AbstractBarrettŌĆÖs esophagus (BE) is the precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), and is caused by chronic gastroesophageal reflux. BE can progress over time from metaplasia to dysplasia, and eventually to EAC. EAC is associated with a poor prognosis, often due to advanced disease at the time of diagnosis. However, if BE is diagnosed early, pharmacologic and endoscopic treatments can prevent progression to EAC. The current standard of care for BE surveillance utilizes the Seattle protocol. Unfortunately, a sizable proportion of early EAC and BE-related high-grade dysplasia (HGD) are missed due to poor adherence to the Seattle protocol and sampling errors. New modalities using artificial intelligence (AI) have been proposed to improve the detection of early EAC and BE-related HGD. This review will focus on AI technology and its application to various endoscopic modalities such as high-definition white light endoscopy, narrow-band imaging, and volumetric laser endomicroscopy.
INTRODUCTIONEsophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) has been increasing in incidence1 and is the sixth leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.2 In the United States and other Western countries, EAC is the leading subtype of esophageal cancer.3 BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus (BE), the replacement of normal esophageal squamous epithelium with columnar intestinal metaplasia, is a known precursor to EAC. BE develops in response to chronic damage from acid reflux, causing a progression from normal tissue to dysplastic tissue. If high-grade dysplasia (HGD) is left untreated, it may eventually progress to EAC at an estimated rate of 7% to 15% per year.4 Due to delayed onset of symptoms, esophageal cancer is often diagnosed at a later stage and carries a 5-year survival rate of <25%.5,6 However, localized EAC carries an improved 5-year survival rate of 50%, making early detection critical.1
The goal of endoscopic screening in a select population is to detect both BE and the progression to dysplasia at early stages, where pharmacologic and endoscopic treatment can be utilized to mitigate the risk of progression to EAC. Hence, there is a consensus that endoscopic evaluation is recommended to screen for BE in at-risk populations. Individuals with at least three risk factors for BE and EAC should be offered endoscopy. These risk factors include male gender, non-Hispanic white, age >50 years, history of smoking, chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease, obesity, or a family history of BE or EAC.7
Endoscopically, BE appears as salmon-pink mucosa extending from the esophagogastric junction proximally into the esophagus. The Seattle protocol is the standard practice for sampling the BE segment to assess for dysplasia. It calls for targeted biopsies of any visible lesions and four random quadrant biopsies every 2 cm for non-dysplastic BE or every 1 cm for dysplastic BE.
THE NEED FOR NOVEL TECHNOLOGY IN THE EARLY DETECTION OF BE-RELATED DYSPLASIAUnfortunately, meta-analyses and cohort studies suggest that a high proportion of BE-related HGD and EAC are missed within the first year following index endoscopy during which the BE diagnosis was made.7 There are multiple reasons for missed dysplasia and neoplasia, including poor adherence to the Seattle protocol, especially in longer segments of BE.8,9 This highlights the importance of a high-quality examination during every screening and surveillance endoscopic evaluation. The American Society of Gastroenterology (ASGE) released the preservation and incorporation of valuable endoscopic innovations (PIVI) initiative in 2016, a standardized criteria for evaluating the effectiveness of advanced imaging techniques. The PIVI initiative sets a per-patient sensitivity of >90%, specificity of >80%, and negative predictive value (NPV) of >98% to define a diagnostic or therapeutic threshold that should be met prior to confidently endorsing the use of a technique or device in clinical practice.10
In addition to the standard endoscopic procedures available, there are new and emerging technologies that may enhance the endoscopistŌĆÖs ability to detect dysplasia. Among the newest of these technologies is the use of artificial intelligence (AI). Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) uses deep-learning techniques to either aid in the detection of pathology, called computer-aided detection (CADe), or in the classification of pathology, called computer-aided diagnosis (CADx). The CADx system can be used to characterize lesions as either non-dysplastic or dysplastic. This tool may be used to assist endoscopists in the detection of dysplastic lesions in a BarrettŌĆÖs segment to improve the accuracy of surveillance.11
The use of advanced imaging technologies aims to better detect dysplastic changes during BE screening and surveillance that may be missed by the Seattle protocol. Early and improved detection of dysplasia allows for treatment modalities to be utilized to achieve complete remission of intestinal metaplasia. Ultimately, with the eradication of the dysplastic BE segment, the incidence of EAC can be reduced. This review presents a discussion of the current modalities for imaging BE, emerging promising technology, and an assessment of the quality of evidence supporting each modality.
