AbstractThe treatment of obesity and its comorbidities ranges from clinical management involving lifestyle changes and medications to bariatric and metabolic surgery. Various endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies (EBMT) recently emerged to address an important therapeutic gap by offering a less invasive alternative to surgery that is more effective than conservative therapies. This article comprehensively reviews the technical aspects, mechanism of action, outcomes, and future perspectives of one of the most promising EBMT, named duodenojejunal bypass liner (DJBL). The DJBL mimics the mechanism of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass by preventing food contact with the duodenum and proximal jejunum, thereby initiating a series of hormonal changes that lead to delayed gastric emptying and malabsorptive effects. These physiological changes result in significant weight loss and improved metabolic control, leading to better glycemic levels, preventing dyslipidemia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and mitigating cardiovascular risk. However, concern exists regarding the safety profile of this device due to the reported high rates of severe adverse events, particularly liver abscesses. Ongoing technical changes aiming to reduce adverse events are being evaluated in clinical trials and may provide more reliable data to support its routine use in clinical practice.
INTRODUCTIONObesity has reached pandemic proportions, with estimates suggesting that by 2035, 51% of the population will be overweight or obese. This escalating crisis comes at a staggering cost of 4 trillion US dollars, encompassing diminished productivity, premature mortality, and increased direct healthcare expenditures.1 Obesity is intricately linked with a range of comorbidities, including dyslipidemia, hypertension, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), obstructive sleep apnea, and others. Notably, among these conditions, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) stands out prominently. The profound correlation between obesity and T2DM has led to the conceptualization of the term ÔÇ£diabesityÔÇØ.2
Bariatric surgery is currently the most effective and durable treatment for obesity and its associated comorbidities.3-5 However, <2% of eligible patients undergo bariatric surgery for a variety of reasons, including surgical risk, personal preference, fear, cost, and access.6 Initial approaches to managing obesity and its related comorbidities involve lifestyle modifications encompassing diet and exercise. Additionally, the use of weight loss medications is increasing due to the higher efficacy than previously available medications. However, poor long-term weight loss, especially after medication discontinuation, often necessitates further therapeutic intervention. Consequently, endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies (EBMTs) have emerged as an alternative for patients with obesity, including those who are ineligible or reluctant to undergo bariatric and metabolic surgical intervention.3,7
The duodenojejunal bypass liner (DJBL) (EndoBarrier; GI Dynamics) (Fig. 1) is a minimally invasive and fully reversible procedure that emulates the metabolic effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) by preventing food contact with the duodenum and proximal jejunum, thereby initiating a series of hormonal changes that lead to delayed gastric emptying and malabsorptive effects. These physiological changes result in significant weight loss and improved metabolic control, leading to better glycemic levels, preventing dyslipidemia and NAFLD, and mitigating cardiovascular risk. However, concern exists regarding the deviceÔÇÖs safety profile due to the reported high rates of severe adverse events (SAEs).7 To increase our understanding of the role of DJBL in the management of obesity and its related comorbidities, this article comprehensively reviews its technical aspects, mechanism of action, outcomes, and future perspectives.
DEVICE CHARACTERISTICS AND ENDOSCOPIC PLACEMENT/REMOVALThe DJBL is a single-use endoscopic device composed of a 60-cm impermeable fluoropolymer liner and a nitinol anchor that enables its fixation in the duodenal bulb. This liner impedes the mixing of chyme with bile and pancreatic secretions prior to the proximal portion of the jejunum.
