Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Prevalence and natural course of incidental gastric subepithelial tumors
- Dae-Hyuk Heo, Min A Yang, Jae Sun Song, Won Dong Lee, Jin Woong Cho
- Received May 4, 2023 Accepted July 16, 2023 Published online March 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2023.124 [Epub ahead of print]
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub 
- Background
/Aims: Gastric subepithelial tumors (SETs) are often encountered during the upper gastrointestinal endoscopic screening. We assessed the prevalence of gastric SETs and the risk factors for their progression.
Methods
We reviewed the electronic medical records of 30,754 patients who underwent upper gastrointestinal endoscopic screening at our medical center between January 2013 and December 2016.
Results
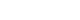
Among the 30,754 patients examined, 599 (1.94%) had gastric SETs. The prevalence increased with age and was 9.56% in patients aged ≥70 years. In total, 262 patients underwent serial endoscopy for more than 6 months. The median age was 68 years (interquartile range [IQR], 61–74), and the number of females was 167 (63.7%). During a median follow-up of 58 months (IQR, 38–75), 22 patients (8.4%) showed significant changes in tumor size. An irregular border (odds ratio, 4.623; 95% confidence interval, 1.093–19.558; p=0.037) was a significant risk factor for progression. Seven patients underwent surgical or endoscopic resections. The pathologies of gastric SETs included leiomyomas (n=3), gastrointestinal stromal tumors (n=2), and lipomas (n=2).
Conclusions
The prevalence of gastric SETs increases with age. Most gastric SETs do not progress during long-term endoscopic examinations, and the risk of an increase in size is low in asymptomatic small SETs without irregular borders.
- 1,579 View
- 33 Download

- Prevalence, natural progression, and clinical practices of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions in Korea: a multicenter study
- Younghee Choe, Yu Kyung Cho, Gwang Ha Kim, Jun-Ho Choi, Eun Soo Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Eun Kwang Choi, Tae Hyeon Kim, Seong-Hun Kim, Do Hoon Kim, The Research Group for Endoscopic Ultrasound in Korean Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
- Clin Endosc 2023;56(6):744-753. Published online August 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2023.005
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub 
- Background
/Aims: This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence and natural progression of subepithelial lesions (SELs) in the upper gastrointestinal (UGI) tract.
Methods
The medical records of patients with UGI SELs who underwent endoscopic screening at eight university hospitals between January and December 2010 were retrospectively investigated. The follow-up evaluations were performed until December 2016.
Results
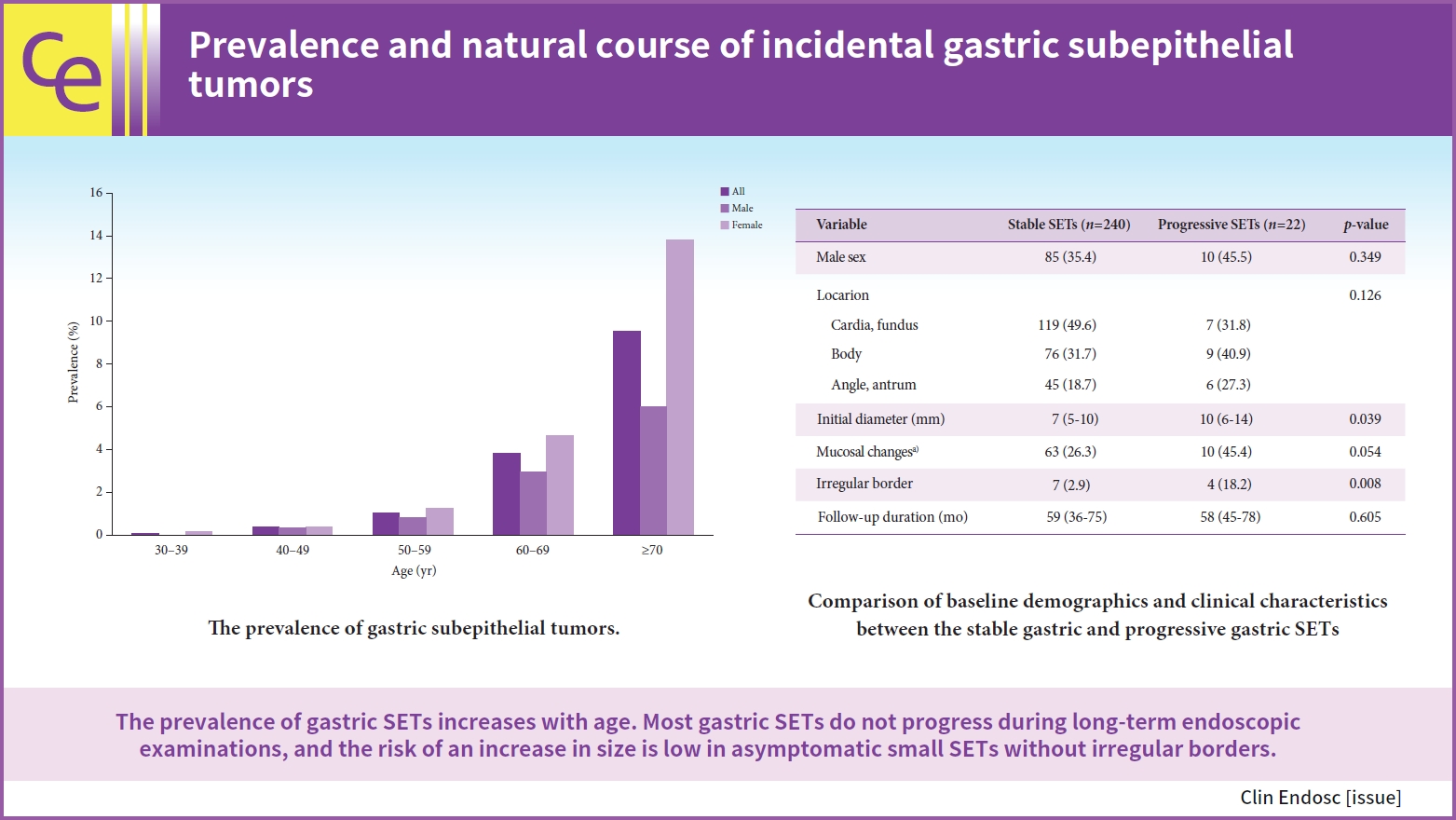
UGI SELs were found in 1,044 of the 65,233 participants screened (endoscopic prevalence, 1.60%; the total number of lesions, 1,062; mean age, 55.1±11.2 years; men, 53.6%). The median follow-up period was 48 (range, 8–74) months. SELs were most frequently found in the stomach (63.8%) and had a mean size of 9.9±6.1 mm. Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) was performed in 293 patients (28.1%). The most common lesions were leiomyomas, followed by gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), and ectopic pancreas. The proportions of SELs with malignant potential according to size were 3% (<1 cm), 22% (1–2 cm), 27% (2–3 cm), and 38% (≥3 cm). In gastric SELs larger than 1 cm, resections were performed in 20 patients because of an increase in size, of which 12 were found to be GISTs.
Conclusions
The prevalence of UGI SELs was 1.60%. Further, 23% of gastric SELs ≥1 cm were precancerous lesions, most followed by EUS and clinical decisions without initial pathological confirmation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Esophageal MALT Lymphoma Mimicking a Subepithelial Tumor
Ha Eun Lee, Gwang Ha Kim, Min Ji Kim, Kyung Bin Kim, Dong Chan Joo, Hye Kyung Jeon, Moon Won Lee, Bong Eun Lee
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 83(4): 157. CrossRef - Small gastric subepithelial lesions: A sand in the eye
Tanyaporn Chantarojanasiri, Nikhil Sonthalia, Rashid N. Lui
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An Esophageal Leiomyoma with Cystic Degeneration Mimicking a Malignant Neoplasm
Gwang Ha Kim, Dong Chan Joo, Moon Won Lee, Bong Eun Lee, Kyungbin Kim
The Ewha Medical Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Case of Esophageal MALT Lymphoma Mimicking a Subepithelial Tumor
- 2,718 View
- 165 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Comparison of diagnostic performances of slow-pull suction and standard suction in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy for gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors
- Joon Seop Lee, Chang Min Cho, Yong Hwan Kwon, An Na Seo, Han Ik Bae, Man-Hoon Han
- Clin Endosc 2022;55(5):637-644. Published online August 17, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.257

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Background
/Aims: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy (EUS-FNB) is integral to the diagnosis of gastrointestinal (GI) subepithelial tumors (SETs). The impact of different EUS-FNB tissue sampling techniques on specimen adequacy and diagnostic accuracy in SETs has not been fully evaluated. This study aimed to compare the diagnostic outcomes of slow-pull (SP) and standard suction (SS) in patients with GI SETs.
Methods
In this retrospective comparative study, 54 patients were enrolled. Medical records were reviewed for location and size of the target lesion, FNB needle type/size, technical order, specimen adequacy, diagnostic yield, and adverse events. The acquisition rate of adequate specimens and diagnostic accuracy were compared according to EUS-FNB techniques.
Results
The mean lesion size was 42.6±36.4 mm, and most patients were diagnosed with GI stromal tumor (75.9%). The overall diagnostic accuracies of the SP and SS techniques were 83.3% and 81.5%, respectively (p=0.800). The rates of obtaining adequate core tissue were 79.6% and 75.9%, respectively (p=0.799). No significant clinical factors affected the rate of obtaining adequate core tissue, including lesion location and size, FNB needle size, and final diagnosis.
Conclusions
SP and SS had comparable diagnostic accuracies and adequate core tissue acquisition for GI SETs via EUS-FNB. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions
Takuto Hikichi, Minami Hashimoto, Takumi Yanagita, Tsunetaka Kato, Jun Nakamura
Journal of Medical Ultrasonics.2024; 51(2): 195. CrossRef - What method can we choose if rapid on-site evaluation is not available for the endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions?
Yu Kyung Cho
Clinical Endoscopy.2024; 57(1): 53. CrossRef - The Diagnostic Approach of Benign Esophageal Tumors: A Narrative Review
Alex R. Jones, Preksha Vankawala, Tarek Sawas
Current Treatment Options in Gastroenterology.2024; 22(2): 44. CrossRef - Diagnostic yield of endoscopic and EUS-guided biopsy techniques in subepithelial lesions of the upper GI tract: a systematic review
Cynthia A. Verloop, Jacqueline A.C. Goos, Marco J. Bruno, Rutger Quispel, Lydi M.J.W. van Driel, Lieke Hol
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2024; 99(6): 895. CrossRef - An Esophageal Leiomyoma with Cystic Degeneration Mimicking a Malignant Neoplasm
Gwang Ha Kim, Dong Chan Joo, Moon Won Lee, Bong Eun Lee, Kyungbin Kim
The Ewha Medical Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence, natural progression, and clinical practices of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions in Korea: a multicenter study
Younghee Choe, Yu Kyung Cho, Gwang Ha Kim, Jun-Ho Choi, Eun Soo Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Eun Kwang Choi, Tae Hyeon Kim, Seong-Hun Kim, Do Hoon Kim
Clinical Endoscopy.2023; 56(6): 744. CrossRef
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions
- 2,523 View
- 126 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Mucosal incision-assisted biopsy versus endoscopic ultrasound-assisted tissue acquisition for subepithelial lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Suprabhat Giri, Shivaraj Afzalpurkar, Sumaswi Angadi, Sridhar Sundaram
- Clin Endosc 2022;55(5):615-625. Published online August 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2022.133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Background
/Aims: Mucosal incision-assisted biopsy (MIAB) for tissue acquisition (TA) from subepithelial lesions (SELs) is emerging as an alternative to endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided TA. Only a limited number of studies compared the diagnostic utility of MIAB and EUS for upper gastrointestinal (GI) SELs; therefore, we conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A comprehensive literature search from January 2020 to January 2022 was performed to compare the diagnostic accuracy and safety of MIAB and EUS-guided TA for upper GI SELs.
Results
Seven studies were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled technical success rate (risk ratio [RR], 0.96; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.89–1.04) and procedural time (mean difference=–4.53 seconds; 95% CI, –22.38 to 13.31] were comparable between both the groups. The overall chance of obtaining a positive diagnostic yield was lower with EUS than with MIAB for all lesions (RR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.71–0.98) but comparable when using a fine-needle biopsy needle (RR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.83–1.04). The positive diagnostic yield of MIAB was higher for lesions <20 mm (RR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.63–0.89). Six studies reported no adverse events.
Conclusions
MIAB can be considered an effective alternative to EUS-guided TA for upper GI SELs without an increased risk of adverse events. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Technical outcomes and postprocedural courses of mucosal incision‐assisted biopsy for possible gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A series of 48 cases (with video)
Eriko Koizumi, Osamu Goto, Shun Nakagome, Tsugumi Habu, Yumiko Ishikawa, Kumiko Kirita, Hiroto Noda, Kazutoshi Higuchi, Takeshi Onda, Teppei Akimoto, Jun Omori, Naohiko Akimoto, Katsuhiko Iwakiri
DEN Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Diagnostic Approach of Benign Esophageal Tumors: A Narrative Review
Alex R. Jones, Preksha Vankawala, Tarek Sawas
Current Treatment Options in Gastroenterology.2024; 22(2): 44. CrossRef - Unroofing of subepithelial lesions in the upper gastrointestinal tract using cold snare: an easy and efficient technique for diagnosis
Bernhard Morell, Frans Olivier The, Christoph Gubler, Fritz Ruprecht Murray
Clinical Endoscopy.2024; 57(2): 274. CrossRef - Diagnostic yield of endoscopic and EUS-guided biopsy techniques in subepithelial lesions of the upper GI tract: a systematic review
Cynthia A. Verloop, Jacqueline A.C. Goos, Marco J. Bruno, Rutger Quispel, Lydi M.J.W. van Driel, Lieke Hol
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2024; 99(6): 895. CrossRef - Small gastric subepithelial lesions: A sand in the eye
Tanyaporn Chantarojanasiri, Nikhil Sonthalia, Rashid N. Lui
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Approach to Small Gastric Subepithelial Lesions
Moon Won Lee, Bong Eun Lee
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2023; 23(1): 28. CrossRef - Is the canalization to obtain deep biopsy of gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors miniprobe-guidded as an alternative to conventional known techniques?
Modesto Varas Lorenzo, Ramón Abad Belando
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Advanced Gastrointestinal Endoscopy in the Comprehensive Management of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms
Harishankar Gopakumar, Vinay Jahagirdar, Jagadish Koyi, Dushyant Singh Dahiya, Hemant Goyal, Neil R. Sharma, Abhilash Perisetti
Cancers.2023; 15(16): 4175. CrossRef
- Technical outcomes and postprocedural courses of mucosal incision‐assisted biopsy for possible gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A series of 48 cases (with video)
- 2,332 View
- 132 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Endoscopic Full-Thickness Resection for Gastric Subepithelial Lesions Arising from the Muscularis Propria
- Ah Lon Jung, Sang Wook Park, Gun Young Hong, Hyeong Chul Moon, Seo Joon Eun
- Clin Endosc 2021;54(1):131-135. Published online August 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2020.070