REAL-TIME ENDOSCOPY AND ADJUNCTIVE TOOLSA diagnosis of BE starts with a thorough evaluation of the esophagus under high-definition white light endoscopy (HD-WLE) (Fig. 1). This high-quality examination allows for the identification of BE, classification of BE per the Prague criteria, examination of abnormal-appearing mucosa, and detection of nodularities/lesions which may be additionally targeted for tissue biopsy. When evaluating the esophagus for possible BE under HD-WLE, differing techniques that have been proposed to improve detection of dysplastic changes include careful inspection techniques, insufflation and deflation, spending adequate time per centimeter of segment, cleaning the mucosal surface, and using a distal attachment cap.4
Several adjunctive tools can be utilized to enhance mucosal visualization and improve detection of dysplasia. Narrow-band imaging (NBI; Olympus), a form of virtual chromoendoscopy, is one of the most commonly employed tools (Fig. 1). The addition of NBI to the exam improves visualization of mucosal and vascular patterns by applying shorter wavelengths (400ŌĆō540 nm) as compared to WLE (400ŌĆō700 nm).11 Dysplastic lesions on NBI appear as areas with irregular mucosal patterning or abnormal blood vessels that are darker than surrounding tissues.12 The addition of NBI to HD-WLE meets the ASGE PIVI threshold with an overall sensitivity of 94.2%, NPV of 97.5%, and specificity of 94.4%.13 It is, overall, a safe and efficacious addition to HD-WLE as it is readily available and does not add additional costs (Table 1).
Chromoendoscopy can also help identify dysplasia. This technique involves applying a dye using a spray catheter to the mucosa. The dye alters the contrast of mucosal vasculature, making it easier to identify BE-related dysplastic lesions. While acetic acid, methylene blue, and indigo carmine are three commonly utilized agents, only acetic acid has met the ASGE PIVI threshold. Acetic acid has a pooled sensitivity of 96.6%, NPV of 98.3%, and specificity of 84.6% (Table 1).4 However, because of the added procedure time using chromoendoscopy with acetic acid (2ŌĆō8 minutes per endoscopic evaluation)14 and the ease and accessibility of virtual chromoendoscopy using NBI, chromoendoscopy is not commonly used in clinical practice.
Despite strict adherence to the Seattle protocol when sampling a BarrettŌĆÖs segment, there can be sampling errors and variations in accuracy for diagnosing dysplasia. This may be due to the expertise of the endoscopist15 and the time-consuming nature of obtaining forceps biopsies (FB).16 A novel device called wide-area transepithelial sampling of the esophagus with computer-assisted three-dimensional analysis (WATS-3D; CDx Diagnostics) allows for a transepithelial specimen of the esophagus to be collected by using a stiff metal brush over a larger area of mucosa containing deeper layers of glandular epithelium. An intact three-dimensional representation of the esophageal mucosa in question is then analyzed by a computer-assisted neural network to identify abnormal cells which may represent dysplasia. After the initial analysis, the sample is presented to a pathologist for confirmation of dysplastic lesions. Typically, WATS-3D specimens are sent to CDx Diagnostics to be evaluated by expert pathologists who receive specialized training in this modality.17 Multiple meta-analyses have evaluated that WATS-3D demonstrates an incremental yield in diagnosing dysplasia.13,18 The most recent meta-analysis conducted by Suresh Kumar et al. in 202018 evaluated 11 studies comparing WATS-3D and FB to FB alone. There was an absolute increase of 16% (p<0.00001) and a relative increase of 1.62 times (p<0.0001) for detection of BE in the WATS-3D and FB group versus FB alone. Additionally, there was a higher rate of identification of dysplasia in the WATS-3D and FB group versus FB alone. The absolute increase was 2% (p=0.001) and relative increase of 2.05 times (p=0.0001). The number needed to treat was 50 patients. However, as was noted by the recently published American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) guidelines from 2022,19 there were several limitations to these studies: (1) WATS-3D was compared to FB alone, but not to FB that were conducted using white light and chromoendoscopy for more targeted biopsies, (2) the studies that showed significant results were all conducted by CDx Diagnostics employed pathologists, and (3) the degree of dysplasia was not quantified. Additionally, most studies focus on the improved diagnostic yield of WATS-3D and do not address the possible limitations in obtaining tissue samples (i.e., mucosal injury). However, a small study of 21 patients with BE who underwent post-radiofrequency ablation surveillance with WATS-3D and FB demonstrated improved detection in terms of BE using these combined modalities. This may suggest that mucosal injury does not impact WATS-3D sampling.20 In conclusion, the ACG was unable to make formal recommendations regarding the use of WATS-3D in clinical practice. However, in conjunction with FB, WLE, and NBI, WATS-3D may be considered to improve surveillance and detection of BE.