The DJBL is placed endoscopically under general anesthesia. First, a guidewire is positioned in the jejunum (as distally as possible) and the device is placed over the guidewire under fluoroscopic and endoscopic assistance. The fluorine polymer liner is then advanced to overlay the duodenum and the proximal jejunum. After the appropriate position is confirmed on fluoroscopy, the anchoring system is deployed and fixed at the duodenal bulb (Fig. 2). Finally, a water-soluble contrast is injected through the working channel to ensure proper device position and the absence of liner obstructions (ÔÇ£kinksÔÇØ).7
The endoscopic removal of the DJBL should performed under general anesthesia and fluoroscopic assistance utilizing a device-specific grasping tool within a suitable foreign body hood (similar to a large cap) positioned at the distal end of the gastroscope.8 The device is ideally removed within 12 months unless early removal is required due to an adverse event. A prior study reveal that DJBL use longer than 12 months (up to 24 months) increases the risk of adverse events without providing clinical benefits.8
PHYSIOLOGICAL ASPECTS/MECHANISM OF ACTIONEBMTs are generally classified into four categories: space occupying, gastric remodeling, aspiration therapy, and small bowel therapies.3 The DJBL is categorized as a small bowel therapy that aims to replicate the mechanisms of action of RYGB, a surgery recognized for its significant metabolic effects.9-13
Among its mechanisms of action, the incretin effect is specifically relevant. Incretins are gut hormones that enhance insulin secretion following food consumption. The main incretins are glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1> (GLP-1).14 GIP is secreted by K enteroendocrine cells in the duodenum and proximal jejunum upon contact with food, thus stimulating insulin synthesis and secretion. Nevertheless, this process may contribute to the onset of T2DM. Conversely, GLP-1 acts in the distal small intestine, stimulating beta cell proliferation, promoting insulin production and secretion, inhibiting glucagon secretion, slowing peristalsis, and promoting satiety.15
Another crucial hormonal effect of DJBL is linked to gastric emptying. Ghrelin, a hormone produced in the gastric fundus and pancreas, stimulates hunger. Conversely, peptide YY (PYY) inhibits gastrointestinal emptying and enhances satiety.15
By preventing food contact with the mucosa of the duodenum and proximal jejunum, DJBL reduces the anti-incretin effect, subsequently improving insulin resistance and glucose regulation. Additionally, the presence of undigested food in the distal portions of the small intestine stimulates incretin secretion and insulin production and enhances glycemic homeostasis.7
A previous meta-analysis demonstrated that, upon device removal, postprandial GLP-1 levels significantly increase and GIP levels decrease compared to baseline values. The same study also evidenced a notable increase in fasting ghrelin and PYY levels.16
A comprehensive analysis of the mechanisms of action revealed comparable effects of DJBL and RYGB. Overall, both strategies elevate GLP-1 and PYY levels while reducing GIP concentrations. Moreover, both methods mechanically exclude the duodenum and proximal jejunum, exposing the distal segments of the small intestine to undigested contents. Divergent findings have emerged concerning the effects on ghrelin; its levels decrease with RYGB but increase with the DJBL. The surgical approach also involves isolation of the cardia, a partial vagotomy, and exclusion of the distal stomach, while the DJBL delays gastric emptying.8,17
CLINICAL OUTCOMESWeight lossA recent systematic review and meta-analysis18 examined the impact of DJBL on weight loss and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels. The meta-analysis included 10 randomized controlled trials (evidence 1A) examining a total of 681 patients (80% with T2DM) who underwent device placement along with 291 controls. The percentage excess weight loss (%EWL) was higher in the DJBL than control group (mean difference [MD], +11.39% [+7.75 to +15.03%]; p<0.00001, I2=91%) as well as absolute weight loss (AWL) and total weight loss (%TWL), with MD values of +6.64 kg [+4.77 to +8.50 kg], p<0.00001, I2=98% and +4.43% [+1.95 to +6.90%], p=0.0005, I2=98%, respectively, compared with other weight loss modalities such as aspiration therapy and intragastric balloon.19,20
All EBMTs carry the risk of weight regain after their removal. In a retrospective study, a follow-up assessment performed 6 months after DJBL removal showed that 66.7% of patients with class I obesity (at baseline) maintained a stable weight or regained only <7%. In contrast, no patients with a body mass index (BMI) >35 kg/m2 (at baseline) were able to maintain or present a weight regain <7%.21 A study evaluated the outcomes at 4 years after DJBL explantation and showed improvement in AWL, %TWL, and BMI. However, none of these parameters were significantly different compared to baseline.22 Thus, the effect of initial DJBL treatment on weight reduction seemed diminished after long-term follow-up. However, larger prospective studies with long-term follow-up periods are needed to clarify its long-term effects.
