. 7557164.
12. Lee SK, Seo DW, Myung SJ, et al. Percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic treatment for hepatolithiasis: an evaluation of long-term results and risk factors for recurrence. Gastrointest Endosc 2001;53:318ŌĆō323. 11231390.
13. Huang MH, Chen CH, Yang JC, et al. Long-term outcome of percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic lithotomy for hepatolithiasis. Am J Gastroenterol 2003;98:2655ŌĆō2662. 14687812.
14. Yoshimoto H, Ikeda S, Tanaka M, Matsumoto S, Kuroda Y. Choledochoscopic electrohydraulic lithotripsy and lithotomy for stones in the common bile duct, intrahepatic ducts, and gallbladder. Ann Surg 1989;210:576ŌĆō582. 2818026.
15. Jeng KS, Chiang HJ, Shih SC. Limitations of percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy in the removal of complicated biliary calculi. World J Surg 1989;13:603ŌĆō610. 2683403.
16. Lo CM, Fan ST. Percutaneous transhepatic choledochoscopic electrohydraulic lithotripsy for common bile duct stones: experience in four high-risk patients. Am J Gastroenterol 1991;86:840ŌĆō842. 2058625.
17. Jeong EJ, Kang DH, Kim DU, et al. Percutaneous transhepatic choledochoscopic lithotomy as a rescue therapy for removal of bile duct stones in Billroth II gastrectomy patients who are difficult to perform ERCP. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;21:1358ŌĆō1362. 19282768.
18. Costamagna G, Mutignani M, Perri V, Gabrielli A, Locicero P, Crucitti F. Diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP in patients with Billroth II gastrectomy. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 1994;57:155ŌĆō162. 8053300.
19. Lin LF, Siauw CP, Ho KS, Tung JC. ERCP in post-Billroth II gastrectomy patients: emphasis on technique. Am J Gastroenterol 1999;94:144ŌĆō148. 9934745.
20. Osnes M, Rosseland AR, Aabakken L. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography and endoscopic papillotomy in patients with a previous Billroth-II resection. Gut 1986;27:1193ŌĆō1198. 3781333.
21. Prat F, Fritsch J, Choury AD, Meduri B, Pelletier G, Buffet C. Endoscopic sphincteroclasy: a useful therapeutic tool for biliary endoscopy in Billroth II gastrectomy patients. Endoscopy 1997;29:79ŌĆō81. 9101143.
22. Freeman ML, Nelson DB, Sherman S, et al. Complications of endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy. N Engl J Med 1996;335:909ŌĆō918. 8782497.
23. Faylona JM, Qadir A, Chan AC, Lau JY, Chung SC. Small-bowel perforations related to endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in patients with Billroth II gastrectomy. Endoscopy 1999;31:546ŌĆō549. 10533739.
24. Stokes KR, Clouse ME. Biliary duct stones: percutaneous transhepatic removal. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 1990;13:240ŌĆō244. 2121350.
25. Garc├Ła-Garc├Ła L, Lanciego C. Percutaneous treatment of biliary stones: sphincteroplasty and occlusion balloon for the clearance of bile duct calculi. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004;182:663ŌĆō670. 14975967.
26. Park YS, Kim JH, Choi YW, et al. Percutaneous treatment of extrahepatic bile duct stones assisted by balloon sphincteroplasty and occlusion balloon. Korean J Radiol 2005;6:235ŌĆō240. 16374081.
Fig.┬Ā1Flow diagram describes the treatment of 443 patients with common bile duct (CBD) stones. ERCP, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; PTCSL, percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopic lithotomy. 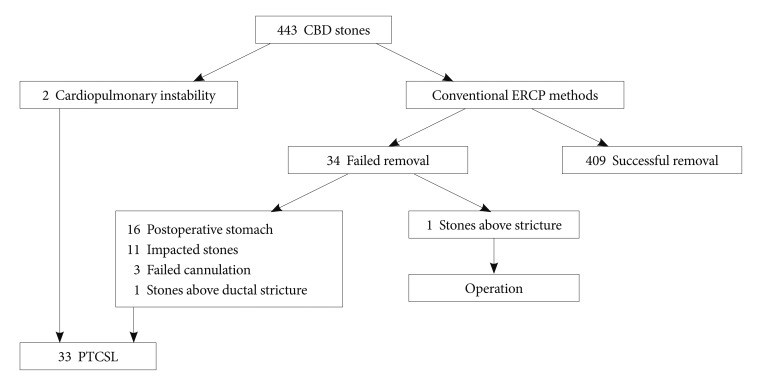
Fig.┬Ā2(A) Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography showing a giant common bile duct (CBD) stone with markedly dilated CBD. (B) Cholangioscopy showing a fragmented stone by electrohydraulic lithotripsy. (C) Cholangiogram showing clear removal state of a previously giant CBD stone. 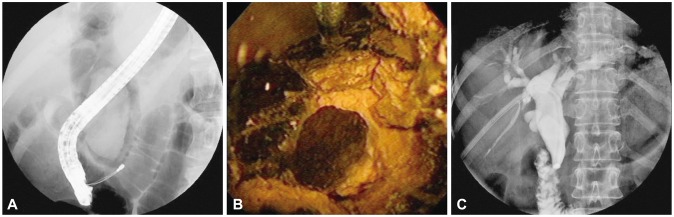
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