APPLICATION OF AI IN HD-WLE AND NBIFinally, the use of AI in the form of CAD represents a compelling new frontier for improving the detection of dysplasia in BE as an adjunct tool to be used with HD-WLE and NBI. A CADe system was developed by de Groof et al.21 to improve the detection of BE during HD-WLE examination (Table 2).11,21-25 The authors primarily developed this system to better differentiate between neoplastic and non-neoplastic lesions in BE. They utilized five large endoscopic databases including general endoscopic images, early-stage neoplasia in BE, and non-dysplastic BE to pre-train the CADe system to detect BE neoplasia and to eventually validate this system. If a neoplastic lesion was identified using the CADe system, it created a heat map that encircled the suspicious neoplastic region. It then flagged what it deemed to be the most concerning part of the lesion within the heat map for more targeted biopsies. The primary outcome of this study was the diagnostic accuracy of this system to correctly identify neoplastic BE from non-neoplastic BE. One of the secondary outcomes was comparing the CAD performance to general endoscopists of all training levels. The system demonstrated an accuracy of 89%, sensitivity of 90%, and specificity of 88% for the detection of BE neoplasia, and when it was compared to general endoscopists, the CAD system achieved higher accuracy (88% vs. 73%), greater sensitivity (93% vs. 72%), and superior specificity (83% vs. 74%). In conclusion, the CADe system performed better than general endoscopists and may represent a useful adjunct modality to better detect BE neoplastic lesions in the future.
Struyvenberg et al.,11 who was part of the original group that described the CADe system, further studied this system to be used with NBI to improve the detection of BE neoplastic lesions. The authors envisioned that the CADe system and this new CADx system would work in tandem. The WLE-CADe system will direct endoscopists to abnormal areas that can then be further characterized by the NBI-CADx system as pathologic and allow for more targeted biopsies (Table 2). Like the CADe system, they used a large database of nearly 500,000 endoscopic images to allow the CADx system to learn how to distinguish between different endoscopic patterns. This was conducted in a stepwise approach. They first provided the CADx system a general overview of endoscopic images and then transitioned to WLE images of BE neoplasia. Eventually, they tested and trained the CADx system on zoom NBI images and NBI videos with the primary endpoint being the diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of this system to characterize BE neoplasia under NBI. The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the CADx system to correctly characterize non-dysplastic BE from BE neoplasia using the NBI images was 84%, 88%, and 78%, respectively. The video-based CADx system demonstrated an accuracy of 83%, sensitivity of 85%, and specificity of 83% for the detection of BE neoplasia. The specificity of the CADx video-based system fared better than the image-based system, which the authors attributed to an increased number of images that were provided by the videos. However, as the authors also noted, a higher specificity would be better to decrease unnecessary esophageal biopsies. Both the CADe and CADx systems may be considered useful adjunctive modalities to be used in BE surveillance in the future. However, investigation with these modalities is nascent, and further studies are needed to optimize the two systems for clinical use.11
ENDOMICROSCOPYConfocal laser endomicroscopyConfocal laser endomicroscopy (CLE) is a system that has been present since the early 2000s and used for various indications other than BE, including adenomatous polyp detection and evaluation of biliary strictures.26,27 It predates other endoscopic image-based modalities such CAD. This modality can obtain images at a histologic level, allowing for the evaluation of tissue architecture during real-time endoscopy (Fig. 2). CLE amplifies the surrounding tissue using a laser-based technology that is emitted from the device. The reflected light is then captured by a lens, producing highly magnified images (resolution of 1 ╬╝m and a depth of 65ŌĆō250 ╬╝m) of the intestinal mucosa with the aid of topical or intravenous fluorescein to further enhance the images.27 CLE is intended to improve diagnostic accuracy and allow for the collection of more precisely targeted biopsies. CLE comes in two variations, either through-the-scope probes (pCLE) or endoscopes with built-in CLE systems (eCLE).27
CLE was first assessed by Pohl et al.28 in a pilot study that enrolled 38 participants. A total of 295 biopsies were first evaluated by pCLE and then histologically by a pathologist. In the per biopsy analysis, evaluated by two expert gastroenterologists, the sensitivity per observer was 75%, the specificity per observer ranged from 89 to 91%, and the NPV was 98% to detect HGD or early EAC. The high NPV of the analysis was reassuring and led to additional studies that assessed whether pCLE provided a diagnostic benefit over HD-WLE and NBI. Sharma et al.29 assessed 101 patients with BE in a randomized controlled trial. HD-WLE alone was compared to NBI and pCLE individually, and the combination of these modalities was also assessed. When pCLE was added to HD-WLE and NBI, there was no statistically significant difference in detection of HGD or EAC when compared to HD-WLE or NBI alone. An additional study also confirmed that NBI has a greater sensitivity and specificity than CLE based on the per-patient and per-lesion analysis.30 Subsequently, two meta-analyses of 8 and 14 studies of 709 and 789 patients, respectively, were conducted and showed a favorable sensitivity of 89% per-patient analysis and a favorable specificity of 89% to 91% per-location analysis suggesting that CLE can be used to detect high-grad dysplastic lesions or early EAC.31,32 However, pCLE was evaluated by the ASGE Technology Committee and was found not to meet the PIVI criteria since its specificity and NPV were below the recommended thresholds.10
These PIVI thresholds were also applied to eCLE and analysis showed that it met the PIVI criteria.10 Unfortunately, eCLE is no longer commercially available. Furthermore, even if available, both pCLE and eCLE had limited clinical use due to cost of the equipment, need for intravenous or topical contrast agents, prolonged length of time during endoscopic evaluation, and lack of interobserver agreement by non-expert gastroenterologists.27,33,34 CLE was thought to increase the diagnostic accuracy for detecting HGD or EAC but, ultimately, the utility of this modality has a limited role in clinical practice due to commercial unavailability and unclear superiority in detecting advanced dysplasia or neoplasia in comparison to other more readily available modalities (Table 1).
