Endoscopic Therapy for Acute Diverticular Bleeding
Article information
Abstract
Diverticular bleeding accounts for approximately 26%–40% of the cases of lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Rupture of the vasa recta at the neck or dome of the diverticula can be the cause of this bleeding. Colonoscopy aids in not only the diagnosis but also the treatment of diverticular bleeding after a steady bowel preparation. Endoscopic hemostasis involves several methods, such as injection/thermal contact therapy, clipping, endoscopic band ligation (EBL), hemostatic powder, and over-the-scope clips. Each endoscopic method can provide a secure initial hemostasis. With regard to the clinical outcomes after an endoscopic treatment, the methods reportedly have no significant differences in the initial hemostasis and early recurring bleeding; however, EBL might prevent the need for transcatheter arterial embolization or surgery. In contrast, the long-term outcomes of the endoscopic treatments, such as a late bleeding and recurrent bleeding at 1 and 2 years, are not well known for diverticular bleeding. With regard to a cure for diverticular bleeding, there should be an improvement in both the endoscopic methods and the multilateral perspectives, such as diet, medicines, interventional approaches, and surgery.
INTRODUCTION
Epidemiology and pathogenesis
Diverticular bleeding accounts for approximately 26%–40% of the cases of lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB) [1-4]. Diverticular bleeding lowers the quality of life, although the mortality rate has been reported to be less than 5% [5,6]. The occurrence of diverticular disease is increasing in Asia, including Korea and Japan, and the frequency of diverticular bleeding, particularly that of LGIB, has increased from 5.9% to 23.0% [7-9]. The pathogenesis of colonic diverticula is believed to involve herniation of the mucosa and submucosa without the muscular layer at the sites of penetration by the vasa recta [5]. The bleeding could be explained by rupture of the vasa recta at the neck or dome of the diverticula (Fig. 1) [6].

Angioarchitecture of the diverticula. Diverticula are formed at the sites where the vasa recta penetrate the muscular wall of the colon. The arteriole is displaced over the dome. Diverticular bleeding is occasionally associated with a rupture of the vasa recta at the neck or dome of the diverticula.
Diagnosis
In the case of LGIB, including diverticular bleeding, colonoscopy should be the initial diagnostic procedure. The diagnostic yield of colonoscopy in patients presenting with LGIB is 90%, at the most [7-10]. In contrast, a meta-analysis reported that the overall sensitivity and specificity of computed tomography (CT) angiography in patients with an episode of an acute gastrointestinal (GI) hemorrhage were 85.2% and 92.1%, respectively [11]. Another study showed that the diagnostic yield of multi-detector row CT for the site and etiology was higher than that of endoscopy [7]. However, colonoscopy has the advantage of a diagnosis followed by an endoscopic hemostasis [8,10].
Bowel preparation
Diverticular bleeding usually occurs as a localized bleeding; thus, poor visualization not only prevents the identification of the bleeding point, but also increases the risk of perforation [9]. Oral lavage approaches, such as polyethylene glycol, help in increasing the diagnostic yield and identifying the stigmata of recent hemorrhage (SRH), defining the bleeding site or the visible vessel after removing the adherent clot [4,12,13]. A retrospective study showed that the visibility was superior in the lavage group when compared with that in the enema group [12,14]. Thus, oral lavage may be important for identifying the hemorrhagic point.
Detection of the bleeding diverticulum
The rate of identification of the diverticulum responsible for the bleeding is relatively low (15%–25% of the cases) partly due to poor bowel preparation [4,15]. To increase the detection rate of the bleeding diverticulum, the hood method and water jet scope should be used before colonoscopy [16,17].
Endoscopic findings for hemostasis
Endoscopic therapy can be performed in patients with an active bleeding, non-bleeding visible vessels, or SRH (Fig. 2). Patients with SRH should be treated owing to the high risk of re-bleeding within 30 days [4,13].