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Most cases of gastric subepithelial lesions follow a good clinical course; however, some lesions progress to malignant tumors, and treatment of tumors with a high risk of malignancy is essential. Surgical excision has been the primary treatment for tumors originating from the propria muscle layer, but it has the disadvantages of being invasive and causing postoperative functional abnormalities. With the development of endoscopic techniques and instruments, the role of endoscopic resection, which is a less invasive method for the removal of gastric subepithelial lesions, has been attracting attention. We performed an endoscopic full-thickness resection for 8 patients with gastric subepithelial lesions originating from the muscularis propria. No fatal complications occurred. Our findings suggest the need to develop various devices for resection and closure and to accumulate further experience through additional studies to prevent complications and specimen loss.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Robotic Platforms for Therapeutic Flexible Endoscopy: A Literature Review
Naoya Tada, Kazuki Sumiyama
Diagnostics.2024; 14(6): 595. CrossRef - Advances of endoscopic and surgical management in gastrointestinal stromal tumors
Lei Yue, Yingchao Sun, Xinjie Wang, Weiling Hu
Frontiers in Surgery.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Status of Endoscopic Full-Thickness Resection for Gastric Subepithelial Tumors: A Literature Review Over Two Decades
Naoya Tada, Hideki Kobara, Noriko Nishiyama, Shintaro Fujihara, Tsutomu Masaki, Noriya Uedo
Digestion.2023; 104(6): 415. CrossRef - Endoscopic Full Thickness Resection: A Systematic Review
Partha Pal, Mohan Ramchandani, Pradev Inavolu, Duvvuru Nageshwar Reddy, Manu Tandan
Journal of Digestive Endoscopy.2022; 13(03): 152. CrossRef
- Robotic Platforms for Therapeutic Flexible Endoscopy: A Literature Review
- 4,223 View
- 119 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Reasons for Diagnostic Failure in Forty-Five Consecutive Mucosal Cutting Biopsy Examinations of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
- Yoshiko Nakano, Toshitatsu Takao, Yoshinori Morita, Shinwa Tanaka, Takashi Toyonaga, Eiji Umegaki, Yuzo Kodama
- Clin Endosc 2020;53(5):575-582. Published online February 14, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.150
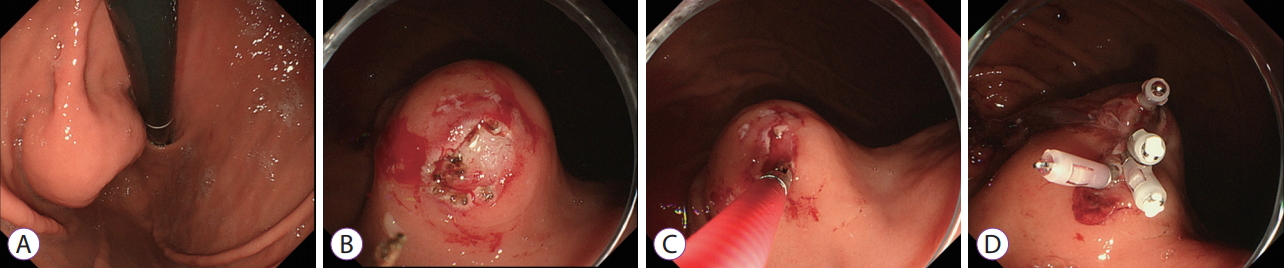
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Background
/Aims: Mucosal cutting biopsy (MCB) is useful for the histopathological diagnosis of gastric subepithelial tumors (SETs). However, there is little information on cases in which MCB did not establish a diagnosis. In the current study, we aimed to investigate the characteristics of cases in which MCB was unsuccessful.
Methods
Cases in which MCB was used to histopathologically diagnose gastric SETs at Kobe University Hospital between August 2012 and October 2018 were retrospectively reviewed.
Results
Forty-five cases in which MCB was used to diagnose 43 gastric SETs in 43 patients were analyzed. The median tumor size was 20 mm (range, 8–50 mm). Pathological examinations resulted in definitive and suspected diagnoses and no diagnosis in 29 (gastrointestinal stromal tumor: n=17, leiomyoma: n=7, aberrant pancreas: n=3, others: n=2), 6, and 10 cases, respectively. Failure to expose the tumor according to retrospective examinations of endoscopic images was significantly associated with no diagnosis. Other possible explanations included a less elevated tumor, biopsy of the surrounding field instead of the tumor due to the mobility, and poor endoscope maneuverability due to the tumor being close to the cardia.
Conclusions
Clear exposure of gastric SETs during MCB may improve the diagnostic rate of such examinations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Technical outcomes and postprocedural courses of mucosal incision‐assisted biopsy for possible gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A series of 48 cases (with video)
Eriko Koizumi, Osamu Goto, Shun Nakagome, Tsugumi Habu, Yumiko Ishikawa, Kumiko Kirita, Hiroto Noda, Kazutoshi Higuchi, Takeshi Onda, Teppei Akimoto, Jun Omori, Naohiko Akimoto, Katsuhiko Iwakiri
DEN Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Utility and advantage of the unroofing technique for gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors: A multicenter retrospective cohort study
Masashi Yamamoto, Tsutomu Nishida, Ryotaro Uema, Takashi Kanesaka, Hiroyuki Ogawa, Shinji Kitamura, Hideki Iijima, Kengo Nagai, Shusaku Tsutsui, Masato Komori, Katsumi Yamamoto, Yoshiki Tsujii, Yoshito Hayashi, Tetsuo Takehara
DEN Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic Endoscopic Approach for Diagnosing Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
Gwang Ha Kim
Gut and Liver.2022; 16(1): 19. CrossRef - The Diagnosis of Small Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Lesions by Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration and Biopsy
Masanari Sekine, Takeharu Asano, Hirosato Mashima
Diagnostics.2022; 12(4): 810. CrossRef - Advancements in the Diagnosis of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
Osamu Goto, Mitsuru Kaise, Katsuhiko Iwakiri
Gut and Liver.2022; 16(3): 321. CrossRef - Mucosal Incision-Assisted Endoscopic Biopsy as an Alternative to Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration/Biopsy for Gastric Subepithelial Tumor
Cheol Woong Choi, Joo Ha Hwang
Clinical Endoscopy.2020; 53(5): 505. CrossRef
- Technical outcomes and postprocedural courses of mucosal incision‐assisted biopsy for possible gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A series of 48 cases (with video)
- 3,548 View
- 109 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of a Colonic Calcifying Fibrous Tumor
- Jaeyoung Kim, Seongyul Ryu, Yeon-Ji Kim
- Clin Endosc 2020;53(4):487-490. Published online January 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.138

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - A 49-year-old woman was referred to our hospital for further treatment due to the suspicion of a submucosal tumor in a routine screening colonoscopy. On colonoscopy, a 1-cm sized subepithelial mass with normal overlying mucosa in the hepatic flexure was found. Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) showed a homogenous hypoechoic lesion arising from the second and third layer. We were unable to make a final diagnosis because the lesion showed a small tumor with atypical macroscopic morphology including EUS findings. Therefore, endoscopic submucosal dissection was performed for the diagnostic treatment of the tumor. Submucosal dissection was performed just above the muscle layer, and the tumor was removed completely and reliably without any acute complications such as perforation. Based on histopathological findings, we diagnosed a benign, calcifying fibrous tumor (CFT). The present case is the first report of successful endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of colonic CFT mimicking a submucosal tumor.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Feasibility of endoscopic resection and impact of endoscopic ultrasound-based surveillance on colorectal subepithelial tumors
Eun Young Park, Dong Hoon Baek, Seung Min Hong, Bong Eun Lee, Moon Won Lee, Gwang Ha Kim, Geun Am Song
Surgical Endoscopy.2023; 37(9): 6867. CrossRef - Submucosal Necrotic Nodule of the Colon: An Enigmatic Entity Potentially Related to Anisakis Infection
Raul S. Gonzalez, Laura G. Pastrián, Sergey Pyatibrat, Hernan Dario Quiceno Arias, Yolanda Rodriguez Gil, Adam L. Booth, Itziar de la Peña Navarro, Maddi Garmendia-Irizar, Jennifer R. Lapointe, Mousa Mobarki, Luiz Miguel Nova-Camacho, Gina Parini, Estefan
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2023; 147(11): 1315. CrossRef
- Feasibility of endoscopic resection and impact of endoscopic ultrasound-based surveillance on colorectal subepithelial tumors
- 4,124 View
- 95 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration and Biopsy in Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Tumors
- Gyu Young Pih, Do Hoon Kim
- Clin Endosc 2019;52(4):314-320. Published online July 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.100
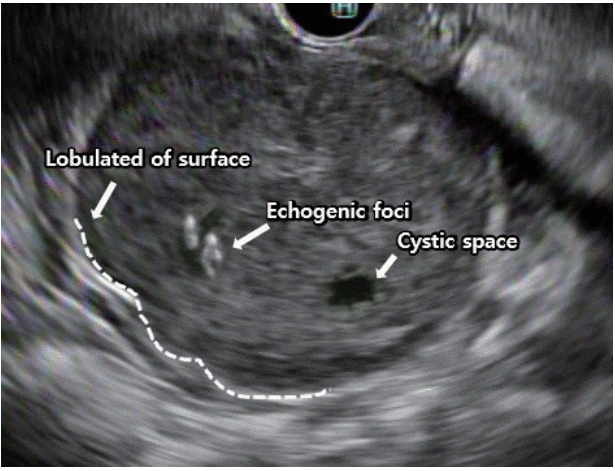
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - The incidence of asymptomatic and incidentally found upper gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors (SETs) is increasing with the implementation of national cancer screening and the development of high-resolution endoscopy in Korea. However, endoscopy alone cannot be used to determine whether SETs are benign or malignant. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is used to further characterize these lesions through the examination of their layered structure, internal echogenicity, size, and relationship to the extramural structure. These provide additional information on whether the lesion is benign or malignant. Nevertheless, the sensitivity and specificity of EUS alone in predicting malignancy is unsatisfactory. Recent guidelines have recommended deciding the timing of EUS-fine needle aspiration and biopsy (EUS-FNA/B) for SETs based on tumor size, malignant features on endoscopy, and high-risk features on EUS. The diagnostic accuracy of EUS-FNA/B is reportedly influenced by factors including needle size, number of needle passes, use of suction, use of a stylet in the needle assembly, fanning technique, availability of an on-site cytopathologist, and experience of the endosonographer. Therefore, according to the characteristics of the SETs, various subsequent methods and techniques should be appropriately employed to improve the diagnostic yield of EUS-FNA/B.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Outcomes of Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Fine Needle Biopsy Using a Novel Hydrostatic Stylet Tissue Acquisition Technique
Patrick T. Magahis, Donevan Westerveld, Malorie Simons, David L. Carr-Locke, Kartik Sampath, Reem Z. Sharaiha, SriHari Mahadev
Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.2024; 58(4): 407. CrossRef - The role of endoscopic ultrasound in assessment of physiological cardia insufficiency during diagnosis of hiatal hernia
B.F. Shevchenko, O.M. Babii, N.V. Prolom, M.V. Titova, S.O. Tarabarov, S.V. Ushchina
GASTROENTEROLOGY.2024; 58(1): 50. CrossRef - Spectrum of endoscopic gastric subepithelial lesions encountered on EUS-FNA: A single center experience
Poojan Agarwal, Pooja Bakshi, Kusum Verma, Vikas Singla, Anil Arora
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2024; 67(2): 374. CrossRef - Ultrasound-Enhanced Fine-Needle Biopsy Improves Yield in Human Epithelial and Lymphoid Tissue
Yohann Le Bourlout, Minna Rehell, Jetta Kelppe, Jaana Rautava, Emanuele Perra, Jouni Rantanen, Gösta Ehnholm, Nick Hayward, Kristofer Nyman, Kenneth P.H. Pritzker, Jussi Tarkkanen, Timo Atula, Katri Aro, Heikki J. Nieminen
Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Pancreatic Rest Presenting as a Sub-epithelial Nodule in the Gastric Antrum
Janak Bahirwani, Rodrigo Duarte-Chavez, Lisa Stoll, Ayaz Matin
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lesiones subepiteliales gástricas únicas. ¿Existen factores predictores de tumores del estroma gastrointestinal que eviten la biopsia?
José Ruiz Pardo, Elisabet Vidaña Márquez, Pedro Antonio Sánchez Fuentes, Iñigo Gorostiaga Altuna, Ricardo Belda Lozano, Ángel Reina Duarte
Gastroenterología y Hepatología.2023; 46(1): 54. CrossRef - Single gastric subepithelial lesions. Are there predictors of gastrointestinal stromal tumors that prevent biopsy?
José Ruiz Pardo, Elisabet Vidaña Márquez, Pedro Antonio Sánchez Fuentes, Iñigo Gorostiaga Altuna, Ricardo Belda Lozano, Ángel Reina Duarte
Gastroenterología y Hepatología (English Edition).2023; 46(1): 54. CrossRef - Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Subepithelial Tumor Treatment in the Upper Digestive Tract: A Western, Multicenter Study
Raffaele Manta, Francesco Paolo Zito, Francesco Pugliese, Angelo Caruso, Santi Mangiafico, Alessandra D’Alessandro, Danilo Castellani, Ugo Germani, Massimiliano Mutignani, Rita Luisa Conigliaro, Luca Reggiani Bonetti, Takahisa Matsuda, Vincenzo De Frances
GE - Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 30(2): 115. CrossRef - Endoscopic ultrasonography in diagnosis of digestive diseases. Review of clinical cases
Yu.M. Stepanov, N.V. Prolom, S.O. Tarabarov, M.V. Titova, I.M. Adamska, O.V. Zeleniuk
GASTROENTEROLOGY.2023; 57(4): 234. CrossRef - A Novel Biopsy Method Based on Bipolar Radiofrequency Biopsy Needles
Huiyang Wang, Haiwei Bao, Lan Yue, Tian’an Jiang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic ability of EUS-FNB with a novel fork-tip needle for upper gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors
Kei Ushikubo, Yuto Shimamura, Mai Fukuda, Raina Fujiyoshi, Hiroyuki Watanabe, Yuusuke Fujiyoshi, Jin Tanaka, Yohei Nishikawa, Haruo Ikeda, Manabu Onimaru, Haruhiro Inoue
Progress of Digestive Endoscopy.2022; 100(1): 67. CrossRef - Underwater endoscopic mucosal resection of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors: A case series pilot study (with video)
Su Jin Kim, Tae Un Kim, Cheol Woong Choi, Hyung Wook Kim, Su Bum Park, Dae Gon Ryu
Medicine.2022; 101(41): e31072. CrossRef - AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Subepithelial Lesions Encountered During Routine Endoscopy: Expert Review
Kaveh Sharzehi, Amrita Sethi, Thomas Savides
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 20(11): 2435. CrossRef - Comparison of diagnostic performances of slow-pull suction and standard suction in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy for gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors
Joon Seop Lee, Chang Min Cho, Yong Hwan Kwon, An Na Seo, Han Ik Bae, Man-Hoon Han
Clinical Endoscopy.2022; 55(5): 637. CrossRef - The role of endoscopic ultrasound investigation in the diagnosis of submucosal neoplasms of the stomach and duodenum (literature review and our clinical observations)
Yu.M. Stepanov, N.V. Prolom, I.S. Konenko, S.O. Tarabarov, N.P. Dementii, I.M. Adamska
GASTROENTEROLOGY.2022; 55(4): 270. CrossRef - Peroral endoscopic tumor resection (POET) with preserved mucosa technique for management of upper gastrointestinal tract subepithelial tumors
Chen-Shuan Chung, Kuo-Hsin Chen, Kuan-Chih Chen, Chiung-Yu Chen, Tzong-Hsi Lee, Cheng-Kuan Lin, Jiann-Ming Wu
Surgical Endoscopy.2021; 35(7): 3753. CrossRef - Gastric Angiolipoma Resected with Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Sang Myung Yeo, Jae Kwang Lee, Hyun Soo Kim, Chang Geun Park, Jae Kwon Jung, Dae Jin Kim, Yun Jin Chung, Han Jun Ryu
Clinical Endoscopy.2021; 54(3): 432. CrossRef - Subepithelial Tumor-like Gastric Cancer
Kyoungwon Jung, Moo In Park
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2021; 21(2): 106. CrossRef - Convolutional neural network‐based object detection model to identify gastrointestinal stromal tumors in endoscopic ultrasound images
Chang Kyo Oh, Taewan Kim, Yu Kyung Cho, Dae Young Cheung, Bo‐In Lee, Young‐Seok Cho, Jin Il Kim, Myung‐Gyu Choi, Han Hee Lee, Seungchul Lee
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 36(12): 3387. CrossRef - Fine needle aspiration cytology of primary and metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumour
Gargi Kapatia, Nalini Gupta, Uma Nahar Saikia, Parikshaa Gupta, Manish Rohilla, Ojas Gupta, Radhika Srinivasan, Arvind Rajwanshi, Pranab Dey
Cytopathology.2020; 31(2): 136. CrossRef - Thoracoscopic surgery combined with endoscopic creation of a submucosal tunnel for a large complicated esophageal leiomyoma
Koki Oyama, Kenoki Ohuchida, Koji Shindo, Taiki Moriyama, Yoshitaka Hata, Masafumi Wada, Eikichi Ihara, Shuntaro Nagai, Takao Ohtsuka, Masafumi Nakamura
Surgical Case Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Mucosal Incision-Assisted Endoscopic Biopsy as an Alternative to Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration/Biopsy for Gastric Subepithelial Tumor
Cheol Woong Choi, Joo Ha Hwang
Clinical Endoscopy.2020; 53(5): 505. CrossRef - Endoscopic diagnosis and management of gastric subepithelial lesions
Thomas R. McCarty, Marvin Ryou
Current Opinion in Gastroenterology.2020; 36(6): 530. CrossRef - Endoscopic submucosal dissection as alternative to surgery for complicated gastric heterotopic pancreas
Jin Hee Noh, Do Hoon Kim, So-Woon Kim, Young Soo Park, Hee Kyong Na, Ji Yong Ahn, Kee Wook Jung, Jeong Hoon Lee, Kee Don Choi, Ho June Song, Gin Hyug Lee, Hwoon-Yong Jung
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2020; 8(20): 4708. CrossRef
- Outcomes of Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Fine Needle Biopsy Using a Novel Hydrostatic Stylet Tissue Acquisition Technique
- 6,970 View
- 185 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref

- Contrast Enhanced Endoscopic Ultrasound Imaging for Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Tumors
- Takashi Tamura, Masayuki Kitano
- Clin Endosc 2019;52(4):306-313. Published online July 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.056
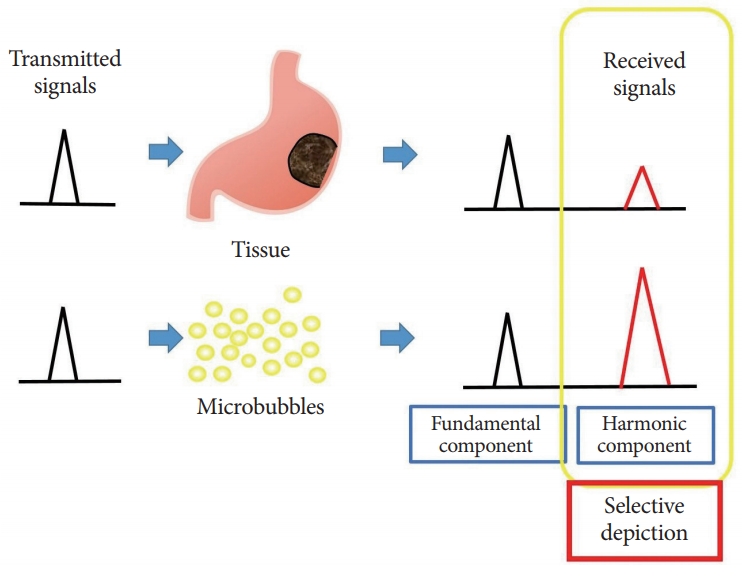
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Subepithelial tumors are divided into benign subepithelial and potentially malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors. It is difficult to distinguish between these tumor types. Contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound is reportedly useful for diagnosing subepithelial tumors, can be safely and easily performed by understanding the principle and method, and can be used to distinguish between tumor types with high sensitivity on the basis of differences in contrast effect. The generated image shows a hyperenhancement pattern in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (sensitivity, 78%–100%; specificity, 60%–100%; accuracy, 60%–100%) and hypoenhancement pattern in benign subepithelial tumors. Contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound can be used to estimate the malignancy potential of gastrointestinal stromal tumors by evaluating the uniformity of the contrast and the blood vessels inside the tumor, with abnormal intra-tumor blood vessels, heterogeneous enhancement, and non-enhancing spots suggesting malignancy. Contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound has a higher sensitivity than other imaging modalities for the detection of vascularity within gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Additionally, it has been reported that treatment effects can be estimated by evaluating the blood flow in the gastrointestinal stromal tumor before and after treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors using contrastenhanced ultrasound. However, there will be subjective-bias and the results depends on the performer’s skill.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The value of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound in differential diagnosis and evaluation of malignant risk of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (<50mm)
Jiali Wu, Mengqi Zhuang, Yubao Zhou, Xiang Zhan, Weiwei Xie
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 58(5): 542. CrossRef - Endoscopic Ultrasound Advanced Techniques for Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumours
Socrate Pallio, Stefano Francesco Crinò, Marcello Maida, Emanuele Sinagra, Vincenzo Francesco Tripodi, Antonio Facciorusso, Andrew Ofosu, Maria Cristina Conti Bellocchi, Endrit Shahini, Giuseppinella Melita
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1285. CrossRef - EUS-Guided Diagnosis of Gastric Subepithelial Lesions, What Is New?
Thomas Vasilakis, Dimitrios Ziogas, Georgios Tziatzios, Paraskevas Gkolfakis, Eleni Koukoulioti, Christina Kapizioni, Konstantinos Triantafyllou, Antonio Facciorusso, Ioannis S. Papanikolaou
Diagnostics.2023; 13(13): 2176. CrossRef - Rapidly Growing, High-Risk Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor of the Stomach: A Case Report
Sung Jin Lim, Han Mo Yoo, Seung-Woo Lee, Hae Joung Sul, Dong Soo Lee
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2023; 23(4): 306. CrossRef - The value of color Doppler ultrasonography combined with serum tumor markers in differential diagnosis of gastric stromal tumor and gastric cancer
Xinyu Cheng, Jianguo Xia, Qi Xu, Huawei Gui
Open Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultrasound imaging of subepithelial rectal tumors (review)
Y. L. Trubacheva, E. M. Bogdanova, A. E. Pershina
Koloproktologia.2022; 21(1): 107. CrossRef - The Asian Federation of Societies for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology (AFSUMB) Guidelines for Contrast-Enhanced Endoscopic Ultrasound
Masayuki Kitano, Yasunobu Yamashita, Ken Kamata, Tiing Leong Ang, Hiroo Imazu, Eizaburo Ohno, Yoshiki Hirooka, Pietro Fusaroli, Dong-Wan Seo, Bertrand Napoléon, Anthony Yuen Bun Teoh, Tae Hyeon Kim, Christoph F. Dietrich, Hsiu-Po Wang, Masatoshi Kudo
Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology.2021; 47(6): 1433. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Endoscopic Treatment for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
Cicilia Marcella, Shakeel Sarwar, Hui Ye, Rui Hua Shi
Clinical Endoscopy.2020; 53(4): 458. CrossRef - Contrast Harmonic-Enhanced Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) Is the Perfect Companion of EUS-Guided Tumor Ablation
Gianmarco Marocchi, Andrea Lisotti, Pietro Fusaroli
Gut and Liver.2020; 14(5): 669. CrossRef
- The value of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound in differential diagnosis and evaluation of malignant risk of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (<50mm)
- 7,249 View
- 184 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Comparison of the Diagnostic Ability of Endoscopic Ultrasonography and Abdominopelvic Computed Tomography in the Diagnosis of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
- Sang Yoon Kim, Ki-Nam Shim, Joo-Ho Lee, Ji Young Lim, Tae Oh Kim, A. Reum Choe, Chung Hyun Tae, Hye-Kyung Jung, Chang Mo Moon, Seong-Eun Kim, Sung-Ae Jung
- Clin Endosc 2019;52(6):565-573. Published online July 17, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.019

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Background
/Aims: Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) is the most efficient imaging modality for gastric subepithelial tumors (SETs). However, abdominopelvic computed tomography (APCT) has other advantages in evaluating the characteristics, local extension, or invasion of SETs to adjacent organs. This study aimed to compare the diagnostic ability of EUS and APCT based on surgical histopathology results.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed data from 53 patients who underwent both EUS and APCT before laparoscopic wedge resection for gastric SETs from January 2010 to December 2017 at a single institution. On the basis of histopathology results, we assessed the diagnostic ability of the 2 tests.
Results
The overall accuracy of EUS and APCT was 64.2% and 50.9%, respectively. In particular, the accuracy of EUS vs. APCT for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), leiomyomas, and ectopic pancreas was 83.9% vs. 74.2%, 37.5% vs. 0.0%, and 57.1% vs. 14.3%, respectively. Most of the incorrect diagnoses with EUS involved hypoechoic lesions originating in the fourth echolayer, with the most common misdiagnosed lesions being GISTs mistaken for leiomyomas and vice versa.
Conclusions
APCT showed a lower overall accuracy than EUS; however, APCT remains a useful modality for malignant/potentially malignant gastric SETs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Guidelines in Practice: The Diagnosis and Management of Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Lesions
Brian C. Jacobson, Vanessa M. Shami
American Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 119(3): 397. CrossRef - Advances in Endoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastric Neuroendocrine Neoplasms
Xinrui Guo, Xiaohan Zhao, Gang Huang, Yanbo Yu
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(1): 27. CrossRef - Diagnostic Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) of the Luminal Gastrointestinal Tract
Giovanna Impellizzeri, Giulio Donato, Claudio De Angelis, Nico Pagano
Diagnostics.2024; 14(10): 996. CrossRef - The value of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound in differential diagnosis and evaluation of malignant risk of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (<50mm)
Jiali Wu, Mengqi Zhuang, Yubao Zhou, Xiang Zhan, Weiwei Xie
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 58(5): 542. CrossRef - ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Lesions
Brian C. Jacobson, Amit Bhatt, Katarina B. Greer, Linda S. Lee, Walter G. Park, Bryan G. Sauer, Vanessa M. Shami
American Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 118(1): 46. CrossRef - Approach to Small Gastric Subepithelial Lesions
Moon Won Lee, Bong Eun Lee
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2023; 23(1): 28. CrossRef - Computed tomography features of gastric leiomyoma versus gastric stromal tumor: a case–control study with propensity score matching
Qi Wang, Lijia Wang, Xiaohui Qi, Xiang Liu, Qiao Xie, Yifeng Wang, Gaofeng Shi
Journal of International Medical Research.2023; 51(5): 030006052311710. CrossRef - EUS-Guided Diagnosis of Gastric Subepithelial Lesions, What Is New?
Thomas Vasilakis, Dimitrios Ziogas, Georgios Tziatzios, Paraskevas Gkolfakis, Eleni Koukoulioti, Christina Kapizioni, Konstantinos Triantafyllou, Antonio Facciorusso, Ioannis S. Papanikolaou
Diagnostics.2023; 13(13): 2176. CrossRef - The effect of endoscopic ultrasound on the precise selection of endoscopic treatment for submucosal tumors in the upper gastrointestinal tract
Jian-Hua Li, Shu-Min Qin, Tian-Wen Liu, Jun-Qian Chen, Ying-Ting Li
BMC Surgery.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic Endoscopic Approach for Diagnosing Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
Gwang Ha Kim
Gut and Liver.2022; 16(1): 19. CrossRef - Endoscopic management of subepithelial lesions including neuroendocrine neoplasms: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline
Pierre H. Deprez, Leon M.G. Moons, Dermot OʼToole, Rodica Gincul, Andrada Seicean, Pedro Pimentel-Nunes, Gloria Fernández-Esparrach, Marcin Polkowski, Michael Vieth, Ivan Borbath, Tom G. Moreels, Els Nieveen van Dijkum, Jean-Yves Blay, Jeanin E. van Hooft
Endoscopy.2022; 54(04): 412. CrossRef - Prediction of Gastric Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors before Operation: A Retrospective Analysis of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
Yu-Ning Lin, Ming-Yan Chen, Chun-Yi Tsai, Wen-Chi Chou, Jun-Te Hsu, Chun-Nan Yeh, Ta-Sen Yeh, Keng-Hao Liu
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(2): 297. CrossRef - Advancements in the Diagnosis of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
Osamu Goto, Mitsuru Kaise, Katsuhiko Iwakiri
Gut and Liver.2022; 16(3): 321. CrossRef - DIAGNOSTIC AND THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT FOR LEIOMYOMA OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT
V. O. Shaprynskyi, Yu. V. Babii
Kharkiv Surgical School.2022; (4-5): 46. CrossRef - A scoring model for radiologic diagnosis of gastric leiomyomas (GLMs) with contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CE-CT): Differential diagnosis from gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs)
Jian-Xia Xu, Qiao-Ling Ding, Yuan-Fei Lu, Shu-Feng Fan, Qin-Pan Rao, Ri-Sheng Yu
European Journal of Radiology.2021; 134: 109395. CrossRef - A Nomogram for Predicting Laparoscopic and Endoscopic Cooperative Surgery during the Endoscopic Resection of Subepithelial Tumors of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
Shun-Wen Hsiao, Mei-Wen Chen, Chia-Wei Yang, Kuo-Hua Lin, Yang-Yuan Chen, Chew-Teng Kor, Siou-Ping Huang, Hsu-Heng Yen
Diagnostics.2021; 11(11): 2160. CrossRef - Ultrasonido endoscópico, aplicaciones actuales en tumores sólidos gastrointestinales
Gabriel Alonso Mosquera-Klinger, Jhon Jaime Carvajal Gutiérrez, Alavaro Andrés Gómez Venegas, Sebastián Niño Ramírez, Raúl Cañadas Garrido
Revista Colombiana de Gastroenterología.2020; 35(4): 506. CrossRef - Diagnosis of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors Using Endoscopic Ultrasonography or Abdominopelvic Computed Tomography: Which is Better?
Eun Young Park, Gwang Ha Kim
Clinical Endoscopy.2019; 52(6): 519. CrossRef
- Guidelines in Practice: The Diagnosis and Management of Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Lesions
- 6,585 View
- 186 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- Current Status of Endoscopic Ultrasonography in Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Tumors
- Sang Gyun Kim, Ji Hyun Song, Joo Ha Hwang
- Clin Endosc 2019;52(4):301-305. Published online July 9, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.024

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors (GSTs) are usually detected incidentally on endoscopic or radiologic examinations. In conventional endoscopy, a GST usually presents as a protuberant lesion with an intact mucosal surface. As the lesion is located beneath the mucosal layer of the gastrointestinal tract, conventional biopsy typically does not reveal the pathologic diagnosis. First, a GST should be differentiated from an extrinsic compression through the positional change of the patient during conventional endoscopic examination. In cases of GSTs originating from the gastrointestinal wall, endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) can be beneficial for narrowing the differential diagnosis through delineation of echo findings and by determining the layer of origin. EUS findings can also help determine the management strategies for GSTs by making a differential diagnosis according to malignant potential.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endoscopic Resection of Upper Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Tumours: Our Clinical Experience and Results
Mehmet Zeki Buldanlı, Oktay Yener
Prague Medical Report.2022; 123(1): 20. CrossRef - Gastric subepithelial tumor: long-term natural history and risk factors for progression
Bokyung Kim, Seungkyung Kang, Eunwoo Lee, Jinju Choi, Hyunsoo Chung, Soo-Jeong Cho, Sang Gyun Kim
Surgical Endoscopy.2022; 36(7): 5232. CrossRef - Traumatic neuroma of remnant cystic duct mimicking duodenal subepithelial tumor: A case report
Dong-Hwan Kim, Ji-Ho Park, Jin-Kyu Cho, Jung-Wook Yang, Tae-Han Kim, Sang-Ho Jeong, Young-Hye Kim, Young- Joon Lee, Soon-Chan Hong, Eun-Jung Jung, Young-Tae Ju, Chi-Young Jeong, Ju-Yeon Kim
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2020; 8(17): 3821. CrossRef
- Endoscopic Resection of Upper Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Tumours: Our Clinical Experience and Results
- 5,687 View
- 228 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Primary Gastric Small Cell Carcinoma: A Case Identified as a Large Subepithelial Tumor from Invisible State in 6 Months
- Yun Im Lee, Hong Kil Jeon, Jae Wook Im, Sang Yu Oh, Kyung Bin Kim, Byunggyu Kim
- Clin Endosc 2019;52(1):76-79. Published online July 6, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2018.062