Optical coherence tomographyOptical coherence tomography (OCT) is a technology that uses infrared light to produce micro-architectural imaging. Second generation OCT technology, termed volumetric laser endomicroscopy (VLE), has been studied in the detection of BarrettŌĆÖs-related dysplasia during endoscopy. VLE uses a laser probe within a balloon catheter to circumferentially evaluate a 6 cm segment of the esophagus to a depth of 3 mm and a resolution of 7 to 10 ╬╝m.35 It allows for two-dimensional cross-sectional images of all four layers of the esophagus at 10 times the resolution of an endoscopic ultrasound. At 7 to 10 ╬╝m, it can visualize glands, crypts, and villi, but not cellular features.36 Unlike CLE, it does not require a fluorescein dye to enhance images; however, it lacks the enhanced resolution of CLE.
Initially, several histologic scoring indices were developed to provide a standardized approach to identify advanced dysplastic lesions using VLE. The first was the OCT-scoring index (OCT-SI), which relied on a two-component scoring system to assess the epithelial surface and glandular structure. The sensitivity and specificity for HGD and intramucosal carcinoma were 83% and 75%, respectively.37 Other scoring systems were subsequently developed, including the VLE diagnostic algorithm and the VLE prediction score, both of which fared better than the OCT-SI, but with sensitivities and specificities of <90% for detecting dysplasia and neoplasia.38,39 These studies suggest that the diagnostic accuracy of scoring systems may only provide a marginal benefit to apply to clinical practice.
Recent advancements in certain features of VLE technology have aided in detection of dysplasia in patients with BE and may be more applicable to clinical use (Fig. 3). VLE laser marking (VLEL) systems allow for superficial cautery marks to be placed on the areas of interest during VLE inspection for targeted biopsies or endoscopic resection (Fig. 4). A retrospective study conducted by Alshelleh et al.40 compared VLEL directed biopsies with biopsies obtained using the standard Seattle protocol (SSP). The VLEL group had a higher detection rate of 33.7% in comparison to 19.7% that was achieved by the SSP group (p=0.03; odds ratio, 2.1). This study demonstrates that laser marking technology exhibited a statically significant increase in dysplasia detection in comparison to SSP and may be a useful modality to use for more targeted biopsies.
Application of AI in VLEAI-assisted models have also been applied to improve the detection of dysplasia with VLE. CAD has been utilized to improve VLE interpretation and has yielded encouraging results (Table 2). In a study conducted by Swager et al.,22 CAD was used to evaluate ex vivo VLE images of HGD and early EAC that had histologic correlates and compared them to VLE prediction scores. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was 0.95, corresponding to a sensitivity of 90% and specificity of 93%. This fared better than VLE prediction scores which had an AUC of 0.81. This computer-based algorithm showed satisfactory performance in the detection of BE-associated neoplasia despite being conducted with ex vivo images. A follow-up study was conducted utilizing ex vivo images with histologic correlates to evaluate the CAD systemŌĆÖs ability to evaluate multiple VLE frames (as opposed to a single-frame approach) aiming to improve overall efficiency. The multi-frame approach performed significantly better than the single-frame system in detection of HGD and early EAC and allowed for a more time efficient interpretation of the VLE images. The authors concluded that this multi-frame CAD system may be applied to real-time endoscopy due to its efficiency and diagnostic accuracy.23 Finally, a study conducted by Struyvenberg et al.24 prospectively evaluated 47 patients during real-time endoscopy using VLE and CAD in attempts to validate this approach. The study demonstrated an accuracy of 85%, sensitivity of 91%, and specificity of 82%. The CAD system had both good accuracy in detecting BE neoplasia and outperformed 10 gastroenterologists with expertise in VLE interpretation. The AUC for the CAD based system was 0.95 with a sensitivity of 91% compared to an AUC of 0.75 and a sensitivity of 70% achieved by VLE experts. This study suggests that this system may be more practical to use by non-expert gastroenterologists. CAD, when used in conjunction with VLE, may have potential use in the future to enhance detection of BE-related neoplasia, however, further prospective studies are needed and comparison of this approach to other commonly used modalities such as NBI is also needed.