Metabolic improvementAs previously emphasized, due to mechanisms akin to RYGB, the DJBL is anticipated to yield significant effects on glycemic control. Notable reductions in HbA1c levels have been demonstrated as in a recent level 1A evidence study, with an MD of ÔÇô1.03 (ÔÇô1.56 to ÔÇô0.50, p=0.0001, I2=65%).18 Within the Worldwide Endobarrier Registry established by the Association of British Clinical Diabetologists, 1,022 patients from 34 centers in 10 countries were registered through October 2022. The registry revealed considerable improvements in weight loss, systolic blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and HbA1c, with more pronounced enhancements observed in patients with higher BMI and HbA1c levels. Notably, there was a reduction of ÔêÆ1.3┬▒1.5 in HbA1c (p<0.001).23
A recent study examined the metabolic effects of DJBL in patients with NAFLD. Over a 48-week duration, 31 patients with obesity and T2DM exhibited a reduction in steatosis and a decreased risk of developing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, although the impact on hepatic fibrosis was limited.24 Another study assessed 71 patients who underwent DJBL treatment for 9ÔÇô12 months, followed by a 6-month follow-up after its removal. This study demonstrated a decrease in the fatty liver index during its use (93.38 vs. 98.22, p<0.001) along with reductions in alanine aminotransferase (29.03 vs. 42.29 U/L, p<0.0001) and cytokeratin-18 fragments (190.6 vs. 276 U/L, p<0.0001), which remained stable in the following 6 months.25
Moreover, a relatively unexplored undesired effect of the DJBL involves vitamin and mineral malabsorption. An analysis of 19 insulin-dependent diabetes patients after 12 months of treatment observed significant decreases in hemoglobin, hematocrit, iron, ferritin, vitamin B12, albumin, and pre-albumin. While no substantial changes in bone mineral density were noted, further research is needed to formulate nutritional recommendations for these patients.26
As a result of enhanced metabolic control, a prospective study of 71 patients indicated a relative risk reduction of cardiovascular events over a 4-year period among patients undergoing DJBL treatment. The risk reduction reached 16.2% at the time of its removal, and the benefits persisted for 6 months thereafter.27
SafetyIn a previous systematic review28 considering the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) grading system,29 the rate of DJBL-related adverse events was 84.4%, with 75.8% classified as mild and 3.7% as severe.28,29 In a more recent meta-analysis,18 SAEs occurred in 19.7% of patients according to the Clavien-Dindo30 and AGREE31 classifications. The majority of adverse eventsÔÇöpredominantly those involving abdominal pain and nauseaÔÇöare linked to the initial adaptation period after device. Within the Worldwide DJBL Registry, 4.2% of patients reportedly experienced SAEs, notably bleeding (2.3%), hepatic abscesses (1.1%), and pancreatitis/cholecystitis (0.4%).23
While most SAEs can be managed through endoscopic removal of the DJBL,18,32 in 2015, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) halted the ENDO trial (NCT01728116) due to the risk of device-related hepatic abscesses.33 To overcome this issue, the company is implementing technical modifications and recommending the discontinuation of proton pump inhibitor intake during DJBL use.
COMPARISON WITH OTHER METHODSCompared to RYGB, despite their physiological similarities, the surgical approach leads to more significant weight loss. In a comparative study of 97 patients (75 treated with RYGB, 25 treated with DJBL) with a 12-month follow-up, the mean BMI reduction (11.54┬▒4.47 kg/m┬▓ vs. 6.23┬▒2.36), %TWL (27.93┬▒8.57% vs. 15.04┬▒5.73), and %EWL (67.26┬▒24.6% vs. 44.48┬▒27.07) were higher in the RYGB group. In terms of metabolic effects, at 1 year of follow-up, glycemic control had improved significantly in both groups with no significant intergroup difference.8
Current FDA-approved EBMTs include intragastric balloon, aspiration therapy, and gastric remodeling therapies such as endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty with the Apollo Overstitch suturing device (Apollo Endosurgery Inc.) as well as gastric suturing using the Endomina platform (Endo Tools Therapeutics S.A.).13 The ASGE/American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) criteria for adopting EBMTs in clinical practice encompass a %EWL 25% versus the control group and an SAE rate 5%.34,35 Therefore, the available data demonstrate that the DJBL does not achieve the ASGE/ASMBS criteria for adoption in clinical practice. More data are expected to be obtained from the ongoing STEP-1 trial (NCT04101669), which was initiated in 2019 and is expected to end in 2025.36
Among the most commonly used EBMTs (Table 1),18,19,37-41 two directly target the small bowel as the DJBL and the duodenal mucosal resurfacing (DMR). While no EBMTs targeting the small bowel have been approved to date by the FDA for routine practice,42 the initial data are promising.