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Primary gastric small cell carcinoma (GSCC) is one of the gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. It is a rare cancer with a very aggressive behavior and a poor prognosis because of the high rate of metastases. It is usually found in far advanced stage. We experienced a case of GSCC which had developed into a large subepithelial tumor (SET) from invisible state in a short period. A 65-year-old man consulted our hospital because of early gastric cancer. He underwent endoscopic submucosal dissection for the early gastric cancer at high body posterior wall. After 6 months, the follow-up endoscopy showed a large newly developed SET-like lesion with central ulceration at the gastric cardia. Endoscopic biopsy revealed GSCC. Total gastrectomy was performed. One out of the 26 perigastric lymph nodes had a metastasis. He received 6 cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy with etoposide and cisplatin. He is still in good health 12 months after operation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lysyl oxidase and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α: biomarkers of gastric cancer
Ya-Lin Han, Li Chen, Rui Qin, Guan-Qing Wang, Xiao-Hua Lin, Guang-Hai Dai
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2019; 25(15): 1828. CrossRef
- Lysyl oxidase and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α: biomarkers of gastric cancer
- 4,924 View
- 125 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Endoscopic Treatment of Subepithelial Tumors
- Su Young Kim, Kyoung-Oh Kim
- Clin Endosc 2018;51(1):19-27. Published online January 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2018.020
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors (SETs) are generally found during endoscopy and their incidence has gradually increased. Although the indications for the endoscopic treatment of patients with SETs remain to be established, the feasibility and safety of endoscopic dissection, including the advantages of this method compared with surgical treatment, have been validated in many studies. The development of endoscopic techniques, such as endoscopic submucosal dissection, endoscopic enucleation, endoscopic excavation, endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection, submucosal tunnel endoscopic resection, and endoscopic full-thickness resection has enabled the removal of SETs while reducing the occurrence of complications. Here, we discuss the endoscopic treatment of patients with SETs, outcomes for endoscopic treatment, and procedure-related complications. We also consider the advantages and disadvantages of the various endoscopic techniques.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Present situation of minimally invasive surgical treatment for early gastric cancer
Chun-Yan Li, Yi-Feng Wang, Li-Kang Luo, Xiao-Jun Yang
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2024; 16(4): 1154. CrossRef - Cold snare endoscopic resection for subepithelial tumors of the upper third of the esophagus
Xiaosan Hu, Lifeng Zhou, Jian Chen, Yunlin Yue
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An Atypical Presentation of a Colonic Lipoma: Avoiding Surgery with a Deeper Endoscopic Look
Mafalda João, Inês Cunha, Elisa Gravito-Soares, Marta Gravito-Soares, Pedro Amaro, Pedro Figueiredo
GE - Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology.2022; 29(1): 45. CrossRef - Endoscopic Resection of Upper Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Tumours: Our Clinical Experience and Results
Mehmet Zeki Buldanlı, Oktay Yener
Prague Medical Report.2022; 123(1): 20. CrossRef - Natural History of Asymptomatic Esophageal Subepithelial Tumors of 30 mm or Less in Size
Seokin Kang, Do Hoon Kim, Yuri Kim, Dongsub Jeon, Hee Kyong Na, Jeong Hoon Lee, Ji Yong Ahn, Kee Wook Jung, Kee Don Choi, Ho June Song, Gin Hyug Lee, Hwoon-Yong Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk stratification in patients with upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors undergoing submucosal tunnel endoscopic resection
Yong Lv, Shaohua Li, Xiuhe Lv, Qing Liu, Yu Zheng, Yang Su, Changbin Yang, Yanglin Pan, Liping Yao, Huahong Xie
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Endoscopic versus surgical resection in the management of gastric schwannomas
Ya-qi Zhai, Ning-li Chai, Wen-gang Zhang, Hui-kai Li, Zhong-sheng Lu, Xiu-xue Feng, Sheng-zhen Liu, En-qiang Linghu
Surgical Endoscopy.2021; 35(11): 6132. CrossRef - Endoscopic Full-Thickness Resection for Gastric Subepithelial Lesions Arising from the Muscularis Propria
Ah Lon Jung, Sang Wook Park, Gun Young Hong, Hyeong Chul Moon, Seo Joon Eun
Clinical Endoscopy.2021; 54(1): 131. CrossRef - A Review of Endoscopic Full-thickness Resection, Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection, and Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Resection of Subepithelial Lesions
Vicky H. Bhagat, Marina Kim, Michel Kahaleh
Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.2021; 55(4): 309. CrossRef - A modified endoscopic full thickness resection for gastric subepithelial tumors from muscularis propria layer: Novel method
Jung Min Lee, In Kyung Yoo, Sung Pyo Hong, Joo Young Cho, Young Kwan Cho
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 36(9): 2558. CrossRef - Endoscopic resection of esophageal and gastric submucosal tumors from the muscularis propria layer: submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection versus endoscopic submucosal excavation: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Fernando Lopes Ponte Neto, Diogo Turiani Hourneaux de Moura, Vitor Massaro Takamatsu Sagae, Igor Braga Ribeiro, Fabio Catache Mancini, Mateus Bond Boghossian, Thomas R. McCarty, Nelson Tomio Miyajima, Edson Ide, Wanderley Marques Bernardo, Eduardo Guimarã
Surgical Endoscopy.2021; 35(12): 6413. CrossRef - The retrospective comparison between submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection and endoscopic submucosal excavation for managing esophageal submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer
Yingtong Chen, Min Wang, Lili Zhao, He Chen, Li Liu, Xiang Wang, Zhining Fan
Surgical Endoscopy.2020; 34(1): 417. CrossRef - Ligation-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection for esophageal granular cell tumors is safe and effective
Shria Kumar, Vinay Chandrasekhara, Michael L Kochman, Nuzhat Ahmad, Sara Attalla, Immanuel K Ho, David L Jaffe, Peter J Lee, Kashyap V Panganamamula, Monica Saumoy, Danielle Fortuna, Gregory G Ginsberg
Diseases of the Esophagus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Endoscopic Full Thickness Resection for Gastrointestinal Tumors - Challenges and Solutions
Hung Leng Kaan, Khek Yu Ho
Clinical Endoscopy.2020; 53(5): 541. CrossRef - Gestielter submuköser Tumor im Jejunum
Tanja Miltner
Der Gastroenterologe.2019; 14(6): 470. CrossRef - Submucosal Tunnel Endoscopic Resection for Esophageal Submucosal Tumors: A Multicenter Study
Sufang Tu, Silin Huang, Guohua Li, Xiaowei Tang, Haitao Qing, Qiaoping Gao, Jingwen Fu, Guoping Du, Wei Gong
Gastroenterology Research and Practice.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef
- Present situation of minimally invasive surgical treatment for early gastric cancer
- 7,531 View
- 272 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

- Advances in the Management of Upper Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Tumor: Pathologic Diagnosis Using Endoscopy without Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy
- Hang Lak Lee
- Clin Endosc 2016;49(3):216-219. Published online May 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.064
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Until now, biopsy methods for subepithelial tumors (SETs) have focused on endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided biopsy; however, these methods have several limitations. We devised a simple method for pathologic diagnosis of SETs. SETs are occasionally diagnosed during endoscopy, and lesions are generally small and asymptomatic. It can be challenging to decide on a management plan for large asymptomatic SETs. EUS imaging provides information regarding the size, layer, and echo pattern of the lesions. Patient management plans have traditionally been determined based on EUS images, whereby the endoscopist chooses to either monitor or remove the tumor. However, EUS alone cannot diagnose and evaluate upper gastrointestinal SETs with high accuracy. As sufficient tissue samples are required for the accurate diagnosis of SETs, EUS-guided biopsy techniques such as EUS fine-needle aspiration and trucut biopsy are currently used. However, these methods have a relatively low diagnostic accuracy and do not always provide information upon immunohistochemical staining. Endoscopists can easily detect a submucosal mass after creating an iatrogenic mucosal ulcer, after which tissue sampling is performed by using endoscopic biopsy. Furthermore, pathologic results can differentiate between benign and premalignant lesions. Here, we introduce a simple method for the pathologic diagnosis of SETs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factors for the failure of endoscopic resection of gastric submucosal tumors: a long-term retrospective case–control study
Yuzhu Yuan, Lixin Sun, Xiaoying Zhou, Han Chen, Xinmin Si, Weifeng Zhang, Yun Wang, Bixing Ye, Nana Tang, Guoxin Zhang, Xueliang Li, Hongjie Zhang, Chunhua Jiao
Gastric Cancer.2022; 25(5): 929. CrossRef - Controversies in EUS: Do we need miniprobes?
Hans Seifert, Pietro Fusaroli, PaoloGiorgio Arcidiacono, Barbara Braden, Felix Herth, Michael Hocke, Alberto Larghi, Bertrand Napoleon, Mihai Rimbas, BogdanSilvio Ungureanu, Adrian Sãftoiu, AnandV Sahai, ChristophF Dietrich
Endoscopic Ultrasound.2021; 10(4): 246. CrossRef - Overcoming the Challenge of Full-Thickness Resection of Gastric Lesions Using a Colonic Full-Thickness Resection Device
Yazan Fahmawi, Patel Krutika, Manoj Kumar, Lindsey Merritt, Meir Mizrahi
ACG Case Reports Journal.2020; 7(3): e00329. CrossRef - Digital image analysis-based scoring system for endoscopic ultrasonography is useful in predicting gastrointestinal stromal tumors
Moon Won Lee, Gwang Ha Kim, Kwang Baek Kim, Yoon Ho Kim, Do Youn Park, Chang In Choi, Dae Hwan Kim, Tae Yong Jeon
Gastric Cancer.2019; 22(5): 980. CrossRef - Endoscopic full‐thickness resection for gastrointestinal submucosal tumors
Ming‐Yan Cai, Francisco Martin Carreras‐Presas, Ping‐Hong Zhou
Digestive Endoscopy.2018; 30(S1): 17. CrossRef
- Risk factors for the failure of endoscopic resection of gastric submucosal tumors: a long-term retrospective case–control study
- 7,245 View
- 180 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Role of Endoscopic Ultrasonography in Guiding Treatment Plans for Upper Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Tumors
- Jeong Seop Moon
- Clin Endosc 2016;49(3):220-225. Published online May 20, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.047
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Gastrointestinal (GI) subepithelial tumors (SETs) are usually observed incidentally by endoscopy and have diverse prognoses, varying from benign to potentially malignant. When a GI SET is suspected, endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) is the most accurate diagnostic method to differentiate it from extraluminal compression. To determine the nature of GI SETs, EUS is also the most accurate diagnostic method, and reveals the precise sonographic nature of the lesion. There are some SETs with typical EUS findings of GI SETs, but most hypoechoic lesions are difficult to diagnose based on EUS images alone. EUS is also helpful to determine GI wall involvement in SETs and optimal treatment methods. For the diagnosis of GI SETs, obtaining a proper specimen is essential. EUS-guided cytology or biopsy methods such as fine-needle aspiration, Tru-Cut biopsy, and the newly introduced fine-needle biopsy (FNB) provide good results. To increase the diagnostic yield for GI SETs, cytology with immunocytochemical staining is used for cytological interpretation, resulting in good diagnostic yields. Recently, EUS-FNB using cheese slicer technology has been introduced, and has been reported to provide good diagnostic results for GI SETs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Orthodontic rubber band traction to facilitate endoscopic resection of gastric submucosal tumor
Linfu Zheng, Dazhou Li, Linxin Zhou, Xiaoyu Zhang, Zewen Zhang, Donggui Hong, Meiyan Liu, Jianxiao Huang, Wen Wang
Arab Journal of Gastroenterology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The value of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound in differential diagnosis and evaluation of malignant risk of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (<50mm)
Jiali Wu, Mengqi Zhuang, Yubao Zhou, Xiang Zhan, Weiwei Xie
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 58(5): 542. CrossRef - Prevalence, natural progression, and clinical practices of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions in Korea: a multicenter study
Younghee Choe, Yu Kyung Cho, Gwang Ha Kim, Jun-Ho Choi, Eun Soo Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Eun Kwang Choi, Tae Hyeon Kim, Seong-Hun Kim, Do Hoon Kim
Clinical Endoscopy.2023; 56(6): 744. CrossRef - Nomogram to predict gas-related complications during transoral endoscopic resection of upper gastrointestinal submucosal lesions
Jia Yang, Zhi-Guo Chen, Xing-Lin Yi, Jing Chen, Lei Chen
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2023; 15(11): 649. CrossRef - Clinical study of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection in the treatment of submucosal tumor originating from the muscularis propria layer of the esophagus
Yue Zhang, Jing Wen, Shuxian Zhang, Xuyang Liang, Ling Ren, Lu Wang, Yunliang Sun, Shouying Li, Kun Wang, Shengxiang Lv, Xiao Qiao
Medicine.2022; 101(51): e32380. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for gastric submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
bendaxin cao, JiaXi Lu, YuYong Tan, DeLiang Liu
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors with more than 1-year' follow-up: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Wei Peng, Shali Tan, Shu Huang, Yutang Ren, Huan Li, Yan Peng, Xiangsheng Fu, Xiaowei Tang
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2019; 54(4): 397. CrossRef - Predicting Malignancy Risk in Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Tumors with Contrast-Enhanced Harmonic Endoscopic Ultrasonography Using Perfusion Analysis Software
Hyun Seok Lee, Chang Min Cho, Yong Hwan Kwon, Su Youn Nam
Gut and Liver.2019; 13(2): 161. CrossRef - Current Status of Endoscopic Ultrasonography in Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Tumors
Sang Gyun Kim, Ji Hyun Song, Joo Ha Hwang
Clinical Endoscopy.2019; 52(4): 301. CrossRef - Comparison of the Diagnostic Ability of Endoscopic Ultrasonography and Abdominopelvic Computed Tomography in the Diagnosis of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
Sang Yoon Kim, Ki-Nam Shim, Joo-Ho Lee, Ji Young Lim, Tae Oh Kim, A. Reum Choe, Chung Hyun Tae, Hye-Kyung Jung, Chang Mo Moon, Seong-Eun Kim, Sung-Ae Jung
Clinical Endoscopy.2019; 52(6): 565. CrossRef - An Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Lymph Node Metastasis Presenting as a Small Subepithelial Tumor
Jang Won Park, Eun Jeong Gong, Myeongsook Seo, Baek Gyu Jun, Hyun Il Seo, Jong Kyu Park, Koon Hee Han, Sang Jin Lee, Young Don Kim, Woo Jin Jeong, Gab Jin Cheon
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2019; 19(4): 272. CrossRef - Diagnosis of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors Using Endoscopic Ultrasonography or Abdominopelvic Computed Tomography: Which is Better?
Eun Young Park, Gwang Ha Kim
Clinical Endoscopy.2019; 52(6): 519. CrossRef - ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND IN DIAGNOSIS OF GASTROINTESTINAL AND PANCREATICOBILIARY DISEASES
Van Huy Tran, Khanh Vinh
Journal of Medicine and Pharmacy.2019; : 87. CrossRef - Feasibility of a 20-gauge ProCore needle in EUS-guided subepithelial tumor sampling: a prospective multicenter study
Do Hoon Kim, Gwang Ha Kim, Chang Min Cho, Chang Hwan Park, Soo-Young Na, Tae Hyeon Kim, Yu Kyung Cho, Ji Hyun Kim, Dong-Wan Seo
BMC Gastroenterology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Is Endoscopic Ultrasonography Adequate for the Diagnosis of Gastric Schwannomas?
Eun Jeong Gong, Kee Don Choi
Clinical Endoscopy.2016; 49(6): 498. CrossRef
- Orthodontic rubber band traction to facilitate endoscopic resection of gastric submucosal tumor
- 7,342 View
- 174 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Long-Term Outcomes after Endoscopic Treatment of Gastric Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
- Jong-Jae Park
- Clin Endosc 2016;49(3):232-234. Published online May 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Endoscopic resection of gastric subepithelial tumors (SETs) has several advantages over biopsy techniques, such as superior diagnostic yield and definite diagnosis. Removal of gastric SETs and histopathologic confirmation should be considered whenever gastric SETs are highly suspected to have malignant potential such as gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) or neuroendocrine tumor. According to our clinical experience, we suggest that endoscopic resection of gastric SETs is feasible for GISTs less than 3.0 cm without positive endoscopic ultrasonography findings or for hypoechoic SETs less than 3.0 cm. However, serious complications such as macroperforation may occur during endoscopic resection, and this procedure is highly dependent on endoscopists’ skills. We recently reported the long-term clinical outcomes of endoscopic resection of gastric GIST, which showed a relatively low recurrence rate (2.2%) during long-term follow-up (46.0±28.5 months) despite the low R0 resection rate (25.0%). We suggest that endoscopic surveillance might be possible without additional surgical resection in completely resected GISTs without residual tumor confirmed to be lower risk, even if they show an R1 resection margin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and Safety of Endoscopic Resection for Gastric Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Originating from the Muscularis Propria
Ji Li, Dong Xu, Wei-Feng Huang, Shao-Kun Hong, Jin-Yan Zhang
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(6): 2184. CrossRef - Clinical outcomes of endoscopic resection for the treatment of intermediate- or high-risk gastric small gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a multicenter retrospective study
Enpan Xu, Qiang Shi, Zhipeng Qi, Bing Li, Huihui Sun, Zhong Ren, Shilun Cai, Dongli He, Zhengtao Lv, Zhanghan Chen, Liang Zhong, Leiming Xu, Xiaobo Li, Shuchang Xu, Pinghong Zhou, Yunshi Zhong
Surgical Endoscopy.2024; 38(6): 3353. CrossRef - Endoscopic resection of extra-luminal gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors using a snare assisted external traction technique (with video)
Jing-wen Zhang, Chang-qing Guo, Shan-shan Zhu, Nan Dai, Ping Liu, Fang-bin Zhang, Hai-ning Zhou, Jian-feng Wang, Si-su Zhou, Xin-Guang Cao
Digestive and Liver Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endoscopic resection penetrating the muscularis propria for gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors: advances and challenges
Jin Woong Cho
Clinical Endoscopy.2024; 57(3): 329. CrossRef - Gastric Inverted Hyperplastic Polyp Removed Using Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Jee Won Boo, Joon Sung Kim, Byung-Wook Kim
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2023; 23(1): 63. CrossRef - Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Endoscopic Treatment of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors in the Stomach
Moon Kyung Joo, Jong-Jae Park, Yeon Ho Lee, Beom Jae Lee, Seong Min Kim, Won Shik Kim, Ah Young Yoo, Hoon Jai Chun, Sang Woo Lee
Gut and Liver.2023; 17(2): 217. CrossRef - Predictors of the difficulty for endoscopic resection of gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor and follow‐up data
Wei Su, Min Wang, Danfeng Zhang, Yan Zhu, Minzhi Lv, Liang Zhu, Jie He, Hao Hu, Pinghong Zhou
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 37(1): 48. CrossRef - Comparison of endoscopic full-thickness resection and cap-assisted endoscopic full-thickness resection in the treatment of small (≤1.5 cm) gastric GI stromal tumors
Jinping Yang, Muhan Ni, Jingwei Jiang, Ximei Ren, Tingting Zhu, Shouli Cao, Shahzeb Hassan, Ying Lv, Xiaoqi Zhang, Yongyue Wei, Lei Wang, Guifang Xu
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2022; 95(4): 660. CrossRef - Endoscopic subserosal dissection for gastric tumors: 18 cases in a single center
Jihyun Han, Jinwoong Cho, Jaesun Song, Mina Yang, Youngjae Lee, Myoungjin Ju
Surgical Endoscopy.2022; 36(11): 8039. CrossRef - Endoscopic Management of Gastric Subepithelial Tumor
Hyunchul Lim
Journal of Digestive Cancer Research.2022; 10(1): 16. CrossRef - Predictors of difficult endoscopic resection of submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer at the esophagogastric junction
Yu-Ping Wang, Hong Xu, Jia-Xin Shen, Wen-Ming Liu, Yuan Chu, Ben-Song Duan, Jing-Jing Lian, Hai-Bin Zhang, Li Zhang, Mei-Dong Xu, Jia Cao
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2022; 14(9): 918. CrossRef - Usefulness of tumor traction with a snare and endoclips in gastric submucosal tumor resection: a propensity-score-matching analysis
Qiang Zhang, Jian-Qun Cai, Zhen Wang
Gastroenterology Report.2021; 9(2): 125. CrossRef - Endoscopic Resection of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: Is It Safe?
Moon Kyung Joo
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2021; 21(3): 180. CrossRef - Microscopic positive tumor margin does not increase the rate of recurrence in endoscopic resected gastric mesenchymal tumors compared to negative tumor margin
Yan Zhu, Mei-Dong Xu, Chen Xu, Xiao-Cen Zhang, Shi-Yao Chen, Yun-Shi Zhong, Yi-Qun Zhang, Wei-Feng Chen, Tian-Yin Chen, Jia-Xin Xu, Li-Qing Yao, Quan-Lin Li, Ping-Hong Zhou
Surgical Endoscopy.2020; 34(1): 159. CrossRef - Mucosectomy device‐assisted endoscopic resection of gastric subepithelial lesions
Lian Yong Li, Bai Wen Li, Parit Mekaroonkamol, Hui Min Chen, Shan Shan Shen, Hui Luo, Sunil Dacha, Yue Xue, Sarah Cristofaro, Steven Keilin, Field Willingham, Qiang Cai
Journal of Digestive Diseases.2020; 21(4): 215. CrossRef - Submucosal Tunnel Endoscopic Resection for Esophageal Submucosal Tumors: A Multicenter Study
Sufang Tu, Silin Huang, Guohua Li, Xiaowei Tang, Haitao Qing, Qiaoping Gao, Jingwen Fu, Guoping Du, Wei Gong
Gastroenterology Research and Practice.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Comparison between submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection and endoscopic full-thickness resection for gastric stromal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer
Yuyong Tan, Xiaoyu Tang, Ting Guo, Dongzi Peng, Yao Tang, Tianying Duan, Xuehong Wang, Liang Lv, Jirong Huo, Deliang Liu
Surgical Endoscopy.2017; 31(8): 3376. CrossRef - Subepithelial rectal gastrointestinal stromal tumor – the use of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration to establish a definitive cytological diagnosis: a case report
Vitor Ottoboni Brunaldi, Martin Coronel, Danielle Azevedo Chacon, Eduardo Turiani Hourneaux De Moura, Sérgio E. Matuguma, Eduardo Guimarães Hourneaux De Moura, Diogo Turiani Hourneaux De Moura
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
Emily Z. Keung, Chandrajit P. Raut
Surgical Clinics of North America.2017; 97(2): 437. CrossRef - Gastroduodenal Intussusception with a Gastric Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Treated by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Kenji Yamauchi, Masaya Iwamuro, Eiji Ishii, Makoto Narita, Nobuto Hirata, Hiroyuki Okada
Internal Medicine.2017; 56(12): 1515. CrossRef
- Efficacy and Safety of Endoscopic Resection for Gastric Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Originating from the Muscularis Propria
- 7,726 View
- 149 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref

- Colorectal Subepithelial Lesions
- Tae Oh Kim
- Clin Endosc 2015;48(4):302-307. Published online July 24, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.4.302
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Most of subepithelial lesion (SEL) being identified was accidentally discovered as small bulging lesion covered with normal mucosa from endoscopic screening. The type of treatment and prognosis vary depending on the type of tumor, it would be crucial to perform an accurate differential diagnosis. Since the differentiation of SEL relied on the indirect findings observed from the mucosal surface using an endoscopy only in the past, it was able to confirm the presence of lesion only but difficult to identify complex detailed nature of the lesion. However, after the endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) was introduced, it became possible to identify extrinsic compression, and size of intramural tumors, internal properties and contour so that it gets possible to have differential diagnosis of lesions and prediction on the lesion whether it is malignant or benign. In addition, the use of EUS-guided fine needle aspiration and EUS-guided core biopsy made it possible to make histological differential diagnosis. This study intended to investigate endoscopic and EUS findings, histological diagnosis, treatment regimen and impression of colorectal SELs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinicopathologic and Endosonographic Characteristics of Colon Subepithelial Tumors Discovered Incidentally
Aryoung Kim, Sung Noh Hong, Dong Kyung Chang, Young-Ho Kim, Ji Eun Kim, Eun Ran Kim
Diagnostics.2024; 14(5): 551. CrossRef - Prone Jack-Knife Transanal Minimally Invasive Surgery: A Safe and Effective Approach for Anterior Low Rectal GI Stromal Tumors
Jothinathan Muniandy, Cheng-Wei Huang, Tao-Wei Ke, William Tzu-Liang Chen
Diseases of the Colon & Rectum.2024; 67(5): e291. CrossRef - Colonoscopy-assisted laparoscopic wedge resection for a large symptomatic colonic lipoma
Julia Hanevelt, Wouter Hugo de Vos Tot Nederveen Cappel, Fiebo Johannes Cornelis ten Kate, Henderik Leendert van Westreenen
BMJ Case Reports.2024; 17(4): e258947. CrossRef - A Review of Colonoscopy in Intestinal Diseases
Seung Hong, Dong Baek
Diagnostics.2023; 13(7): 1262. CrossRef - Application of rubber band and clip traction for removal of a submucosal fecalith mimicking a submucosal tumor of the appendix under colonoscopy
Longping Chen, Linfu Zheng, Zhiping Chen, Dazhou Li, Wen Wang
Endoscopy.2023; 55(S 01): E835. CrossRef - Az alsó tápcsatornai endoszkópos ultrahangvizsgálat
Anna Fábián, Renáta Bor, Zsófia Bősze, Tibor Tóth, Péter Bacsur, Anita Bálint, Klaudia Farkas, Tamás Resál, Mariann Rutka, Tamás Molnár, Zoltán Szepes
Orvosi Hetilap.2023; 164(30): 1176. CrossRef - Spontaneous regression of a rectal tonsil presenting as a large submucosal tumor
Toru Matsui, Eri Naitoh, Kengo Furutani, Tomoji Katoh, Katsuya Kobayashi, Kenichiro Sekigawa, Hiroshi Mitsui
DEN Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Endoscopic submucosal dissection of a small rectal submucosal lesion: a rare case of rectal liposarcoma
Lucile Héroin, Pierre Lafeuille, Thomas Lambin, Pierre Mayer, Martin Bordet, Florian Rostain, Mathieu Pioche
Endoscopy.2022; 54(09): E504. CrossRef - An Atypical Presentation of a Colonic Lipoma: Avoiding Surgery with a Deeper Endoscopic Look
Mafalda João, Inês Cunha, Elisa Gravito-Soares, Marta Gravito-Soares, Pedro Amaro, Pedro Figueiredo
GE - Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology.2022; 29(1): 45. CrossRef - EUS and EUS-guided FNA/core biopsies in the evaluation of subepithelial lesions of the lower gastrointestinal tract: 10-year experience
IrinaM Cazacu, BenS Singh, AdrianaA Luzuriaga Chavez, Pramoda Koduru, Shamim Ejaz, BrianR Weston, WilliamA Ross, JeffreyH Lee, Sinchita Roy-Chowdhuri, ManoopS Bhutani
Endoscopic Ultrasound.2020; 9(5): 329. CrossRef - Cellular Angiofibroma Presenting as a Subepithelial Rectal Mass
Jennifer Bloom, Eric Jordan, Vanessa M. Baratta, Xuchen Zhang, Atin Saha, George Yavorek, Vadim Kurbatov
ACG Case Reports Journal.2020; 7(11): e00471. CrossRef - Should We Collect a Biopsy From This Submucosal Lesion in the Cecum?
Paul Vincent Co, Richard Benya, Mukund Venu
Gastroenterology.2019; 156(1): 34. CrossRef - Rectal Endoscopic Ultrasound in Clinical Practice
Stephen Hasak, Vladimir Kushnir
Current Gastroenterology Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Status of Endoscopic Ultrasonography in Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Tumors
Sang Gyun Kim, Ji Hyun Song, Joo Ha Hwang
Clinical Endoscopy.2019; 52(4): 301. CrossRef - Radial Endoscopic Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Chronic Schistosomiasis in the Colorectum
Chun-Hua Zhou, Wei-Xia Zhou, Duan-Min Hu
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2017; 15(10): e151. CrossRef - Highlights from the 52nd Seminar of the Korean Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Eun Young Kim, Il Ju Choi, Kwang An Kwon, Ji Kon Ryu, Ki Baik Hahm
Clinical Endoscopy.2015; 48(4): 269. CrossRef
- Clinicopathologic and Endosonographic Characteristics of Colon Subepithelial Tumors Discovered Incidentally
- 9,762 View
- 205 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