Additional AI-based technologies have also been incorporated with VLE in attempt to make it more interpretable by general gastroenterologists. Intelligent real-time image segmentation (IRIS) was developed using AI technology to highlight areas of concern using various color schemes in real-time to VLE images (Table 2). This computer-based algorithm highlights features that are associated with dysplasia. For example, areas highlighted in pink may represent decreased cellular maturation, blue may suggest altered architecture, and orange may suggest a lack of a layered architecture.41 A 2020 randomized cross-over study conducted by Kahn et al.25 evaluated a total of 133 participants who were randomized to IRIS with VLE or VLE alone and then crossed over to the other arm. When IRIS was used first, unenhanced VLE interpretations were more efficiently interpreted in 2.4 minutes compared to 3.8 minutes (p<0.01). Also, when IRIS was initially used, 100% of the dysplastic sites were accurately identified as compared to 76.9% of the unenhanced VLE group (p=0.06). IRIS may be an important additional component to be utilized with VLE to improve BE neoplasia detection rates but currently there is only one prospective randomized controlled study published.
VLE was not assessed by the ASGE Technology Committee to evaluate whether it meets the PIVI criteria. The beneficial diagnostic yield of VLE alone is still unclear in comparison to other standard endoscopy techniques. Additionally, VLE alone may be limited by cost, commercial availability, lack of standardized protocol for image interpretation, and the need for additional training to develop competency in VLE interpretation (Table 1).35,42,43 However, recent advancements in VLE technology such as CAD, IRIS, and laser marking have shown promising results and may offer a diagnostic benefit for detection of BE-related dysplasia in the future.
NON-ENDOSCOPIC SCREENING FOR BENon-endoscopic OCT technology without the need for sedation has also been studied to evaluate BE, but this technology is still in development. Tethered capsule endoscopy (TCE) uses a small capsule (11 mm├Ś25 mm) attached to a string that is swallowed without sedation and is operated manually by the tether that is outside the patientŌĆÖs mouth (Table 3).44 Real-time images of the mucosa can then be interpreted for BE. Several studies have evaluated the feasibility and reliability of this device.44,45 Approximately 80% to 90% of study participants were able to successfully swallow the device. A strong positive correlation has been demonstrated with both the circumferential and longitudinal extent of BE compared to upper endoscopy.44,45 Presently, however, TCE is not commercially available, and further studies are needed to validate this device for clinical use.
Other non-endoscopic approaches have been evaluated to improve the detection of BE and recommended by recent ACG guidelines as an alternative to screening patients with risk factors for BE. Like TCE, these devices are attached to a string and swallowed by the participant to obtain cytology samples from the esophagus. However, unlike TCE, real-time images are not obtained during the exam. These devices come in two forms; a self-expandable spherical sponge called Cytosponge (Medtronic), and an inflatable silicone balloon called EsoCheck (Lucid Dx Labs) (Fig. 5).19 When these devices are paired with certain biomarkers, they have a 10-fold increase in detecting BE in comparison to using patient risk factors alone.46 However, these nascent devices have yet to be adopted widely in clinical practice (Table 3).
CONCLUSIONSEarly detection of BE-associated dysplasia is essential to prevent progression to EAC. The SSP has its limitations and dysplasia could be missed during esophageal biopsies. Novel developments utilizing enhanced imaging techniques to improve the detection of BE-related dysplastic lesions are being actively studied with promising results. Currently, however, they do not have a definite clinical role due to their limited availability and unclear improvement in diagnostic accuracy compared to the standard of care. Older, unenhanced endomicroscopic techniques such as pCLE and VLE have not shown improved dysplastic detection rates as compared to quicker, cheaper, and more standardized techniques such as NBI. However, more recent advancements in VLE using AI-assisted technologies such as IRIS and CAD have been encouraging but these techniques are not yet commercially available, and their generalizability is still uncertain. Therefore, close mucosal inspection with HD-WLE and NBI along with the SSP remain the mainstay of endoscopic surveillance. There are data, however, that indicate the standard of care needs to be improved. Although still nascent and undergoing further evaluation, recent advancements in AI technology using CAD with NBI and HD-WLE may have a role in BE surveillance in the future.
NOTESConflicts of Interest
Irving Waxman: Consultant for Boston Scientific, Medtronic and Cook Medical. Neal Mehta: Consultant for Boston Scientific, Conmed and Medtronic. The other authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Funding
Netanel Zilberstein: Reports support from the National Research Service Award under grant award 5TL1TR002388. The contents of this paper are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of NCATS/NIH (USA).