The DMR involves thermal ablation of the duodenal mucosa that aims to enhance glycemic control in patients with T2DM. A meta-analysis of four studies including 127 patients demonstrated reductions in HbA1c by 1.72% and 0.94% at 3 and 6 months of follow-up, respectively. This improvement was accompanied by improved hepatic function markers such as alanine aminotransferase. Interestingly, DMR did not influence weight loss. These findings suggest that DMR could be an option for achieving at least short-term glycemic control and managing hepatic steatosis in non-insulin-dependent T2DM patients.38 Thus, the limited effect on weight loss of DMR seems to favor the use of DJBL in patients with both T2DM and over­weight/obesity.
Among the various EBMTs, device selection must consider several factors such as personal and local experience, device availability, patient preference, and cost.
FUTURE PERSPECTIVESAs the EBMT field evolves, several areas must be addressed to optimize outcomes. Patient selection is key to achieving better outcomes. Several factors that may interfere in the mechanism of action of EBMTs are being investigated, such as gastric motility, bile acid metabolism, the gut microbiome, enteral hormones, and genetics. The combined use of two EBMT devices, applied simultaneously or sequentially, as well as that of an EBMT with weight loss medications, appear to improve efficacy and are under investigation. As any other medical treatment, a great doctorÔÇôpatient relationship is crucial to achieving satisfactory outcomes, including close follow-up with a multidisciplinary team.
Larger randomized controlled trials with long-term follow-up are still required to gather more robust evidence for EBMT utilization, mainly therapies targeting the small bowel such as the DJBL.
CONCLUSIONSAlthough the ASGE/ASMBS thresholds for the adoption of DJBL in the endoscopic management of obesity was not reached by studies to date, the DJBL may still play a role in the management of obesity and T2DM. DJBL is a minimally invasive therapy with higher efficacy than control groups in high-quality comparative studies. Safety remains a concern due to its non-negligible rate of SAEs. Therefore, the device requires modification with the aim of improving its safety profile. Additionally, standardized training is needed to enhance outcomes and facilitate its broad adoption. As an EBMT, the DJBL may become an important tool in the armamentarium for the battle against the diabesity pandemic.
NOTESFig. 2.Photographs of step by step duodenojejunal bypass liner (DJBL) placement process. (A) Endoscopic evaluation followed by distal guidewire placement. (B) DJBL placement over the guidewire. (C) Anchor system deployment in the duodenal bulb. (D) Final appearance after successful DJBL placement. 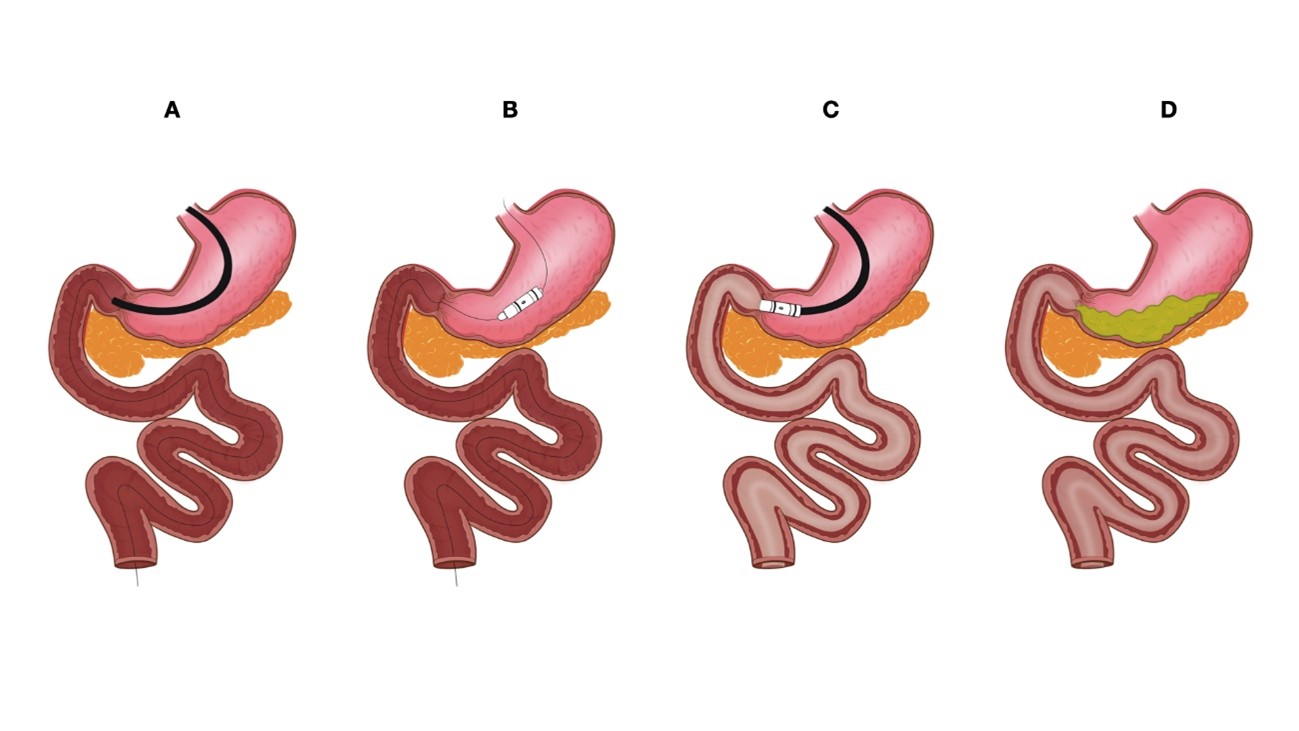