- Yields and Utility of Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided 19-Gauge Trucut Biopsy versus 22-Gauge Fine Needle Aspiration for Diagnosing Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
- Hee Kyong Na, Jeong Hoon Lee, Young Soo Park, Ji Yong Ahn, Kwi-Sook Choi, Do Hoon Kim, Kee Don Choi, Ho June Song, Gin Hyug Lee, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Jin-Ho Kim
- Clin Endosc 2015;48(2):152-157. Published online March 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.2.152
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Background/Aims To evaluate the yields and utility of 19-gauge (G) Trucut biopsy (TCB) versus 22 G fine needle aspiration (FNA) for diagnosing gastric subepithelial tumors (SETs).
Methods We retrieved data for 152 patients with a gastric SET larger than 2 cm who had undergone endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)-guided 19 G TCB (
n =90) or 22 G FNA (n =62). Relevant clinical, tumor-specific, and EUS procedural information was reviewed retrospectively.Results A specific diagnosis was made for 76 gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) and 51 non-GIST SETs. The diagnostic yield of TCB was greater than that of FNA (77.8% vs. 38.7%,
p <0.001). The percentage of non-diagnostic specimens (suspicious and insufficient) was significantly lower in the TCB group (6.7% and 15.5%, respectively) than in the FNA group (22.6% and 38.7%, respectively; bothp <0.001). TCB accurately diagnosed 90.9% of GISTs and 81.1% of non-GIST SETs, whereas FNA accurately diagnosed 68.8% of GISTs and 14.3% of non-GIST SETs. There were nine technical failures with TCB, and the rate of adverse events did not differ between the groups (TCB vs. FNA, 3.3% vs. 8.1%;p =0.27).Conclusions Nineteen-gauge TCB is safe and highly valuable for diagnosing gastric SETs larger than 2 cm if technical failure can be avoided.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Natural history of gastric leiomyoma
Kwangbeom Park, Ji Yong Ahn, Hee Kyong Na, Kee Wook Jung, Jeong Hoon Lee, Do Hoon Kim, Kee Don Choi, Ho June Song, Gin Hyug Lee, Hwwon-Yong Jung
Surgical Endoscopy.2024; 38(5): 2726. CrossRef - Diagnostic yield of endoscopic and EUS-guided biopsy techniques in subepithelial lesions of the upper GI tract: a systematic review
Cynthia A. Verloop, Jacqueline A.C. Goos, Marco J. Bruno, Rutger Quispel, Lydi M.J.W. van Driel, Lieke Hol
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2024; 99(6): 895. CrossRef - Comparison of endoscopic ultrasound‐guided fine needle aspiration cytology versus endoscopic biopsy for the diagnosis of subepithelial lesions of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract: A 10‐year retrospective single institution analysis
Katrina Collins, Bianca Puello Yocum, Hector Mesa, Harvey Cramer, Omer Saeed
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2023; 51(7): 434. CrossRef - Utility of endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle biopsy (EUS-FNB) for diagnosing small subepithelial lesions (< 20 mm)
Masanari Sekine, Takaya Miura, Junichi Fujiwara, Takeshi Uehara, Takeharu Asano, Satohiro Matsumoto, Hiroyuki Miyatani, Hirosato Mashima
Journal of Ultrasound.2022; 25(1): 35. CrossRef - Advancements in the Diagnosis of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
Osamu Goto, Mitsuru Kaise, Katsuhiko Iwakiri
Gut and Liver.2022; 16(3): 321. CrossRef - Necessity of Individualized Approach for Gastric Subepithelial Tumor Considering Pathologic Discrepancy and Surgical Difficulty Depending on the Gastric Location
Sung Gon Kim, Bang Wool Eom, Hongman Yoon, Myeong-Cheorl Kook, Young-Woo Kim, Keun Won Ryu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(16): 4733. CrossRef - Accuracy of visual on-site evaluation (Vose) In predicting the adequacy of Eus-guided fine needle biopsy: A single center prospective study
Serena Stigliano, Valerio Balassone, Dario Biasutto, Francesco Covotta, Marianna Signoretti, Francesco Maria Di Matteo
Pancreatology.2021; 21(1): 312. CrossRef - Utility of a 20G needle with a core trap in EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy for gastric submucosal tumors: A multicentric prospective trial
Ken Kamata, Akira Kurita, Satoru Yasukawa, Yasutaka Chiba, Hiroko Nebiki, Masanori Asada, Hiroaki Yasuda, Hideyuki Shiomi, Takeshi Ogura, Makoto Takaoka, Noriyuki Hoki, Reiko Ashida, Minoru Shigekawa, Akio Yanagisawa, Masatoshi Kudo, Masayuki Kitano
Endoscopic Ultrasound.2021; 10(2): 134. CrossRef - Endoscopic Resection of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: Is It Safe?
Moon Kyung Joo
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2021; 21(3): 180. CrossRef - Efficacy of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Biopsy in Gastric Subepithelial Tumors Located in the Cardia
Ga Hee Kim, Ji Yong Ahn, Chung Sik Gong, Mimi Kim, Hee Kyong Na, Jeong Hoon Lee, Kee Wook Jung, Do Hoon Kim, Kee Don Choi, Ho June Song, Gin Hyug Lee, Hwoon-Yong Jung
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2020; 65(2): 583. CrossRef - Comparison of the treatment outcomes of endoscopic and surgical resection of GI stromal tumors in the stomach: a propensity score–matched case-control study
Ga Hee Kim, Kee Don Choi, Chung Sik Gong, In-Seob Lee, Young Soo Park, Minkyu Han, Hee Kyong Na, Ji Yong Ahn, Jeong Hoon Lee, Kee Wook Jung, Do Hoon Kim, Ho June Song, Gin Hyug Lee, Hwoon-Yong Jung
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2020; 91(3): 527. CrossRef - EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling versus FNA in the diagnosis of subepithelial lesions: a large multicenter study
Diogo T.H. de Moura, Thomas R. McCarty, Pichamol Jirapinyo, Igor B. Ribeiro, Victor K. Flumignan, Fedaa Najdawai, Marvin Ryou, Linda S. Lee, Christopher C. Thompson
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2020; 92(1): 108. CrossRef Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors of the Small Intestine: Progress in Diagnosis and Treatment Research
Fangxing Peng, Yao Liu
Cancer Management and Research.2020; Volume 12: 3877. CrossRef- Prospective, multicenter, observational study of tissue acquisition through EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy using a 25G Franseen needle
Ryo Sugiura, Masaki Kuwatani, Kei Yane, Yoko Taya, Hideyuki Ihara, Manabu Onodera, Kazunori Eto, Itsuki Sano, Taiki Kudo, Tomoko Mitsuhashi, Akio Katanuma, Naoya Sakamoto
Endoscopic Ultrasound.2019; 8(5): 321. CrossRef - Randomized crossover trial comparing EUS‐guided fine‐needle aspiration with EUS‐guided fine‐needle biopsy for gastric subepithelial tumors
Tomohisa Iwai, Mitsuhiro Kida, Hiroshi Imaizumi, Shiro Miyazawa, Kosuke Okuwaki, Hiroshi Yamauchi, Toru Kaneko, Rikiya Hasegawa, Eiji Miyata, Wasaburo Koizumi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2018; 46(3): 228. CrossRef - Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition of subepithelial masses
Jared J. Rejeski, Girish Mishra
Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2018; 20(1): 15. CrossRef - The diagnostic and cellularity yield of reverse bevel versus fork‐tip fine needle biopsy
Mohamed M Abdelfatah, Ahmed Hamed, Nicholas J. Koutlas, F. Zahra Aly
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2018; 46(8): 649. CrossRef - Endobronchial Ultrasound-guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration With a 19-G Needle Device
Alain Tremblay, Seamus McFadden, Martina Bonifazi, Valentina Luzzi, Samuel V. Kemp, Stefano Gasparini, Alex Chee, Paul MacEachern, Elaine Dumoulin, Christopher A. Hergott, Pallav L. Shah
Journal of Bronchology & Interventional Pulmonology.2018; 25(3): 218. CrossRef - EUS-FNA WITH 19 OR 22 GAUGES NEEDLES FOR GASTRIC SUBEPITHELIAL LESIONS OF THE MUSCLE LAYER
César Vivian LOPES, Antônio Atalíbio HARTMANN, Everson Luiz de Almeida ARTIFON
ABCD. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cirurgia Digestiva (São Paulo).2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of EUS-guided fine needle aspiration in autoimmune pancreatitis: a single center prospective study
Li Cao, Yun Wang, Jinlin Wang, Qiaozhen Guo, Qian Chen, Xiaoli Wu, Shou-Jiang Tang, Bin Cheng
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2018; 53(12): 1604. CrossRef - Feasibility of a 20-gauge ProCore needle in EUS-guided subepithelial tumor sampling: a prospective multicenter study
Do Hoon Kim, Gwang Ha Kim, Chang Min Cho, Chang Hwan Park, Soo-Young Na, Tae Hyeon Kim, Yu Kyung Cho, Ji Hyun Kim, Dong-Wan Seo
BMC Gastroenterology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Subepithelial rectal gastrointestinal stromal tumor – the use of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration to establish a definitive cytological diagnosis: a case report
Vitor Ottoboni Brunaldi, Martin Coronel, Danielle Azevedo Chacon, Eduardo Turiani Hourneaux De Moura, Sérgio E. Matuguma, Eduardo Guimarães Hourneaux De Moura, Diogo Turiani Hourneaux De Moura
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - GEIS guidelines for gastrointestinal sarcomas (GIST)
Andrés Poveda, Xavier García del Muro, Jose Antonio López-Guerrero, Ricardo Cubedo, Virginia Martínez, Ignacio Romero, César Serrano, Claudia Valverde, Javier Martín-Broto
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2017; 55: 107. CrossRef - The role of endoscopy in subepithelial lesions of the GI tract
Ashley L. Faulx, Shivangi Kothari, Ruben D. Acosta, Deepak Agrawal, David H. Bruining, Vinay Chandrasekhara, Mohamad A. Eloubeidi, Robert D. Fanelli, Suryakanth R. Gurudu, Mouen A. Khashab, Jenifer R. Lightdale, V. Raman Muthusamy, Aasma Shaukat, Bashar J
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2017; 85(6): 1117. CrossRef - Contrast‐enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography for differential diagnosis of submucosal tumors of the upper gastrointestinal tract
Ken Kamata, Mamoru Takenaka, Masayuki Kitano, Shunsuke Omoto, Takeshi Miyata, Kosuke Minaga, Kentaro Yamao, Hajime Imai, Toshiharu Sakurai, Tomohiro Watanabe, Naoshi Nishida, Takaaki Chikugo, Yasutaka Chiba, Haruhiko Imamoto, Takushi Yasuda, Andrea Lisott
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2017; 32(10): 1686. CrossRef - How best to manage gastrointestinal stromal tumor
Gandhi Lanke, Jeffrey H Lee
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2017; 8(2): 135. CrossRef - EUS-guided 22-gauge fine needle biopsy for the diagnosis of gastric subepithelial tumors larger than 2 cm
Jeong Hoon Lee, Charles J. Cho, Young Soo Park, Ji Yong Ahn, Do Hoon Kim, Hee Kyong Na, Kee Don Choi, Ho June Song, Gin Hyug Lee, Hwoon-Yong Jung
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2016; 51(4): 486. CrossRef - Response:
Moon Kyung Joo, Jong-Jae Park
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2016; 83(4): 851. CrossRef - EUS-guided fine needle biopsy sampling using a novel fork-tip needle: a case-control study
Pujan Kandel, Ghassan Tranesh, Aziza Nassar, Russell Bingham, Massimo Raimondo, Timothy A. Woodward, Victoria Gomez, Michael B. Wallace
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2016; 84(6): 1034. CrossRef - Is Endoscopic Ultrasonography Adequate for the Diagnosis of Gastric Schwannomas?
Eun Jeong Gong, Kee Don Choi
Clinical Endoscopy.2016; 49(6): 498. CrossRef - A Case of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor That Underwent Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Aspiration with a 25-Gauge Biopsy Needle
Minoru Tomizawa, Fuminobu Shinozaki, Yasufumi Motoyoshi, Takao Sugiyama, Shigenori Yamamoto, Naoki Ishige
Case Reports in Gastroenterology.2016; 10(1): 173. CrossRef - Cytology of the gastrointestinal tract: opportunities to be tapped
Darshana Jhala
Diagnostic Histopathology.2015; 21(12): 462. CrossRef - Which Needle Is Better for Diagnosing Subepithelial Lesions?
Eun Young Kim
Clinical Endoscopy.2015; 48(2): 91. CrossRef
- Natural history of gastric leiomyoma
- 9,270 View
- 124 Download
- 36 Web of Science
- 33 Crossref

- An Extremely Rare Case of Gastric Subepithelial Tumor: Gastric Endometriosis
- Jong Kun Ha, Cheol Woong Choi, Hyung Wook Kim, Dae Hwan Kang, Su Bum Park, Su Jin Kim, Jeong Beom Hong
- Clin Endosc 2015;48(1):74-77. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.1.74
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Endometriosis is a disease characterized by the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity. It is common in women of childbearing age, and is most frequently located in the pelvic cavity. Approximately 10% of endometriosis cases occur outside of the pelvic cavity in locations such as the intestines, genitourinary system, kidneys, lungs, and skin. However, there have been few reports of endometriosis in the stomach. Here, we report a rare case of endometriosis that presented as a subepithelial stomach tumor.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gastric Endometriosis
Bendeguz Metz, Yael Tovia, Dimitrios R. Kalaitzopoulos, Nicolas Samartzis
Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Müllerian‐type carcinosarcoma arising in gastric endometriosis: Case report and review of the literature
Rayne Peerenboom, Sabrina Wang, Ryan Morgan, Seth Sankary, Lindsay Yassan, Katherine Kurnit, Mitchell C. Posner
Clinical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcoelomic and Lympho-Hematogenous Dissemination of Endometrioid Heterotopias – the Mechanism of Extragenital Endometriosis Formation
R. V. Ukrainets, Yu. S. Korneva
Journal of Anatomy and Histopathology.2021; 10(1): 85. CrossRef - Molecular and Cellular Changes in the Pathogenesis of Endometriosis
K. A. Toniyan, O. I. Orlov, V. V. Boyarintsev, I. V. Ogneva
Human Physiology.2021; 47(6): 690. CrossRef - Imaging of gastrointestinal endometriosis: what the radiologist should know
Adrian Jaramillo-Cardoso, Anuradha S. Shenoy-Bhangle, Wendaline M. VanBuren, Giancarlo Schiappacasse, Christine O. Menias, Koenraad J. Mortele
Abdominal Radiology.2020; 45(6): 1694. CrossRef
- Gastric Endometriosis
- 7,002 View
- 58 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Intramural Gastric Abscess Caused by a Toothpick Presenting as a Subepithelial Tumor
- Wang Guk Oh, Mun Chul Kim, Hyun Ju Yoon, Jae Woo Park, Min A Yang, Cheon Beom Lee, Ji Woong Kim, Jin Woong Cho
- Clin Endosc 2014;47(3):254-257. Published online May 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2014.47.3.254
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub In the present report, we describe an unusual case of an intramural gastric abscess caused by a foreign body, detected in the form of a subepithelial tumor. A 64-year-old woman was referred to our gastroenterology clinic for further evaluation of a gastric subepithelial tumor. The patient presented with a 1-month history of sustained dull epigastric pain. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy revealed an ill-demarcated, round, smooth, protruding lesion with a small central erosion on the great curvature of the proximal antrum. Endoscopic ultrasonography indicated the presence of an ovoid, heterogeneous, hypoechoic lesion with small echogenic foci located in the submucosa and muscularis propria layers. An abdominal computed tomography scan showed focal gastric wall thickening and regional lymph node enlargement. Endoscopic submucosal dissection was performed for definite diagnosis and management. Thus, we detected a toothpick and removed it using grasping forceps. The final diagnosis was an intramural gastric abscess caused by a toothpick.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intramural gastric abscesses in a dog
I. Otero Balda, M. Augusto, C. Lassaigne, M. P. Maurin
Journal of Small Animal Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic challenges in differentiating intramural gastric abscess from gastric cancer
Youwei Chen, Yong Han, Jing Du
Medicine.2018; 97(43): e12756. CrossRef - Forgotten Swallowed Wooden Toothpick Detected on Ultrasound
Gauri R. Khorjekar, Michael C. Hill, Olena Hartwell, Nadia J. Khati
Ultrasound Quarterly.2015; 31(3): 227. CrossRef - Highlights from the 50th Seminar of the Korean Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Eun Young Kim, Il Ju Choi, Kwang An Kwon, Ji Kon Ryu, Seok Ho Dong, Ki Baik Hahm
Clinical Endoscopy.2014; 47(4): 285. CrossRef
- Intramural gastric abscesses in a dog
- 6,657 View
- 60 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Addition of Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration and On-Site Cytology to EUS-Guided Fine Needle Biopsy Increases Procedure Time but Not Diagnostic Accuracy
- Rajesh N. Keswani, Kumar Krishnan, Sachin Wani, Laurie Keefer, Srinadh Komanduri
- Clin Endosc 2014;47(3):242-247. Published online May 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2014.47.3.242
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Background/Aims Although the diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound with fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) in pancreas adenocarcinoma is high, endoscopic ultrasound with fine needle biopsy (EUS-FNB) is often required in other lesions; in these cases, it may be possible to forgo initial EUS-FNA and rapid on-site cytology evaluation (ROSE). The aim of this study was to compare the diagnostic accuracy of EUS-FNB alone (EUS-FNB group) with a conventional sampling algorithm of EUS-FNA with ROSE followed by EUS-FNB (EUS-FNA/B group) in nonpancreas adenocarcinoma lesions.
Methods Retrospective cohort study of subjects who underwent EUS sampling of nonpancreatic adenocarcinoma lesions between February 2011 and May 2013.
Results Over the study period, there were 43 lesions biopsied in 41 unique patients in the EUS-FNB group and 53 patients in the EUS-FNA/B group. Overall diagnostic accuracy was similar between the EUS-FNB and EUS-FNA/B groups (83.7% vs. 84.9%;
p =1.0). In the subgroup of subepithelial mass lesions, diagnostic accuracy remained similar in the EUS-FNB and EUS-FNA/B groups (81.0% and 70.6%;p =0.7). EUS-FNB procedures were significantly shorter than those in the EUS-FNA/B group (58.4 minutes vs. 73.5 minutes;p <0.0001).Conclusions EUS-FNB without on-site cytology provides a high diagnostic accuracy in nonpancreas adenocarcinoma lesions. There appears to be no additive benefit with initial EUS-FNA but this requires further study in a prospective study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic yield of endoscopic and EUS-guided biopsy techniques in subepithelial lesions of the upper GI tract: a systematic review
Cynthia A. Verloop, Jacqueline A.C. Goos, Marco J. Bruno, Rutger Quispel, Lydi M.J.W. van Driel, Lieke Hol
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2024; 99(6): 895. CrossRef - Methods of tissue preparation after EUS‐guided tissue acquisition without rapid on‐site assessment: Results of a randomized study
Vinh‐An Phan, Andrew Ruszkiewicz, Romina Safaeian, Joshua Zobel, Nam Q. Nguyen
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2023; 38(5): 733. CrossRef - High Diagnostic Accuracy and Safety of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration in Malignant Lymph Nodes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Linbin Chen, Yin Li, Xiaoyan Gao, Shiyong Lin, Longjun He, Guangyu Luo, Jianjun Li, Chunyu Huang, Guobao Wang, Qing Yang, Hongbo Shan
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2021; 66(8): 2763. CrossRef - Endoscopic ultrasound fine needle aspiration vs fine needle biopsy for pancreatic masses, subepithelial lesions, and lymph nodes
Irving Levine, Arvind J Trindade
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(26): 4194. CrossRef - Factors associated with diagnostic accuracy, technical success and adverse events of endoscopic ultrasound‐guided fine‐needle biopsy: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
De‐Feng Li, Jian‐yao Wang, Mei‐feng Yang, Feng Xiong, Ding‐guo Zhang, Zheng‐lei Xu, Min‐Han Luo, Zhen‐dong Jing, Kai‐Xuan Wang, Li‐sheng Wang, Jun Yao
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2020; 35(8): 1264. CrossRef - Factors affecting the accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound‐guided fine needle aspiration for the diagnosis of small (≤20 mm) pancreatic lesions
Hong Zhen Li, Chun Yan Peng, Shan Shan Shen, Lei Wang, Song Zhang, Gui Fang Xu, Bo Kong, Helmut Friess, Xiao Ping Zou, Ying Lv
Journal of Digestive Diseases.2020; 21(7): 416. CrossRef - Endoscopic Ultrasound Fine-Needle Aspiration versus Fine-Needle Biopsy for Lymph Node Diagnosis: A Large Multicenter Comparative Analysis
Diogo Turiani Hourneaux de Moura, Thomas R. McCarty, Pichamol Jirapinyo, Igor Braga Ribeiro, Galileu Ferreira Ayala Farias, Marvin Ryou, Linda S. Lee, Christopher C. Thompson
Clinical Endoscopy.2020; 53(5): 600. CrossRef - Recent advancement in EUS-guided fine needle sampling
Pujan Kandel, Michael B. Wallace
Journal of Gastroenterology.2019; 54(5): 377. CrossRef - A “Back Light System” for Identification of Sites for Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration in Solid Pancreatic Masses: A Prospective, Randomized Study with a Crossover Design
Ryo Harada, Hironari Kato, Soichiro Fushimi, Hirofumi Inoue, Daisuke Uchida, Yutaka Akimoto, Takeshi Tomoda, Kazuyuki Matsumoto, Yasuhiro Noma, Naoki Yamamoto, Shigeru Horiguchi, Koichiro Tsutsumi, Hiroyuki Okada
Clinical Endoscopy.2019; 52(4): 334. CrossRef - Present and Future of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition in Solid Pancreatic Tumors
Jae Keun Park, Kwang Hyuck Lee
Clinical Endoscopy.2019; 52(6): 541. CrossRef - Cytology and histology: Complementary diagnostic modalities during endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition
Norge Vergara, Roseann I. Wu, Stuti Shroff, Cindy M. McGrath
Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2018; 20(1): 10. CrossRef - AGA White Paper: Optimizing Endoscopic Ultrasound–Guided Tissue Acquisition and Future Directions
Sachin Wani, V. Raman Muthusamy, Cindy M. McGrath, Antonia R. Sepulveda, Ananya Das, Wells Messersmith, Michael L. Kochman, Janak Shah
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2018; 16(3): 318. CrossRef - Advanced EUS Guided Tissue Acquisition Methods for Pancreatic Cancer
Pujan Kandel, Michael B. Wallace
Cancers.2018; 10(2): 54. CrossRef - Devices for endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition
Thiruvengadam Muniraj, Harry R. Aslanian
Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2018; 20(1): 2. CrossRef - New Developments in Endoscopic Ultrasound Tissue Acquisition
Thiruvengadam Muniraj, Harry R. Aslanian
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Clinics of North America.2017; 27(4): 585. CrossRef - Imaging modalities for characterising focal pancreatic lesions
Lawrence MJ Best, Vishal Rawji, Stephen P Pereira, Brian R Davidson, Kurinchi Selvan Gurusamy
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling with a new core needle on the need for onsite cytopathologic assessment: a preliminary study
Eduardo Rodrigues-Pinto, Sujai Jalaj, Ian S. Grimm, Todd H. Baron
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2016; 84(6): 1040. CrossRef - Rapid On-Site Evaluation for Endoscopic Ultrasound–Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration Diagnosis of Pancreatic Lesions
Guoping Cai, Xiu Sun, Harry R. Aslanian, David Chhieng
Pathology Case Reviews.2015; 20(4): 164. CrossRef - Endoscopic Ultrasound–Guided Pancreatic Core Biopsy
James J. Farrell
Pathology Case Reviews.2015; 20(4): 156. CrossRef - Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Biopsy without Rapid On-Site Cytologic Examination: A Time to Change the Paradigm?
Yeon Suk Kim
Clinical Endoscopy.2014; 47(3): 207. CrossRef - EUS-guided tissue acquisition: an evidence-based approach (with videos)
Sachin Wani, V. Raman Muthusamy, Srinadh Komanduri
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2014; 80(6): 939. CrossRef
- Diagnostic yield of endoscopic and EUS-guided biopsy techniques in subepithelial lesions of the upper GI tract: a systematic review
- 5,690 View
- 87 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref

- Endoscopic Treatment of Various Gastrointestinal Tract Defects with an Over-the-Scope Clip: Case Series from a Tertiary Referral Hospital
- Woong Cheul Lee, Weon Jin Ko, Jun-Hyung Cho, Tae Hee Lee, Seong Ran Jeon, Hyun Gun Kim, Joo Young Cho
- Clin Endosc 2014;47(2):178-182. Published online March 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2014.47.2.178
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Recently, increasingly invasive therapeutic endoscopic procedures and more complex gastrointestinal surgeries such as endoscopic mucosal resection, endoscopic submucosal dissection, and novel laparoscopic approaches have resulted in endoscopists being confronted more frequently with perforations, fistulas, and anastomotic leakages, for which nonsurgical closure is desired. In this article, we present our experiences with the use of over-the-scope clip (OTSC) for natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) closure, prevention of perforation, anastomotic leakages, and fistula closures. The OTSC is a valuable device for closing intestinal perforations and fistulas, for NOTES closure, and for the prevention of perforation after the excision of a tumor from the proper muscle layer. Furthermore, it seems to be quite safe to perform, even by endoscopists with little experience of the technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experimental Evaluation of the Optimal Suture Pattern With a Flexible Endoscopic Suturing System
Peter Halvax, Michele Diana, Yoshihiro Nagao, Jacques Marescaux, Lee Swanström
Surgical Innovation.2017; 24(3): 201. CrossRef - Management of non-acute gastrointestinal defects using the over-the-scope clips (OTSCs): a retrospective single-institution experience
Joshua S. Winder, Afif N. Kulaylat, Jane R. Schubart, Hassan M. Hal, Eric M. Pauli
Surgical Endoscopy.2016; 30(6): 2251. CrossRef - Early endoscopic closure of colocutaneous fistula adjacent to unmatured low colorectal anastomosis with the Over-The-Scope Clip (OTSC)
Constantinos Avgoustou, K. Paraskeva
Hellenic Journal of Surgery.2016; 88(3): 193. CrossRef - Endoscopic Closure for Full-Thickness Gastrointestinal Defects: Available Applications and Emerging Innovations
Nobuyoshi Takeshita, Khek Yu Ho
Clinical Endoscopy.2016; 49(5): 438. CrossRef
- Experimental Evaluation of the Optimal Suture Pattern With a Flexible Endoscopic Suturing System
- 6,115 View
- 58 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Fine Needle Aspiration versus Core Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Subepithelial Tumors
- Kevin Webb, Joo Ha Hwang
- Clin Endosc 2013;46(5):441-444. Published online September 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2013.46.5.441
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Subepithelial lesions are frequently encountered and remain a diagnostic challenge. Imaging of subepithelial lesions using endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) can be helpful in narrowing the differential diagnosis of the lesion; however, definitive diagnosis typically requires tissue. Many methods for acquiring tissue exist including EUS-guided fine needle aspiration, Trucut biopsy, and fine needle biopsy. Obtaining adequate tissue is important for cytologic and histologic exams including immunohistochemical stains, thus a great deal of effort has been made to increase tissue acquisition in order to improve diagnostic yield in subepithelial lesions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endoscopic Management of Gastric Subepithelial Tumor
Hyunchul Lim
Journal of Digestive Cancer Research.2022; 10(1): 16. CrossRef - Magnetically Actuated Soft Capsule Endoscope for Fine-Needle Biopsy
Donghoon Son, Hunter Gilbert, Metin Sitti
Soft Robotics.2020; 7(1): 10. CrossRef - Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine‐needle aspiration vs core needle biopsy for solid pancreatic lesions: Comparison of diagnostic accuracy and procedural efficiency
Aslam Syed, Olivia Babich, Bharat Rao, Shailendra Singh, Neil Carleton, Abhishek Gulati, Archana Kulkarni, Mrinal Garg, Katie Farah, Gursimran Kochhar, Suzanne Morrissey, Marcia Mitre, Abhijit Kulkarni, Manish Dhawan, Jan F. Silverman, Majed Pharaon, Shya
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2019; 47(11): 1138. CrossRef - Cytology and histology: Complementary diagnostic modalities during endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition
Norge Vergara, Roseann I. Wu, Stuti Shroff, Cindy M. McGrath
Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2018; 20(1): 10. CrossRef - Echoendoscopic ablative therapy for solid pancreatic tumors
Woo Hyun Paik, Dong Wan Seo
Journal of Digestive Diseases.2017; 18(3): 135. CrossRef - Via mucosa incision EUS-guided sampling for the diagnosis of conventional endoscopic biopsy-negative gastric wall thickening
Hongbo Shan, Xiaoyan Gao, Guangyu Luo, Jieqing Xiang, Bilv Zhong, Xiaofang Qiu, Shiyong Lin, Shuhong Li, Yin Li, Guoliang Xu, Rong Zhang
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnosis of Gastric Subepithelial Tumor: Focusing on Endoscopic Ultrasonography
Eun Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2015; 15(1): 9. CrossRef - Which Needle Is Better for Diagnosing Subepithelial Lesions?
Eun Young Kim
Clinical Endoscopy.2015; 48(2): 91. CrossRef
- Endoscopic Management of Gastric Subepithelial Tumor
- 6,172 View
- 53 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Concordance of Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Diagnosis with the Final Diagnosis in Subepithelial Lesions
- Erkan Çağlar, İbrahim Hatemi, Deniz Atasoy, Gürhan Şişman, Hakan Şentürk
- Clin Endosc 2013;46(4):379-383. Published online July 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2013.46.4.379
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Background/Aims In this study we aimed to determine the rate of concordance of endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)-guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) diagnosis with the final diagnosis obtained by surgery or endoscopic resection and follow-up in upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions.
Methods We retrospectively studied patients with subepithelial lesions who underwent EUS at our center from 2007 to 2011.
Results We had a final diagnosis in 67 patients (mean age±SD, 51.23±12.48 years; 23 [34.3%] female, 44 [65.6%] male). EUS-FNA was performed in all of the patients. On-site pathology was not performed. In nine of the patients, the obtained material which was obtained was insufficient. The cytologic examination was benign in 31 and malignant in 27 of the patients. Based on the final diagnosis, the EUS-FNA had a sensitivity of 96%, a specificity of 100%, and a diagnostic yield of 85%.
Conclusions The diagnostic yield of EUS-FNA, in the absence of the on-site cytopathologist, is feasible for the diagnosis of subepithelial lesions of the upper gastrointestinal system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic yield of endoscopic and EUS-guided biopsy techniques in subepithelial lesions of the upper GI tract: a systematic review
Cynthia A. Verloop, Jacqueline A.C. Goos, Marco J. Bruno, Rutger Quispel, Lydi M.J.W. van Driel, Lieke Hol
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2024; 99(6): 895. CrossRef - Use of Artificial Intelligence in the Prediction of Malignant Potential of Gastric Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
Gulseren Seven, Gokhan Silahtaroglu, Koray Kochan, Ali Tuzun Ince, Dilek Sema Arici, Hakan Senturk
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2022; 67(1): 273. CrossRef - Natural History of Asymptomatic Esophageal Subepithelial Tumors of 30 mm or Less in Size
Seokin Kang, Do Hoon Kim, Yuri Kim, Dongsub Jeon, Hee Kyong Na, Jeong Hoon Lee, Ji Yong Ahn, Kee Wook Jung, Kee Don Choi, Ho June Song, Gin Hyug Lee, Hwoon-Yong Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Differentiating Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors from Leiomyomas Using a Neural Network Trained on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Images
Gulseren Seven, Gokhan Silahtaroglu, Ozden Ozluk Seven, Hakan Senturk
Digestive Diseases.2022; 40(4): 427. CrossRef - Subepithelial esophageal tumors: a single-center review of resected and surveilled lesions
Don C. Codipilly, Hongfei Fang, Jeffrey A. Alexander, David A. Katzka, Karthik Ravi
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2018; 87(2): 370. CrossRef - Extra-mucosal enucleation is still a safe and feasible treatment option of giant esophageal leiomyomas
Azhar Perwaiz, Vinay Kumar Shaw, Amanjeet Singh, Adarsh Chaudhary
Indian Journal of Gastroenterology.2018; 37(1): 63. CrossRef - The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnostic Assessment of Subepithelial Lesions of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
Francisca Dias de Castro, Joana Magalhães, Sara Monteiro, Sílvia Leite, José Cotter
GE Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology.2016; 23(6): 287. CrossRef - Which Needle Is Better for Diagnosing Subepithelial Lesions?
Eun Young Kim
Clinical Endoscopy.2015; 48(2): 91. CrossRef - EUS-guided tissue acquisition: an evidence-based approach (with videos)
Sachin Wani, V. Raman Muthusamy, Srinadh Komanduri
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2014; 80(6): 939. CrossRef - Diagnosis of Subepithelial Lesion: Still "Tissue Is the Issue"
Eun Young Kim
Clinical Endoscopy.2013; 46(4): 313. CrossRef
- Diagnostic yield of endoscopic and EUS-guided biopsy techniques in subepithelial lesions of the upper GI tract: a systematic review
- 6,349 View
- 47 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Endoscopic Ultrasound, Where Are We Now in 2012?
- Eun Young Kim
- Clin Endosc 2012;45(3):321-323. Published online August 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2012.45.3.321
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Topics related with endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) made up considerable portion among many invited lectures presented in International Digestive Endoscopy Network 2012 meeting. While the scientific programs were divided into the fields of upper gastrointestinal (UGI), lower gastrointestinal, and pancreato-biliary (PB) categories, UGI and PB parts mainly dealt with EUS related issues. EUS diagnosis in subepithelial lesions, estimation of the invasion depth of early gastrointestinal cancers with EUS, and usefulness of EUS in esophageal varices were discussed in UGI sessions. In the PB part, pancreatic cystic lesions, EUS-guided biliopancreatic drainage, EUS-guided tissue acquisition, and improvement of diagnostic yield in indeterminate biliary lesions by using intraductal ultrasound were discussed. Advanced techniques such as contrast-enhanced EUS, EUS elastography and forward-viewing echoendoscopy were also discussed. In this paper, I focused mainly on topics of UGI and briefly mentioned about advanced EUS techniques since more EUS related papers by other invited speakers were presented afterwards.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Indications for Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) in Patients with Pancreatic and Biliary Disease—Novel Interventional Procedures
Manfred Prager, Elfi Prager, Christian Sebesta, Christian Sebesta
Current Oncology.2022; 29(9): 6211. CrossRef - Systematic review of endoscopy ultrasound-guided thermal ablation treatment for pancreatic cancer
SabrinaGloria Giulia Testoni, AndrewJames Healey, ChristophF Dietrich, PaoloGiorgio Arcidiacono
Endoscopic Ultrasound.2020; 9(2): 83. CrossRef - The surgical management of locally advanced well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma: changes over the years according to the AJCC 8th edition Cancer Staging Manual
Alessio Metere, Valerio Aceti, Laura Giacomelli
Thyroid Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Echoendoscopic ablative therapy for solid pancreatic tumors
Woo Hyun Paik, Dong Wan Seo
Journal of Digestive Diseases.2017; 18(3): 135. CrossRef - The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnostic Assessment of Subepithelial Lesions of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
Francisca Dias de Castro, Joana Magalhães, Sara Monteiro, Sílvia Leite, José Cotter
GE Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology.2016; 23(6): 287. CrossRef - Colorectal Subepithelial Lesions
Tae Oh Kim
Clinical Endoscopy.2015; 48(4): 302. CrossRef
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Indications for Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) in Patients with Pancreatic and Biliary Disease—Novel Interventional Procedures
- 4,353 View
- 39 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Endoscopic Resection of Subepithelial Tumors
- Gwang Ha Kim
- Clin Endosc 2012;45(3):240-244. Published online August 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2012.45.3.240
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Subepithelial tumors (SETs) are often incidentally found during endoscopic examinations. Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) is a good method for differential diagnosis of SETs, but a definite diagnosis cannot be made based on EUS features alone in some cases. Periodic follow-up examinations by endoscopy and EUS remains the recommended management strategy, which involves issues related to patient compliance, cost-effectiveness, and the risk associated with repeated endoscopic procedures and delayed diagnosis of malignancy. Endoscopic resection of the SETs is another technique to treat them as well as to obtain tissue specimens for accurate histologic diagnosis. Herein, a various endoscopic techniques ranging from simple snare resection to endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for the management of SETs will be reviewed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of endoscopic full-thickness resection and ligation-assisted endoscopic full-thickness resection for small (≤ 1.5 cm) gastric subepithelial tumors originating from muscularis propria
Lei Gu, Yu Wu, Jun Yi, Miao Ouyang, Xiaowei Liu
Surgical Endoscopy.2023; 37(5): 3796. CrossRef - Subepitheliale Tumoren im oberen Gastrointestinaltrakt
Benjamin Meier, Karel Caca
Der Gastroenterologe.2022; 17(2): 103. CrossRef - Endoskopische Diagnostik, Therapie und Nachsorge von Polypen des oberen Gastrointestinaltrakts
B. Meier, K. Caca
Der Internist.2021; 62(2): 145. CrossRef - Endoscopic resection of esophageal and gastric submucosal tumors from the muscularis propria layer: submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection versus endoscopic submucosal excavation: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Fernando Lopes Ponte Neto, Diogo Turiani Hourneaux de Moura, Vitor Massaro Takamatsu Sagae, Igor Braga Ribeiro, Fabio Catache Mancini, Mateus Bond Boghossian, Thomas R. McCarty, Nelson Tomio Miyajima, Edson Ide, Wanderley Marques Bernardo, Eduardo Guimarã
Surgical Endoscopy.2021; 35(12): 6413. CrossRef - Endoscopic full-thickness resection of gastric subepithelial tumors with the gFTRD-system: a prospective pilot study (RESET trial)
Benjamin Meier, Arthur Schmidt, Nicolas Glaser, Alexander Meining, Benjamin Walter, Andreas Wannhoff, Bettina Riecken, Karel Caca
Surgical Endoscopy.2020; 34(2): 853. CrossRef - Third Space Endoscopy
Amol Bapaye, Sravan K. Korrapati, Siddharth Dharamsi, Nachiket Dubale
Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology.2020; 54(2): 114. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for gastric submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
bendaxin cao, JiaXi Lu, YuYong Tan, DeLiang Liu
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection: An effective and safe therapy for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer
Chen Du, Ning-Li Chai, En-Qiang Ling-Hu, Zhen-Juan Li, Long-Song Li, Jia-Le Zou, Lei Jiang, Zhong-Sheng Lu, Jiang-Yun Meng, Ping Tang
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2019; 25(2): 245. CrossRef - Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection for Gastric Submucosal Tumors: a Comparison Between Cardia and Non-cardia Location
Yuyong Tan, Bingyi Zhou, Shilan Zhang, Feihong Deng, Rong Li, Shan Gao, Jirong Huo, Deliang Liu
Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2019; 23(11): 2129. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors with more than 1-year' follow-up: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Wei Peng, Shali Tan, Shu Huang, Yutang Ren, Huan Li, Yan Peng, Xiangsheng Fu, Xiaowei Tang
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2019; 54(4): 397. CrossRef - Current Status of Endoscopic Resection of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
Huimin Chen, Baiwen Li, Lianyong Li, Cicily T. Vachaparambil, Vladimir Lamm, Yuan Chu, Meidong Xu, Qiang Cai
American Journal of Gastroenterology.2019; 114(5): 718. CrossRef - Factors affecting the effectiveness and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for esophageal submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer
Chen Du, Lianjun Ma, Ningli Chai, Ying Gao, Xiaotong Niu, Yaqi Zhai, Zhenjuan Li, Jiangyun Meng, Ping Tang, Enqiang Linghu
Surgical Endoscopy.2018; 32(3): 1255. CrossRef - Endoscopic Treatment of Subepithelial Tumors
Su Young Kim, Kyoung-Oh Kim
Clinical Endoscopy.2018; 51(1): 19. CrossRef - Comparison between submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection and video-assisted thoracoscopic enucleation for esophageal submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer: a randomized controlled trial
Ningli Chai, Chen Du, Ying Gao, Xiaotong Niu, Yaqi Zhai, Enqiang Linghu, Yang Liu, Bo Yang, Zhongsheng Lu, Zhenjuan Li, Xiangdong Wang, Ping Tang
Surgical Endoscopy.2018; 32(7): 3364. CrossRef - Subepitheliale Raumforderungen
N. Glaser, R. Thimme, A. Schmidt
Der Gastroenterologe.2018; 13(2): 113. CrossRef - Treatment of cardial submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer: submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection versus endoscopic submucosal excavation
Chen Du, Ningli Chai, Enqiang Linghu, Ying Gao, Zhenjuan Li, Longsong Li, Yaqi Zhai, Zhongsheng Lu, Jiangyun Meng, Ping Tang
Surgical Endoscopy.2018; 32(11): 4543. CrossRef - Endoskopische Therapie subepithelialer Tumoren
M. Röhling, O. Pech
Der Gastroenterologe.2017; 12(3): 214. CrossRef - Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection for the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Submucosal Tumors Originating from the Muscularis Propria Layer
Chen Du, Enqiang Linghu
Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2017; 21(12): 2100. CrossRef - Comparison between submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for large esophageal leiomyoma originating from the muscularis propria layer
Yuyong Tan, Liang Lv, Tianying Duan, Junfeng Zhou, Dongzi Peng, Yao Tang, Deliang Liu
Surgical Endoscopy.2016; 30(7): 3121. CrossRef - Response:
Moon Kyung Joo, Jong-Jae Park
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2016; 83(4): 851. CrossRef - Endoscopic full-thickness resection of upper gastrointestinal lesions
Ivan Jovanovic, Paul Thomas Kröner, Klaus Mönkemüller
Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2015; 17(3): 115. CrossRef - Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer
Haiqin Wang, Yuyong Tan, Yuqian Zhou, Yongjun Wang, Chenji Li, Junfeng Zhou, Tianying Duan, Jie Zhang, Deliang Liu
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2015; 27(7): 776. CrossRef - Endoskopische Resektion submukosaler Tumoren
A. Schmidt, M. Bauder, K. Caca
Der Gastroenterologe.2014; 9(3): 270. CrossRef - Endoscopic resection of subepithelial tumors
Arthur Schmidt
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2014; 6(12): 592. CrossRef - Upper Endoscopy in International Digestive Endoscopy Network 2012: Towards Upper End of Quality
Il Ju Choi
Clinical Endoscopy.2012; 45(3): 217. CrossRef
- Comparison of endoscopic full-thickness resection and ligation-assisted endoscopic full-thickness resection for small (≤ 1.5 cm) gastric subepithelial tumors originating from muscularis propria
- 7,321 View
- 70 Download
- 25 Crossref