Fig.┬Ā1.High-quality endoscopic BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus examination using high-definition white light endoscopy (A) and narrow-band imaging (B) to identify dysplastic lesions. 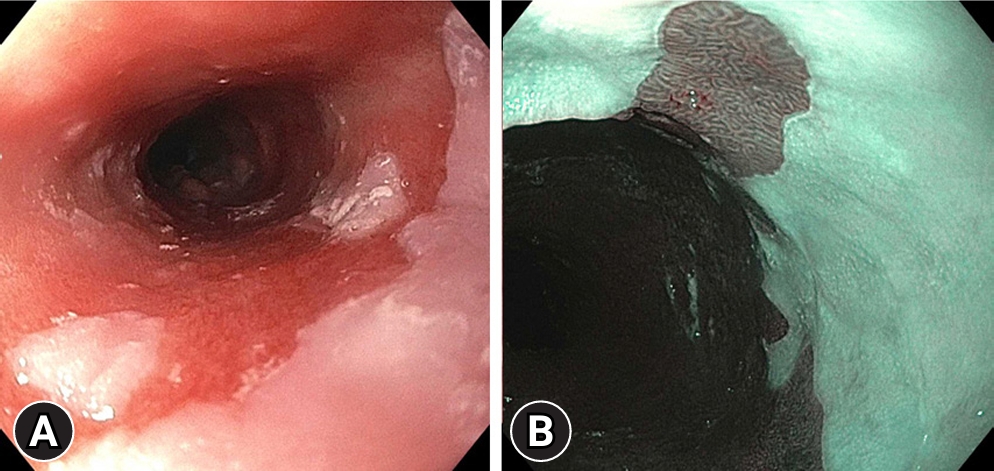
Fig.┬Ā2.Images of confocal laser endomicroscopy using a through-the-scope probe showing. (A) Non-dysplastic BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus. (B) Dysplastic BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus. 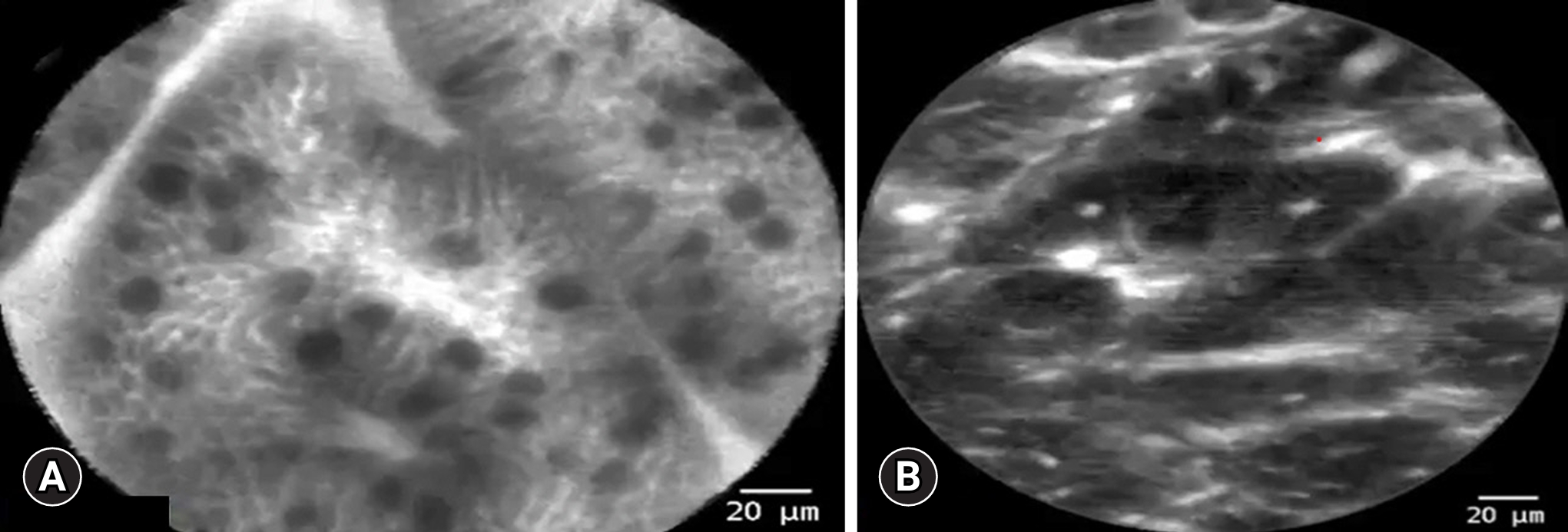
Fig.┬Ā3.Volumetric laser endomicroscopy (VLE) images showing a classic VLE image with BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus dysplasia (A) and magnified image of A showing the dysplastic area (B). 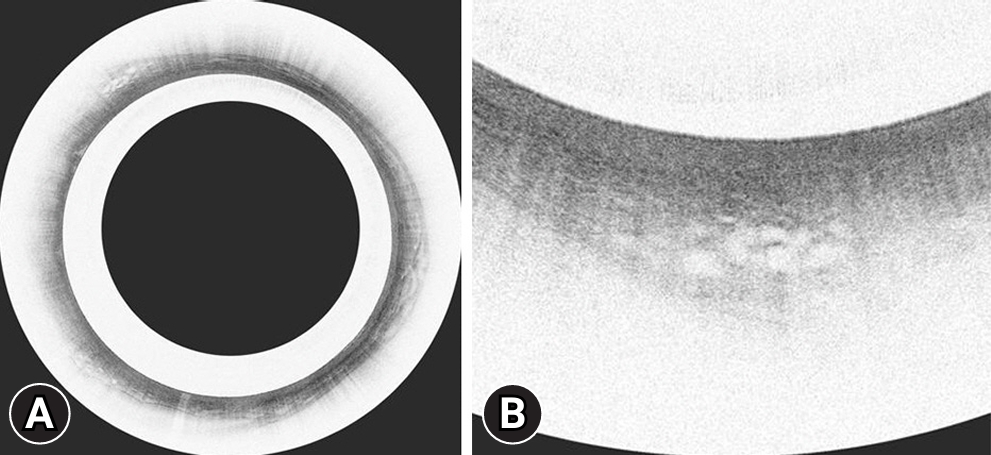
Table┬Ā1.Summary of advanced BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus devices PIVI, preservation and incorporation of valuable endoscopic innovations; eCLE, endoscopes with built-in confocal laser endomicroscopy systems; pCLE, through-the-scope confocal laser endomicroscopy probes; WATS 3D, wide-area transepithelial sampling of the esophagus with computer-assisted three-dimensional analysis. Table┬Ā2.Summary of adjunct AI-based technologies and the associated validation studies
Table┬Ā3.Non-endoscopic approaches to diagnosing BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus REFERENCES1. Edgren G, Adami HO, Weiderpass E, et al. A global assessment of the oesophageal adenocarcinoma epidemic. Gut 2013;62:1406ŌĆō1414.
2. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394ŌĆō424.
3. Coleman HG, Xie SH, Lagergren J. The epidemiology of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018;154:390ŌĆō405.
4. Konda VJ, Ellison A, Codipilly DC, et al. Quality in BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus: diagnosis and management. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc 2022;24:364ŌĆō380.
5. Thein HH, Jembere N, Thavorn K, et al. Estimates and predictors of health care costs of esophageal adenocarcinoma: a population-based cohort study. BMC Cancer 2018;18:694.
6. Then EO, Lopez M, Saleem S, et al. Esophageal cancer: an updated surveillance epidemiology and end results database analysis. World J Oncol 2020;11:55ŌĆō64.
7. Muthusamy VR, Wani S, Gyawali CP, et al. AGA clinical practice update on new technology and innovation for surveillance and screening in BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus: expert review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;20:2696ŌĆō2706.
8. Wani S, Williams JL, Komanduri S, et al. Endoscopists systematically undersample patients with long-segment BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus: an analysis of biopsy sampling practices from a quality improvement registry. Gastrointest Endosc 2019;90:732ŌĆō741.
9. Peters FP, Curvers WL, Rosmolen WD, et al. Surveillance history of endoscopically treated patients with early BarrettŌĆÖs neoplasia: nonadherence to the Seattle biopsy protocol leads to sampling error. Dis Esophagus 2008;21:475ŌĆō479.
10. ASGE Technology Committee, Thosani N, Abu Dayyeh BK, et al. ASGE Technology Committee systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations thresholds for adopting real-time imaging-assisted endoscopic targeted biopsy during endoscopic surveillance of Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2016;83:684ŌĆō698.
11. Struyvenberg MR, de Groof AJ, van der Putten J, et al. A computer-assisted algorithm for narrow-band imaging-based tissue characterization in Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2021;93:89ŌĆō98.
12. Boeriu A, Boeriu C, Drasovean S, et al. Narrow-band imaging with magnifying endoscopy for the evaluation of gastrointestinal lesions. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015;7:110ŌĆō120.
13. ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Qumseya B, Sultan S, et al. ASGE guideline on screening and surveillance of BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2019;90:335ŌĆō359.
14. Canto MI. Acetic-acid chromoendoscopy for BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus: the ŌĆ£prosŌĆØ. Gastrointest Endosc 2006;64:13ŌĆō16.
15. Amamra N, Touzet S, Colin C, et al. Current practice compared with the international guidelines: endoscopic surveillance of BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus. J Eval Clin Pract 2007;13:789ŌĆō794.
16. Abrams JA, Kapel RC, Lindberg GM, et al. Adherence to biopsy guidelines for BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus surveillance in the community setting in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;7:736ŌĆō742.
17. Odze RD, Goldblum J, Kaul V. Role of wide-area transepithelial sampling with 3D computer-assisted analysis in the diagnosis and management of BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 2021;12:e00422.
18. Suresh Kumar VC, Harne P, Patthipati VS, et al. Wide-area transepithelial sampling in adjunct to forceps biopsy increases the absolute detection rates of BarrettŌĆÖs oesophagus and oesophageal dysplasia: a meta-analysis and systematic review. BMJ Open Gastroenterol 2020;7:e000494.
19. Shaheen NJ, Falk GW, Iyer PG, et al. Diagnosis and management of BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus: an updated ACG guideline. Am J Gastroenterol 2022;117:559ŌĆō587.
20. Kataria R, Smith M. Wide area transepithelial sampling (WATS-3D) improves detection of BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus following endoscopic ablation. Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:S22.