METHODS OF ENDOSCOPIC HEMOSTASIS
Injection/thermal contact therapy
The effectiveness of epinephrine injections or thermal contact therapy for diverticular bleeding has been recognized in the last decade [4,18]. Thermal contact therapies, such as heater probe therapy and bipolar coagulation, are usually indicated alone or in combination with an epinephrine injection for hemostasis in diverticular bleeding [4,18,19]. Epinephrine injection therapy alone can show vasoconstrictive and mechanical effects, resulting in an insufficient treatment involving the risk of re-bleeding. Thermal contact therapy can lead to an increase in the incidence of perforation owing to the thermal influence on the thin wall of the colon or the mucosa and submucosa without the muscular layer [20]. It is highly recommended that excessive thermal injury be avoided, considering the thermal influences [21].
Endoscopic clipping
Endoscopic clipping (EC) is a popular method because it induces less tissue injury than other endoscopic modalities and enables continued treatment without withdrawal of the colonoscope for re-setting to achieve hemostasis as well as injection/thermal contact therapy [22]. Ideally, a direct placement (Fig. 3) of the hemoclips at the bleeding point is associated with a secure deployment [8,23]. When a direct placement is not possible owing to a dome location, massive hemorrhage, or a small diverticular orifice, an indirect placement in a zipper fashion (Fig. 4) allows endoscopic hemostasis through compression [3]. However, caution must be exercised in the indirect method because it may induce sepsis owing to the translocation of bacteria from the diverticulum to blood vessels in very rare cases [24].

Direct placement method. (A) Identification of the bleeding point using a distal attachment cap, which is useful for uncovering the bleeding point. The endoscope is fitted with a distal attachment cap. (B) Direct placement of the clip targeting the visible vessel with the cap. (C) Successful clipping.
Endoscopic band ligation
Endoscopic band ligation (EBL) can be a secure method with a tight closure for the muscularis propria compressed by an O-band involving the bleeding vessels [25]. After identifying the bleeding point, a marking clip is placed at the nearest point for preparation of EBL, followed by reinsertion of the colonoscope with the application of a releasing O-ring for a tight ligation by an EBL device (Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Subsequently, the colonic diverticulum is suctioned into the endoscopic ligator cup, and a syringe with air releases the elastic O-ring (Fig. 5). According to a recent meta-analysis, all three methods (i.e., EBL, coagulation, and clipping) exert beneficial effects on the initial hemostasis and early recurring bleeding. However, EBL has an advantage over coagulation and clipping in terms of the proportions of surgical treatment and transcatheter arterial embolization [21]. With regard to the difference in the long-term outcomes between EBL and EC for the treatment of colonic diverticular bleeding, EBL has been proven to be more effective in decreasing re-bleeding when compared with EC [26]. However, a delayed perforation might develop as a rare complication of EBL [27].

Endoscopic band ligation. (A) Placement of a marking clip near the responsible diverticulum followed by reinsertion of the colonoscope with an endoscopic band ligation device. (B) Easy identification of the bleeding point with the marking clip. (C) View after releasing the O-ring, which ideally ligates both sides of the muscular wall involving the bleeding point.
Hemostatic powder
Hemostatic powder is not a popular hemostatic method for diverticular bleeding, and its usage in LGIB has not been licensed worldwide. Presently, the following three hemostatic powders are commercially available: Hemospray (Cook Medical, Winston-Salem, NC, USA), EndoClot (AMP; EndoClot Plus Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA), and ABS (Ankaferd Health Products Ltd., Istanbul, Turkey). These hemostatic powders as topical sprays have been shown to be effective in the surgical field over the past 50 years [28]. In the recent years, this approach has been shown to be effective for achieving hemostasis in GI bleeding [29-35]. With regard to hemostasis for diverticular bleeding, some case reports have shown the potency of the hemostatic powder [36,37]. It could be an important salvage therapy in case of an unidentified source of bleeding or bleeding that is untreatable with other endoscopic methods because it is simple and reliable for hemostasis [38,39].