- A Case of Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Presenting as a Subepithelial Tumor Diagnosed by ESD
- Dae Hyun Baek, M.D., Seong Hwan Kim, M.D., Jun Young Jung, M.D., Byoung Kwan Son, M.D., Yunju Jo, M.D., Young Sook Park, M.D. and Won Mi Lee, M.D.*
- Korean J Gastrointest Endosc 2011;42(4):236-240. Published online April 28, 2011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A gastric neuroendocrine carcinoma is very rare, and the histological diagnosis is very difficult. These carcinomas result in a poor prognosis because they are preceded by severe lymphovascular invasion and early metastasis. In particular, it is difficult to distinguish between adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine carcinoma by endoscopy when no specific symptoms are present (e.g., dyspepsia, nausea). According to published articles in Korea, most cases were diagnosed as adenocarcinoma initially; however, they were confirmed postoperatively as neuroendocrine carcinoma based on a histological examination using immunohistochemical staining. A case of a 55-year-old man, who had an incidental finding of a subepithelial tumor during his health check-up, was recommended for an endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). But the patient was lost to follow-up for 4 years. When he was examined again, the size of the tumor had increased from the previous exam. He underwent ESD and was diagnosed with a well-differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma. (Korean J Gastrointest Endosc 2011;42:236-240)
- 2,498 View
- 12 Download

- Diagnostic Use of Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Trucut Biopsy in Various Diseases
- Jin Ho Lee, M.D., Jung Hwan Lee, M.D., Jung Hoon Song, M.D., Kyung Sun Ok, M.D., Won Cheol Jang, M.D., Soo Hyung Ryu, M.D., You Sun Kim, M.D. and Jeong Seop Moon, M.D.
- Korean J Gastrointest Endosc 2010;40(1):9-15. Published online January 30, 2010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
/Aims: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided trucut biopsy (EUS-TCB) is a relatively new method, which facilitates obtaining a core biopsy through the gut wall. We evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of EUS-TCB based on the types of lesions.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the database of 37 cases in 35 patients (mean age, 57.2±2.3 years; 23 men) with thoracic and abdominal masses who got EUS-TCB between January 2007 and June 2008. Final diagnoses were determined by malignant positive EUS specimens, surgical pathology, or the clinical course.
Results
Adequate samples were obtained by EUS-TCB in 78.4% (29/37) of the cases. The overall diagnostic accuracies of the EUS-TCB were 73.0%. The mean size of the masses was 3.7±2.6 cm. The diagnostic accuracies of EUS-TCB according to the lesions were as follows: lymph node, 85.7% (18/21); subepithelial lesion, 60.0% (6/10); and solid tumor, 50% (3/6). With respect to accuracy, lymph nodes were significantly superior to non-lymph node lesions (p=0.046). There was a minor bleeding controlled by hemoclipping (2.7%).
Conclusions
EUS-TCB is a useful technique for the diagnosis of lymph nodes, subepithelial tumors, and solid tumors that were not able to be diagnosed by other methods. In addition, EUS-TCB is a safe and minimally invasive method. (Korean J Gastrointest Endosc 2010;40:9-15)
- 2,264 View
- 8 Download

- Catheter Probe Endoscopic Ultrasonography Using the Jelly-Filled Method for Esophageal Subepithelial Lesions
- Tae In Ha, M.D., Gwang Ha Kim, M.D., Jae Sup Eum, M.D., Chan Ho Park, M.D., Hyoung Yoel Park, M.D., Cheul Woong Choi, M.D., Kyung Yeob Kim, M.D., Il Du Kim, M.D., Pyo Jun Kim, M.D., Hye Jeong Lee, M.D., Sun Mi Lee, M.D., Tae Oh Kim, M.D., Dae Hwan Kang, M
- Korean J Gastrointest Endosc 2008;36(3):125-131. Published online March 30, 2008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
/Aims: The catheter probe endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) system is widely used to evaluate upper gastrointestinal tract lesions. The depiction of the esophageal wall by probe EUS remains problematic due to the difficulty of the filling of water in the esophageal lumen. In addition, filling the esophagus with water can be associated with an increased risk of aspiration. To resolve such problems, we recently applied the use of probe EUS with the jelly-filled method for the evaluation of subepithelial lesions. The procedure is characterized by filling the esophageal lumen with jelly. In this study, we evaluated the efficacy of probe EUS by using the jelly-filled method for esophageal subepithelial lesions. Methods: We analyzed the records of the patients with suspected subepithelial lesions at the time of endoscopy that was performed from November 2005 to June 2007. Esophageal subepithelial lesions with both EUS findings and pathological reports were retrospectively compared. Results: The study included 181 patients (96 males, 85 females), with an average age of 55.5 years (age range, 29∼78 years). Sixty-eight patients had lesions in the upper esophagus, 60 patients had lesions in the middle esophagus and 53 patients had lesions in the lower esophagus. Secondary layers of esophageal lesions were predominant (91/181) in the cases. Pathological findings were available for 34 patients. Compared with the pathological findings, the diagnostic accuracy of EUS was 91.1%. Conclusions: Probe EUS by using the jelly-filled method is convenient and safe to perform and provides clear and full-circumferential imaging of a lesion. It is an alternative method to use in place of previously used probe-EUS procedures for the assessment of esophageal subepithelial lesions. (Korean J Gastrointest Endosc 2008;36:125-131)
- 2,413 View
- 18 Download

- Endoscopic Ultrasonography in Upper Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Lesions
- Tae Kyoung Won, M.D., Eun Young Kim, M.D., Chang Jin Seo, M.D., Byung Seok Kim, M.D., Young Sup Kim, M.D., Kyu Hyun Cho, M.D., Jin Tae Jung, M.D., Joong Goo Kwon, M.D., Chang Hyeong Lee, M.D. and Ho Gak Kim, M.D.
- Korean J Gastrointest Endosc 2006;32(5):313-319. Published online May 30, 2006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
/Aims: Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) is known for its value to characterize incidentally found subepithelial lesions, and we so reviewed our data to validate the norm. Methods: We analyzed the records of the patients with suspected subepithelial lesions at the time of endoscopy, which was performed from Aug. 2001 to Oct. 2004. Results: The data includes 622 patients (248 males) with average age of 52 years (age range 15∼83 years). Extraluminal compression was noted in 10.1% of the patients. Intraluminal lesions were dominant in the stomach and their average size was 14.8 mm. The inner three wall layers were the predominant layers of origin. Mesenchymal tumors were the most frequent EUS impression. Pathologic findings were available for 88 patients and 80.7% of them were benign. Compared with the pathology, the diagnostic accuracy of EUS was 78.4%. The differentiation of malignant and benign GISTs by the EUS findings was 56.3%. Among the 60 EUS cases that had follow up data available (at mean interval of 12.2 months) and who also had less than 3 cm benign lesions, growth was detected only in 10 cases (17%). Pathology confirmed that the lesions in 3 of them were benign. Conclusions: More than 10% of the subepithelial lesions found from endoscopy were extraluminal compression. The majority of intramural lesions were benign. The EUS impression was relatively accurate and helpful for the management of upper gastrointestinal submucosal lesions. (Korean J Gastrointest Endosc 2006;32:313319)
- 2,111 View
- 11 Download


 KSGE
KSGE


 First
First Prev
Prev