21. de Groof AJ, Struyvenberg MR, van der Putten J, et al. Deep-learning system detects neoplasia in patients with BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus with higher accuracy than endoscopists in a multistep training and validation study with benchmarking. Gastroenterology 2020;158:915ŌĆō929.
22. Swager AF, van der Sommen F, Klomp SR, et al. Computer-aided detection of early BarrettŌĆÖs neoplasia using volumetric laser endomicroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2017;86:839ŌĆō846.
23. Struyvenberg MR, van der Sommen F, Swager AF, et al. Improved BarrettŌĆÖs neoplasia detection using computer-assisted multiframe analysis of volumetric laser endomicroscopy. Dis Esophagus 2020;33:doz065.
24. Struyvenberg MR, de Groof AJ, Fonoll├Ā R, et al. Prospective development and validation of a volumetric laser endomicroscopy computer algorithm for detection of BarrettŌĆÖs neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc 2021;93:871ŌĆō879.
25. Kahn A, McKinley MJ, Stewart M, et al. Artificial intelligence-enhanced volumetric laser endomicroscopy improves dysplasia detection in BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus in a randomized cross-over study. Sci Rep 2022;12:16314.
26. Wang KK, Carr-Locke DL, Singh SK, et al. Use of probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (pCLE) in gastrointestinal applications: a consensus report based on clinical evidence. United European Gastroenterol J 2015;3:230ŌĆō254.
27. ASGE Technology Committee. Confocal laser endomicroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2014;80:928ŌĆō938.
28. Pohl H, R├Čsch T, Vieth M, et al. Miniprobe confocal laser microscopy for the detection of invisible neoplasia in patients with BarrettŌĆÖs oesophagus. Gut 2008;57:1648ŌĆō1653.
29. Sharma P, Meining AR, Coron E, et al. Real-time increased detection of neoplastic tissue in BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus with probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy: final results of an international multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc 2011;74:465ŌĆō472.
30. Song J, Zhang J, Wang J, et al. Meta-analysis of the effects of endoscopy with narrow band imaging in detecting dysplasia in BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus. Dis Esophagus 2015;28:560ŌĆō566.
31. Wu J, Pan YM, Wang TT, et al. Confocal laser endomicroscopy for detection of neoplasia in BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus: a meta-analysis. Dis Esophagus 2014;27:248ŌĆō254.
32. Xiong YQ, Ma SJ, Zhou JH, et al. A meta-analysis of confocal laser endomicroscopy for the detection of neoplasia in patients with Barrett's esophagus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;31:1102ŌĆō1110.
33. Becker V, von Delius S, Bajbouj M, et al. Intravenous application of fluorescein for confocal laser scanning microscopy: evaluation of contrast dynamics and image quality with increasing injection-to-imaging time. Gastrointest Endosc 2008;68:319ŌĆō323.
34. Kiesslich R, Anagnostopoulos GK, Axon A, et al. Interobserver variation and standardized training for confocal laser endomicroscopy image interpretation in the upper and lower GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc 2007;65:AB354.
35. Elsbernd BL, Dunbar KB. Volumetric laser endomicroscopy in BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc 2021;23:69ŌĆō76.
36. Wallace MB. Detecting dysplasia with optical coherence tomography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;4:36ŌĆō37.
37. Evans JA, Poneros JM, Bouma BE, et al. Optical coherence tomography to identify intramucosal carcinoma and high-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;4:38ŌĆō43.
38. Leggett CL, Gorospe EC, Chan DK, et al. Comparative diagnostic performance of volumetric laser endomicroscopy and confocal laser endomicroscopy in the detection of dysplasia associated with Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2016;83:880ŌĆō888.
39. Swager AF, Tearney GJ, Leggett CL, et al. Identification of volumetric laser endomicroscopy features predictive for early neoplasia in BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus using high-quality histological correlation. Gastrointest Endosc 2017;85:918ŌĆō926.
40. Alshelleh M, Inamdar S, McKinley M, et al. Incremental yield of dysplasia detection in BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus using volumetric laser endomicroscopy with and without laser marking compared with a standardized random biopsy protocol. Gastrointest Endosc 2018;88:35ŌĆō42.
41. Trindade AJ, McKinley MJ, Fan C, et al. Endoscopic surveillance of BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus using volumetric laser endomicroscopy with artificial intelligence image enhancement. Gastroenterology 2019;157:303ŌĆō305.
42. Smith MS, Cash B, Konda V, et al. Volumetric laser endomicroscopy and its application to BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus: results from a 1,000 patient registry. Dis Esophagus 2019;32:doz029.
43. Trindade AJ, Inamdar S, Smith MS, et al. Learning curve and competence for volumetric laser endomicroscopy in BarrettŌĆÖs esophagus using cumulative sum analysis. Endoscopy 2018;50:471ŌĆō478.
44. Gora MJ, Qu├®n├®herv├® L, Carruth RW, et al. Tethered capsule endomicroscopy for microscopic imaging of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum without sedation in humans (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2018;88:830ŌĆō840.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