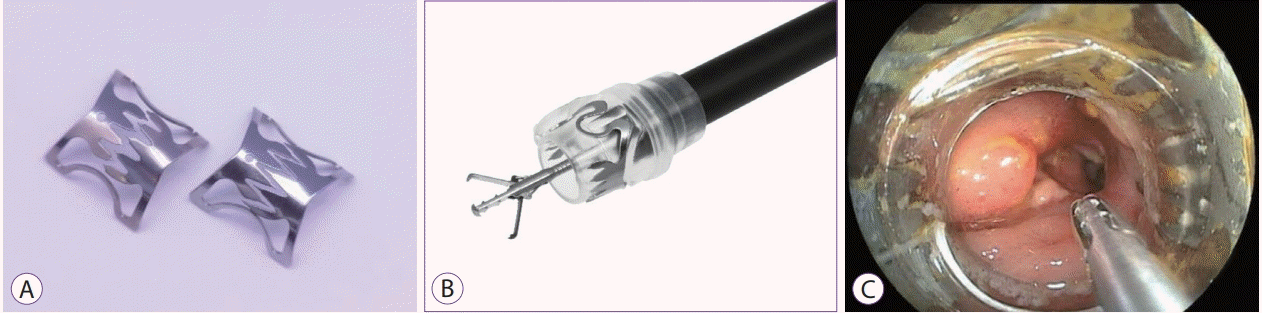
Over-the-scope clip
The over-the-scope clip (OTSC) system (Ovesco Endoscopy AG, Tübingen, Germany) is designed for a full-thickness tight closure by using saw-like teeth of a shark (Fig. 6), and can treat a GI perforation or post-surgery leakage or fistula [40-42]. However, there are limited case reports on the use of the OTSC system for diverticular bleeding [43]. The OTSC system, which is a relatively complex and costly system, is not popular for diverticular bleeding.
CLINICAL OUTCOMES AFTER ENDOSCOPIC TREATMENT
The issue of a high rate of late bleeding (0%–40%) from different diverticula remains unsolved. A long-term hemorrhage may occur if this issue is not solved under the existing conditions of hemostasis methods [8,44-46]. Additionally, several studies have reported high recurrent bleeding rates of 30% and 40% at 1 and 2 years, respectively [47-49].
CHOOSING AN ENDOSCOPIC TREATMENT
After identifying the diverticulum responsible for the bleeding, there are three choices for endoscopic treatment: EBL, EC, or thermal contact therapy.
(1) Whichever is selected, marking the clip deployment is required for subsequent treatment in the cases with an active bleeding. Such patients usually have multiple diverticula. Without the clip, an active bleeding or residual stool would make it difficult to identify the responsible diverticulum.
(2) Epinephrine injection might be effective for temporary hemostasis prior to the definitive treatment if massive bleeding occurs, owing to its vasoconstrictive and mechanical effects. Epinephrine injection therapy is insufficient for curative homeostasis [3,8,22,23,25,26].
(3) Considering the long-term outcomes, EBL might be the best available option for endoscopic hemostasis. In some cases, the patients’ anatomy makes the O-ring ligation difficult [25,26]. In those patients, it is advisable to switch to EC or thermal contact therapy as the definitive treatment [3,4,8,18,22,23,25,26].
CONCLUSIONS
The present review indicates that various endoscopic therapies allow a secure initial hemostasis for diverticular bleeding. However, the existing endoscopic therapies have still not solved the issues of high rates of early and late re-bleeding (Table 1). With regard to a cure for diverticular bleeding, not only the endoscopic methods but also the multilateral perspectives, such as the diet, medicines, interventional approaches, and surgery, should be improved at present.
Notes
Conflicts of Interest: The author has no financial conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
I express my gratitude to Dr. Hiroko Inomata for her beautiful schema of the manuscript.