Table 1.EBMT, endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapy; TWL, total weight loss; EWL, excess weight loss; SAE, severe adverse event; DJBL, duodenaljejunal bypass liner; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; IGB, intragastric balloon; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; ESG, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty; RCT, randomized controlled trial; POSE, primary obesity surgery endoluminal; DMR, duodenal mucosal resurfacing; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. REFERENCES1. World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas 2023 [Internet]. World Obesity Federation; 2023 [cited 2023 Apr 8]. Available from: https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/?cat=19.
2. Michaelidou M, Pappachan JM, Jeeyavudeen MS. Management of diabesity: current concepts. World J Diabetes 2023;14:396ÔÇô411.
3. Na HK, De Moura DT; Study Group for Endoscopic Bariatric and Metabolic Therapies of the Korean Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Various novel and emerging technologies in endoscopic bariatric and metabolic treatments. Clin Endosc 2021;54:25ÔÇô31.
4. Cambi MP, Baretta GA, Magro DO, et al. Multidisciplinary approach for weight regain-how to manage this challenging condition: an expert review. Obes Surg 2021;31:1290ÔÇô1303.
5. Colquitt JL, Pickett K, Loveman E, et al. Surgery for weight loss in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;2014:CD003641.
6. Nguyen NT, Masoomi H, Magno CP, et al. Trends in use of bariatric surgery, 2003-2008. J Am Coll Surg 2011;213:261ÔÇô266.
7. Tatarian T, Rona KA, Shin DH, et al. Evolving procedural options for the treatment of obesity. Curr Probl Surg 2020;57:100742.
8. G├╝nthert SJ, Aksan A, Schr├Âder O, et al. Glycemic control and BMI changes after endoscopic implantation of a duodenojejunal bypass liner compared with laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery: a propensity score matching analysis. Surg Endosc 2022;36:5979ÔÇô5985.
9. Betzel B, Cooiman MI, Aarts EO, et al. Clinical follow-up on weight loss, glycemic control, and safety aspects of 24 months of duodenal-jejunal bypass liner implantation. Surg Endosc 2020;34:209ÔÇô215.
10. Simons M, Sharaiha RZ. Updates in metabolic bariatric endoscopy. Dig Endosc 2023 Jul 5 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1111/den.14633.
11. Shenoy A, Schulman AR. Advances in endobariatrics: past, present, and future. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf) 2023;11:goad043.
12. Dave N, Dawod E, Simmons OL. Endobariatrics: a still underutilized weight loss tool. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol 2023;21:172ÔÇô184.
13. McCarty TR, Thompson CC. The current state of bariatric endoscopy. Dig Endosc 2021;33:321ÔÇô334.
14. Campbell JE, Drucker DJ. Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of incretin hormone action. Cell Metab 2013;17:819ÔÇô837.
15. Chen JH, Yu ZH, Liu QF, et al. Research progress of duodenal-jejunal bypass liner in the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2022;15:3319ÔÇô3327.
16. Jirapinyo P, Haas AV, Thompson CC. Effect of the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes with obesity: a meta-analysis with secondary analysis on weight loss and hormonal changes. Diabetes Care 2018;41:1106ÔÇô1115.
17. de Moura EG, Lopes GS, Martins BC, et al. Effects of Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Liner (EndoBarrier┬«) on gastric emptying in obese and type 2 diabetic patients. Obes Surg 2015;25:1618ÔÇô1625.
