A Novel Endoscopic Mouthpiece for COVID-19 Prevention
Article information
During the present coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, gastrointestinal endoscopy is regarded as a risky procedure because virus transmission can occur via an airborne route. To reduce the spread of aerosolized droplets, several devices have been developed [1-7]. This novel mouthpiece consists of a conventional mouthpiece made of polypropylene and a hat-shaped aerosol droplet guard, which are connected together. (Fig. 1A and B). The aerosol droplet guard, which is made of a thermoplastic elastomer, has a width of 90 mm and a height of 50 mm, and can prevent aerosolized droplets from being ejected from the mouth (Fig. 1C). The center of the aerosol droplet guard has four slits that are 6 mm long and are oriented to allow the scope to pass through them. (Fig. 1D), while also acting as valves to prevent aerosolized droplet diffusion.

Appearance of the new mouthpiece. (A, B) Side view. The mouthpiece is connected to a hat-shaped aerosol droplet guard. (C, D) Front view. The guard prevents aerosolized droplets from exiting the mouth when the patient coughs. The red arrow shows the slit that the scope is passed through.
The effectiveness of the new mouthpiece in preventing aerosolized droplet diffusion was compared to that of a conventional mouthpiece. As an experimental model, simulated saliva was sprayed from the mouth of a mannequin using a cough machine. The simulated saliva was prepared by adding 76 g of glycerin to 1 L of water [8]. With the endoscope inserted into the mouthpiece, saliva was sprayed in the following conditions: duration, 0.2 sec; velocity, 10.7 m/sec; volume, 75.4 mL; and pressure, 0.08 MPa [8]. Three technical repeats were completed, and the diffusion of the aerosolized droplets was photographed by a camera in a darkened room with a Polarion light. Although there was significant aerosolized droplet diffusion when using the conventional mouthpiece (Fig. 2A), it was only minimally detectable with the new mouthpiece (Fig. 2B).
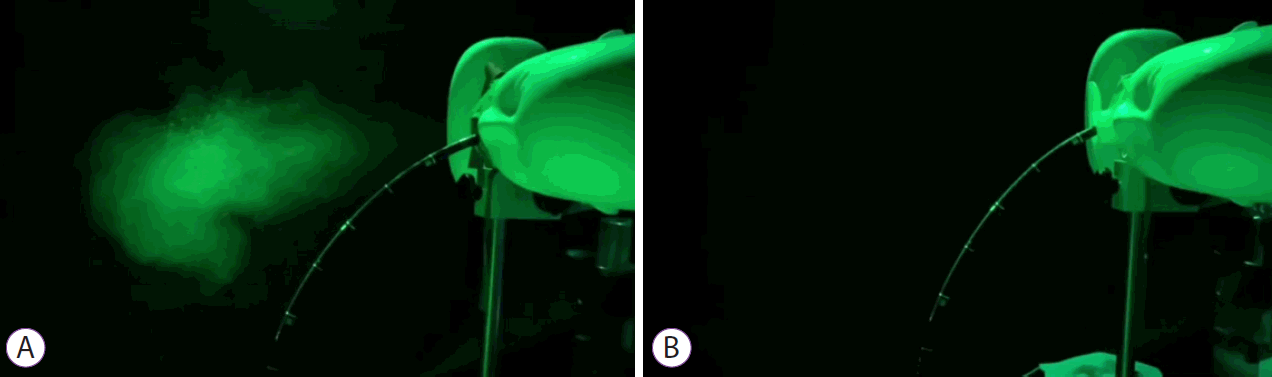
A comparison of the spread of aerosolized droplets during coughing. (A) Significant droplet diffusion was observed when using a conventional mouthpiece. (B) Significant reduction in the amount of diffused droplets when using the new mouthpiece.
The aerosol droplet guard not only prevents diffusion in the area from where the scope is inserted, but also blocks diffusion from the gap between the mouthpiece and the mouth, which is a distinct feature not found in conventional mouthpieces. As the new mouthpiece has not yet been applied clinically, its effect on respiratory and circulatory dynamics during endoscopy is still unknown. However, when used in a virtual clinical setting, there was no apparent breathing discomfort (Fig. 3A and B).

The virtual clinical application of the mouthpiece. (A) Front view. The hat-shaped aerosol droplet guard is larger than a person’s mouth. (B) The aerosol-droplet guard is located 16.5 mm from the mouth and therefore does not affect respiration.
In conclusion, this new mouthpiece can protect clinicians from infection when carrying out endoscopic procedures, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Notes
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Funding
None.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Takuto Hikichi
Investigation: TH
Methodology: TH, Jun Nakamura, Koichi Hamada, Daiki Nemoto
Project administration: TH
Resources: TH
Supervision: TH
Validation: TH
Visualization: TH
Writing-original draft: TH
Writing-review&editing: JN, KH, DN
Acknowledgements
We wish to express our deepest appreciation to Mr. Ichiro Sato and Mr. Taiki Ogawa at KSM Co., Ltd. for creating the mouthpiece; to Mr. Shoichi Uratani, Ms. Rieko Takahashi, and Mr. Kenichi Tabata at the Advanced Technology Center, corporate R&D headquarters, Konica Minolta, Inc. for their basic experimental support; to Mr. Tsuyoshi Ishibashi and Ms. Emiko Hayashi at the Medical Industry Cluster Promotion Unit, Fukushima Prefectural Government; to Mr. Keita Suzuki at the Fukushima Medical Device Industry Promotion Agency for their advice on this study; to Dr. Ryoichiro Kobashi at the Department of Endoscopy, Fukushima Medical University Hospital; and to Dr. Hiroshi Shimizu and Dr. Naoto Abe at the Department of Gastroenterology, Fukushima Medical University for their basic experimental support and advice on this study.