18. Yvamoto EY, de Moura DT, Proen├ºa IM, et al. The effectiveness and safety of the Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Liner (DJBL) for the management of obesity and glycaemic control: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Surg 2023;33:585ÔÇô599.
19. Jirapinyo P, de Moura DT, Horton LC, et al. Effect of aspiration therapy on obesity-related comorbidities: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Endosc 2020;53:686ÔÇô697.
20. Cho JH, Bilal M, Kim MC, et al. The clinical and metabolic effects of intragastric balloon on morbid obesity and its related comorbidities. Clin Endosc 2021;54:9ÔÇô16.
21. Boonchaya-Anant P, Bueter M, Gubler C, et al. Sustained weight loss after duodenal-jejunal bypass liner treatment in patients with body mass index below, but not above 35 kg/m2: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Obes 2023;13:e12561.
22. van Rijn S, Roebroek YG, de Jonge C, et al. Effect of the EndoBarrier device: a 4-year follow-up of a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Obes Surg 2019;29:1117ÔÇô1121.
23. Ryder RE, Laubner K, Benes M, et al. Endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass liner treatment for type 2 diabetes and obesity: glycemic and cardiovascular disease risk factor improvements in 1,022 patients treated worldwide. Diabetes Care 2023;46:e89ÔÇôe91.
24. Karlas T, Petroff D, Feisthammel J, et al. Endoscopic bariatric treatment with duodenal-jejunal bypass liner improves non-invasive markers of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Obes Surg 2022;32:2495ÔÇô2503.
25. Roehlen N, Laubner K, Nicolaus L, et al. Impact of duodenal-jejunal bypass liner (DJBL) on NAFLD in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrition 2022;103-104:111806.
26. Vilarrasa N, Fabregat A, Toro S, et al. Nutritional deficiencies and bone metabolism after endobarrier in obese type 2 patients with diabetes. Eur J Clin Nutr 2018;72:1447ÔÇô1450.
27. Roehlen N, Laubner K, Bettinger D, et al. Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Liner (DJBL) improves cardiovascular risk biomarkers and predicted 4-year risk of major CV events in patients with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Obes Surg 2020;30:1200ÔÇô1210.
28. Betzel B, Drenth JP, Siersema PD. Adverse events of the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner: a systematic review. Obes Surg 2018;28:3669ÔÇô3677.
29. Cotton PB, Eisen GM, Aabakken L, et al. A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest Endosc 2010;71:446ÔÇô454.
30. Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 2004;240:205ÔÇô213.
31. Nass KJ, Zwager LW, van der Vlugt M, et al. Novel classification for adverse events in GI endoscopy: the AGREE classification. Gastrointest Endosc 2022;95:1078ÔÇô1085.
32. De Moura EG, de Moura DT, Galv├úo-Neto M, et al. Endoscopic management of anchor erosion adjacent to the pylorus following duodenal-jejunal bypass sleeve. Obes Surg 2019;29:2003ÔÇô2004.
33. Laubner K, Riedel N, Fink K, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a case control study. Diabetes Obes Metab 2018;20:1868ÔÇô1877.
34. ASGE/ASMBS Task Force on Endoscopic Bariatric Therapy. A pathway to endoscopic bariatric therapies. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2011;7:672ÔÇô682.
35. ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force and ASGE Technology Committee, Abu Dayyeh BK, Kumar N, et al. ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting endoscopic bariatric therapies. Gastrointest Endosc 2015;82:425ÔÇô438.
36. Mauro A, Lusetti F, Scalvini D, et al. A comprehensive review on bariatric endoscopy: where we are now and where we are going. Medicina (Kaunas) 2023;59:636.
37. Singh S, Bazarbashi AN, Khan A, et al. Primary obesity surgery endoluminal (POSE) for the treatment of obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 2022;36:252ÔÇô266.
38. de Oliveira GH, de Moura DT, Funari MP, et al. Metabolic effects of endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Surg 2021;31:1304ÔÇô1312.
39. Kotinda AP, de Moura DT, Ribeiro IB, et al. Efficacy of intragastric balloons for weight loss in overweight and obese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Surg 2020;30:2743ÔÇô2753.
40. de Miranda Neto AA, de Moura DT, Ribeiro IB, et al. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty at mid term in the management of overweight and obese patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Surg 2020;30:1971ÔÇô1987.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
